گويانا
جمهورية گويانا التعاونية | |
|---|---|
الشعار الحادي: "شعب واحد، أمة واحدة، قدر واحد" | |
 موقع غيانا (الأخضر الداكن) in أمريكا الجنوبية (الرمادي) | |
| العاصمة | جورجتاون 6°46′N 58°10′W / 6.767°N 58.167°W |
| أكبر مدينة | العاصمة |
| اللغات الرسمية | الإنگليزية |
| اللغات الإقليمية المعترف بها | 10 indigenous languages
|
| اللغة الدارجة | الكريولية الگويانية |
| لغات أخرى | 6 languages
|
| الجماعات العرقية (2012) |
|
| الدين | |
| صفة المواطن | گويانيون |
| الحكومة | Unitary presidential constitutional republic[2] |
• الرئيس | عرفان علي |
| مارك فليپس | |
| التشريع | المجلس الوطني |
| التشكيل | |
| 1667–1814 | |
| 1814–1966 | |
| 26 مايو 1966 | |
• الجمهورية | 23 فبراير 1970 |
| 6 أكتوبر 1980 | |
| المساحة | |
• الإجمالية | 214.970 km2 (83.000 sq mi) (رقم 83) |
• الماء (%) | 8.4 |
| التعداد | |
• تقدير 2016 | 786,391[3] (رقم 164) |
• إحصاء 2012 | 747.884[4] |
• الكثافة | 3.502/km2 (9.1/sq mi) (رقم 232) |
| ن.م.إ. (ق.ش.م.) | تقدير 2020 |
• الإجمالي | ▲ 13.506 بليون دولار [5] |
• للفرد | ▲ 17.163 دولار [5] |
| ن.م.إ. (الإسمي) | تقدير 2020 |
• الإجمالي | ▲ 8.065 بليون دولار [5] |
• للفرد | ▲ 10.249 دولار [5] |
| م.ت.ب. (2018) | 0.670[6] medium · رقم 123 |
| العملة | دولار گويانا (GYD) |
| التوقيت | UTC-4 (ت.أ") |
| جانب السواقة | اليسار |
| مفتاح الهاتف | +592 |
| النطاق العلوي للإنترنت | .gy |
گويانا (تُنطق /ɡaɪˈɑːnə/ أو /ɡaɪˈænə/),[7][8] رسمياً جمهورية گويانا التعاونية،[9]، هي دولة تقع على الساحل الشمالي لأمريكا الجنوبية، وتتبع منطقة الكاريبي وكانت ذات يوم جزءاً من جزر الهند الغربية البريطانية التاريخية.[10][8][9] عاصمتها وأكبر مدنها هي جورجتاون. يحدها من الشمال المحيط الأطلسي، ومن الجنوب والجنوب الشرقي البرازيل، ومن الغرب ڤنزويلا، ومن الشرق سورينام.
بمساحة أرض تبلغ 214.969 كم²، تعد گويانا ثالث أصغر دولة سيادية من حيث المساحة في أمريكا الجنوبية بعد أوروگواي وسورينام، وهي ثاني الدول السيادية سكاناً في أمريكا الجنوبية بعد سورينام؛ كما أنها واحدة من أقل كثافة سكانية على وجه الأرض.[11] اللغة الرسمية للبلاد هي الإنگليزية، مع أن جزءاً كبيراً من السكان يتحدثون الإنگليزية بالإضافة إلى اللغات الأصلية. تتميز البلاد بتنوع طبيعي واسع وتنوع بيولوجي كبير. كما تضم جزءاً من غابة الأمازون المطيرة، وهي أكبر غابة مطيرة مدارية وأكثرها تنوعاً بيولوجياً في العالم.
عام 2017، كان 41% من سكان گويانا يعيشون تحت خط الفقر.[12] يشهد اقتصاد گويانا تحولاً منذ اكتشاف النفط الخام عام 2015 والحفر التجاري عام 2019، حيث نما اقتصادها بنسبة 49% عام 2020، مما يجعلها، بحسب بعض التقديرات، أسرع اقتصاد نمواً في العالم حالياً. ويُقال إن احتياطياتها النفطية تبلغ 11 بليون برميل،[13] ومن المتوقع أن تصبح گويانا واحدة من أكبر البلدان المنتجة للنفط للفرد في العالم بحلول عام 2025.[14] يعد اكتشاف أكثر من 11 بليون برميل من احتياطيات النفط قبالة سواحل گويانا منذ عام 2017 أكبر إضافة إلى احتياطيات النفط العالمية منذ السبعينيات.[15] تحتل گويانا حالياً المرتبة الرابعة من حيث نصيب الفرد من الناتج المحلي الإجمالي في الأمريكتين بعد الولايات المتحدة وكندا والبهاماز. ووفقاً لتوقعات البنك الدولي لعام 2023، لا يزال الفقر المدقع قائماً، وتواجه البلاد مخاطر كبيرة في إدارة نموها الهيكلي.[16]
التسمية
اسم "گويانا" (Guyana) مشتق من "گويانا" (Guiana)، الاسم الأصلي للمنطقة التي كانت في السابق تضم گويانا (گويانا البريطانية)، وسورينام (گويانا الهولندية)، وگويانا الفرنسية، وأجزاء من كولومبيا، ڤنزويلا، والبرازيل. وبحسب قاموس أكسفورد الإنگليزي، فإن اسم گويانا مشتق من لغة أمريكية هندية أصلية، ويعني "أرض المياه الوفيرة".[17]
التاريخ
There are nine indigenous tribes residing in Guyana: the Wai Wai, Macushi, Patamona, Lokono, Kalina, Wapishana, Pemon, Akawaio and Warao.[18] Historically the Lokono and Kalina tribes dominated Guyana. Although Christopher Columbus was the first European to sight Guyana during his third voyage (in 1498), and Sir Walter Raleigh wrote an account in 1596, the Dutch were the first Europeans to establish colonies: Essequibo (1616), Berbice (1627), and Demerara (1752). After the British assumed control in 1796,[19] the Dutch formally ceded the area in 1814. In 1831 the three separate colonies became a single British colony known as گويانا البريطانية.
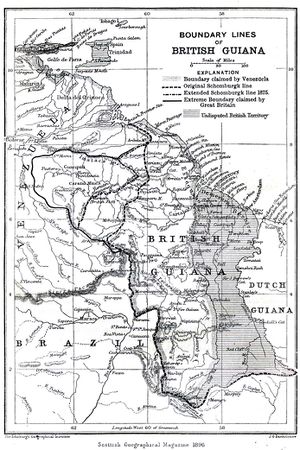
Since its independence in 1824 Venezuela has claimed the area of land to the west of the Essequibo River. سيمون بوليڤار wrote to the British government warning against the Berbice and Demerara settlers settling on land which the Venezuelans, as assumed heirs of Spanish claims on the area dating to the sixteenth century, claimed was theirs. In 1899 an international tribunal ruled the land belonged to Great Britain. The British territorial claim stemmed from Dutch involvement and colonization of the area also dating to the sixteenth century, which was ceded to the British.
Guyana achieved independence from the United Kingdom on 26 May 1966 and became a republic on 23 February 1970, remaining a member of the Commonwealth. The US State Department and the US وكالة المخابرات المركزية (CIA), along with the British government, played a strong role in influencing political control in Guyana during this time. The American government supported Forbes Burnham during the early years of independence because Cheddi Jagan was identified as a Marxist. They provided secret financial support and political campaign advice to Burnham's People's National Congress, to the detriment of the Jagan-led People's Progressive Party, which was mostly supported by Guyanese of East Indian background.
In 1978, Guyana received international notice when 918 members of the American cult, Peoples Temple, died in a mass murder/suicide drinking cyanide-laced Flavor Aid. However, most of the suicides were by Americans and not Guyanese. More than 300 children were killed; the people were members of a group led by Jim Jones in Jonestown, the settlement which they had created. Jim Jones's bodyguards had earlier attacked people taking off at a small remote airstrip close to Jonestown, killing five people, including Leo Ryan, a US congressman.
In May 2008, President Bharrat Jagdeo was a signatory to the UNASUR Constitutive Treaty of the Union of South American Nations. Guyana has ratified the treaty.
الجغرافيا
الموقع
تطل جويانا على الساحل الشمالي الشرقي لأمريكا الجنوبية المشرف على المحيط الأطلنطي ، وتحدها جمهورية فنزويلا من الغرب ، وسورينام من الشرق ، والبرازيل من الجنوب ، وتقع في حيز النطاق الاستوائي . الأرض تقسم أرض جويانا إلى نطاقات ثلاثة ، فالقسم الأول من أرضها والمطل على الساحل سهلي منخفض ، يصل في يعض مناطقة إلى ما دون مستوي البحر ، ُثم تبدأ الأرض في الأرتفاع التدريجي نحو الجنوب الغربي ، ويغطي هذا القسم بالغابات الأستوائية الكثيفة ، وتبلغ أرض جويانا أقصي ارتفاع لها في الجنوب الغربي ، وهنا ينتقل النطاق النباتي إلى حشائش السافانا ، وبها عدة أنهار قصيرة تصرف مياهها في المحيط الأطلنطي .
المناخ
استوائي ترتفع حرارته معظم شهور السنة ، ويلطف الماء من حدة حرارة السواحل ، والأمطار غزيرة وتسقط في فصلين ، الأول من إبريل إلى أغسطس ، والثاني من نوفمبر إلى يناير . السكان يتكون سكان جويانا من الهنود والباكستانيين ، وهؤلاء حوالي 55% من جملة سكان البلاد ، ويشكل الأفريقيون ثلث السكان ، وهناك أكثر من 30 ألفاً من الهنود الامريكين ، وهم البقية الباقية من سكان البلاد الاصليين وحوالي 2000 من الأوروبيين ، ويوجد حوالي 10000 من أصل صيني ، والأقلية الباقية خليط من العناصر السابقة . وتعدد العناصر بجويانا سبب التوتر والقلاقل العديدة التي تشهدها البلاد ، وتستعمل اللغتان الإنجليزية والهندية ( الآسيوية ) والبعض يستعمل اللغتين الصينية والبرتغالية .
مجالس المناطق والأحياء
تنقسم گويانا إلى 10 مناطق:[20][21]
| No | المنطقة | المساحة كم² | التعداد (إحصاء 2012) |
الكثافة السكانية لكل كم² |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | باريما-وايني | 20,339 | 26,941 | 1.32 |
| 2 | Pomeroon-Supenaam | 6,195 | 46,810 | 7.56 |
| 3 | Essequibo Islands-West Demerara | 3,755 | 107,416 | 28.61 |
| 4 | Demerara-Mahaica | 2,232 | 313,429 | 140.43 |
| 5 | Mahaica-Berbice | 4,190 | 49,723 | 11.87 |
| 6 | East Berbice-Corentyne | 36,234 | 109,431 | 3.02 |
| 7 | Cuyuni-Mazaruni | 47,213 | 20,280 | 0.43 |
| 8 | Potaro-Siparuni | 20,051 | 10,190 | 0.51 |
| 9 | Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo | 57,750 | 24,212 | 0.42 |
| 10 | Upper Demerara-Berbice | 17,040 | 39,452 | 2.32 |
| الإجمالي | 214,999 | 747,884 | 3.48 |
The regions are divided into 27 neighbourhood councils.[22]
النزاعات الحدودية
World Heritage sites
الاقتصاد
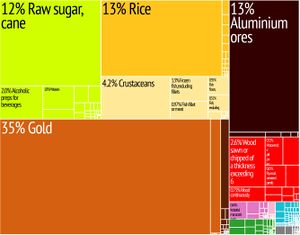
The main economic activities in Guyana are agriculture (production of rice and Demerara sugar), bauxite and gold mining, timber, shrimp fishing and minerals. In 2015 the first of several significant deep water oil discoveries were found, which will have a significant effect on the economy. Chronic problems include a shortage of skilled labour and a deficient infrastructure. In 2008, the economy witnessed a 3% increase in growth amid the global economic crisis, grew an impressive 5.4% in 2011 and 3.7% in 2012.
Until recently, the government was juggling a sizeable external debt against the urgent need for expanded public investment. Low prices for key mining and agricultural commodities combined with troubles in the bauxite and sugar industries, had threatened the government's tenuous fiscal position and dimmed prospects for the future. However, the Guyanese economy has rebounded slightly and exhibited moderate economic growth since 1999, thanks to an expansion in the agricultural and mining sectors, a more favourable atmosphere for business initiatives, a more realistic exchange rate, fairly low inflation, and the continued support of international organisations.
The sugar industry, which accounts for 28% of all export earnings, is largely run by the company GuySuCo, which employs more people than any other industry. Many industries have a large foreign investment. For example, the mineral industry is heavily invested in by the American company Reynolds Metals and the British-Australian Rio Tinto's Rio Tinto Alcan subsidiary; the Korean/Malaysian Barama Company has a large stake in the logging industry.
The production of balatá (natural latex) was once big business in Guyana. Most of the balata bleeding in Guyana took place in the foothills of the Kanuku Mountains in the Rupununi. Early exploitation also took place in the North West District, but most of the trees in the area were destroyed by illicit bleeding methods that involved cutting down the trees rather than making incisions in them. Uses of balatá included the making of cricket balls, the temporary filling of troublesome tooth cavities, and the crafting of figurines and other decorative items (particularly by the Macushi people of the Kanuku mountains).
Major private sector organisations include the Private Sector Commission (PSC)[23] and the Georgetown Chamber of Commerce & Industry (GCCI);[24]
The government initiated a major overhaul of the tax code in early 2007. ضريبة القيمة المضافة (VAT) was brought into effect, replacing six different taxes. Prior to the implementation of the VAT, it had been relatively easy to evade sales tax, and many businesses were in violation of tax code. Many businesses were very opposed to VAT introduction because of the extra paperwork required; however, the Government has remained firm on the VAT. By replacing several taxes with one flat tax rate, it will also be easier for government auditors to spot embezzlement. This was prevalent under the former PPP/C regime who authorised the VAT to be equal to 50% of the value of the good. While the adjustment to VAT has been difficult, it may improve day-to-day life because of the significant additional funds the government will have available for public spending.
President Bharrat Jagdeo had made debt relief a foremost priority of his administration. He was quite successful, getting US$800 million of debt written off by the صندوق النقد الدولي (IMF), البنك الدولي وInter-American Development Bank (IDB), in addition to millions more from other industrial nations. Jagdeo was lauded by IDB President Moreno for his strong leadership and negotiating skills in pursuing debt relief for Guyana and several other regional countries.
ملخص

|
|
النشاط البشري
الزراعة والتعدين دعامة اقتصاد جويانا وتشغل الزراعة 1% من جملة مساحة الأرض ، وأهم الغلات قصب السكر والأرز ،ويزرع الموز ، والذرة وجوز الهند في مساحات محدودة والماشية هي من الأغنام والماعز وجويانا من أهم الدول المنتجة لخام البوكسيت ، ويشغل الألمنيوم المركز الثاني في صادراتها ، ويصنع الألمنيوم محلياً ، ووضعت عدة محاولات لتصنيعة والتقليل من تصديره خاماً ، وبلغ إنتاجها السنوي من الذهب 11000 أوقية ، ومن الماس 10200 قيراط ، هذا إلى جانب المنغنيز ، كما يستخرج النحاس واليورانيوم .
Largest cities
| Rank | Name | Region | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Georgetown | Demerara-Mahaica | 235,017 |
| 2 | Linden | Upper Demerara-Berbice | 44,690 |
| 3 | New Amsterdam | East Berbice-Corentyne | 35,039 |
| 4 | Anna Regina | Pomeroon-Supenaam | 12,448 |
| 5 | Bartica | Cuyuni-Mazaruni | 11,157 |
| 6 | Skeldon | East Berbice-Corentyne | 5,859 |
| 7 | Rosignol | Mahaica-Berbice | 5,782 |
| 8 | Mahaica (village) | Demerara-Mahaica | 4,867 |
| 9 | Parika | Essequibo Islands-West Demerara | 4,081 |
| 10 | Vreed en Hoop | Demerara-Mahaica | 3,073 |
Language
English is the official language of Guyana and is used for education, government, media, and services. The vast majority of the population speaks Guyanese Creole, an English-based creole with slight African and East Indian influence, as their native tongue.[27] In addition, Cariban languages (Akawaio, Wai-Wai, and Macushi) are spoken by a small minority, while Indic languages are retained for cultural and religious reasons.
Religion
Religion in Guyana (2012 census)[28]
Government and politics
هذا section يحتاج المزيد من الأسانيد للتحقق. (December 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Telecommunications
قالب:CIA-Sect Per the CIA World Factbook:[25]
Telephone system
- Telephones : 154,200 main telephone lines (2012)
- Telephones – mobile cellular: 600,000+ (2014)
- Domestic: microwave radio relay network for trunk lines; fixed-line teledensity is about 20 per 100 persons; many areas still lack fixed-line telephone services; mobile-cellular teledensity reached 70 per 100 persons in 2011
- International: country code – 592; tropospheric scatter to Trinidad; satellite earth station – 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean)
Guyana Telephone & Telegraph (GT&T) is the main mobile phone provider [29]
Digicel is also present in Guyana since 2007 providing mobile service for its citizens
Internet system
- Internet country code: .gy
- Internet hosts: 6,218 (2008)[بحاجة لمصدر]
- Internet users: 270,200 (2014)
الثقافة
| 1 January | New Year's Day |
| Spring | Youman Nabi |
| 23 February | Republic Day / Mashramani |
| March | Phagwah |
| March / April | Good Friday |
| March / April | Easter Sunday |
| 1 May | Labour Day |
| 5 May | Indian Arrival Day |
| 26 May | Independence Day |
| First Monday in July | CARICOM Day |
| 1 August | Emancipation Day |
| October / November | Diwali |
| 25 December | Christmas |
| 26 or 27 December | Boxing Day |
المصدر
- الأقليات المسلمة في الامريكتين والبحر الكاريبي – سيد عبد المجيد بكر .
انظر أيضاً
- Index of Guyana-related articles
- LGBT rights in Guyana
- List of international rankings
- Outline of Guyana
Notes
- ^ Mostly made up of other Protestants, but also Eastern Orthodox, Mormons, Jehovah's Witnesses and other Christians.
References
- ^ أ ب Compedium 2: Population Composition. Bureau of Statistics, Guyana. July 2016. Archived from the original on 9 July 2018. Retrieved 25 August 2018.
- ^ قالب:Cite constitution
- ^ "World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision". ESA.UN.org (custom data acquired via website). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 10 September 2017.
- ^ Guyana 2012 Census Archived 6 أغسطس 2014 at the Wayback Machine GeoHive– Guyana. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- ^ أ ب ت ث "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2019". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ^ "2019 Human Development Report" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2019. Retrieved 9 December 2019.
- ^ Wells, John C. (1990). Longman pronunciation dictionary. Harlow, England: Longman. ISBN 0-582-05383-8. entry "Guyana"
- ^ أ ب "Guyana – Dictionary definition and pronunciation – Yahoo! Education". Education.yahoo.com. Archived from the original on 29 أكتوبر 2013. Retrieved 30 مارس 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ أ ب "Independent States in the World". state.gov. خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صالح؛ الاسم "ISW" معرف أكثر من مرة بمحتويات مختلفة. - ^ Wells, John C. (1990). Longman pronunciation dictionary. Harlow, England: Longman. ISBN 978-0-582-05383-0. entry "Guyana"
- ^ "Guyana". 13 February 2024. Archived from the original on 7 January 2021. Retrieved 23 January 2021.
- ^ "" Guyana no recuerda a Walter Rodney " – Le Monde diplomatique en español". mondiplo.com. Archived from the original on 25 September 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- ^ Valle, Sabrina (26 April 2022). "Exxon makes three new oil discoveries in Guyana and boosts reserves". Reuters. Archived from the original on 25 December 2022. Retrieved 2 November 2022 – via www.reuters.com.
- ^ Bajpai, Prableen (16 October 2020). "The Five Fastest Growing Economies In The World". NASDAQ. Archived from the original on 7 December 2022. Retrieved 30 December 2022.
- ^ Blackmon, David. "Why The Oil Bonanza Offshore Guyana Has Global Implications". Forbes. Archived from the original on 2 November 2022. Retrieved 2 November 2022.
- ^ "Macro Poverty Outlook for Guyana : April 2023". World Bank (in الإنجليزية). Archived from the original on 2 December 2023. Retrieved 2023-11-27.
- ^ "Guyana". Oxford Dictionaries. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ^ "Ministry of Amerindian Affairs – Georgetown, Guyana". Amerindian.gov.gy. Archived from the original on 2 يونيو 2013. Retrieved 30 مارس 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "South America 1744–1817 by Sanderson Beck".
- ^ Bureau of Statistics – Guyana Archived 2 سبتمبر 2012 at WebCite, CHAPTER III: POPULATION REDISTRIBUTION AND INTERNAL MIGRATION, Table 3.4: Population Density, Guyana: 1980–2002
- ^ Guyana – Government Information Agency, National Profile. gina.gov.gy Archived 14 أغسطس 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Government of Guyana, Statistics" (PDF). Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- ^ RedSpider, Romona Khan. "Private Sector Commission". Psc.org.gy. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- ^ "Georgetown Chamber of Commerce & Industry (GCCI)". Georgetownchamberofcommerce.org. Archived from the original on 17 ديسمبر 2010. Retrieved 2 مايو 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ أ ب "The World Factbook: Guyana". CIA. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ "Biggest Cities Guyana".
- ^ Damoiseau, Robert (2003) Eléments de grammaire comparée français-créole guyanais Ibis rouge, Guyana, ISBN 2-84450-192-3
- ^ "Data" (PDF). www.state.gov.
- ^ "Guyana Telephone & Telegraph Taps Comverse". Billingworld.com. 5 July 2011. Retrieved 4 March 2012.
<ref> ذو الاسم "imf2" المُعرّف في <references> غير مستخدم في النص السابق.Further reading
- Brock, Stanley E. (1999). All the Cowboys Were Indians (Commemorative, illustrated (reprint of Jungle Cowboy) ed.). Lenoir City, TN: Synergy South, Inc. ISBN 978-1-892329-00-4. OCLC 51089880. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Brock, Stanley E. (1972). Jungle Cowboy (illustrated ed.). London: Robert Hale Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7091-2972-1. OCLC 650259. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Donald Haack, Bush Pilot in Diamond Country
- Hamish MacInnes, Climb to the Lost World (1974)
- Andrew Salkey, Georgetown Journal (1970)
- Marion Morrison, Guyana (Enchantment of the World Series)
- Bob Temple, Guyana
- Noel C. Bacchus, Guyana Farewell: A Recollection of Childhood in a Faraway Place
- Marcus Colchester, Guyana: Fragile Frontier
- Matthew French Young, Guyana: My Fifty Years in the Guyanese Wilds
- Margaret Bacon, Journey to Guyana
- Father Andrew Morrison SJ, Justice: The Struggle For Democracy in Guyana 1952–1992
- Daly, Vere T. (1974). The Making of Guyana. Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-333-14482-4. OCLC 1257829. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - D. Graham Burnett, Masters of All They Surveyed: Exploration, Geography and a British El Dorado
- Ovid Abrams, Metegee: The History and Culture of Guyana
- Waugh, Evelyn (1934). Ninety-two days: The account of a tropical journey through British Guiana and part of Brazil. New York: Farrar & Rinehart. OCLC 3000330. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Gerald Durrell, Three Singles To Adventure
- Cheddi Jagan. The West on Trial: My Fight for Guyana's Freedom
- Cheddi Jagan. My Fight For Guyana's Freedom: With Reflections on My Father by Nadira Jagan-Brancier.
- Colin Henfrey, Through Indian Eyes: A Journey Among the Indian Tribes of Guiana.
- Stephen G. Rabe, US Intervention in British Guiana: A Cold War Story.
- Charles Waterton, Wanderings in South America.
- David Attenborough, Zoo Quest to Guiana (Lutterworth Press, London: 1956).
- John Gimlette, Wild Coast: Travels on South America's Untamed Edge, 2011.
- Clementi, Cecil (1915). The Chinese in British Guiana (PDF). Georgetown, British Guiana: The Argosy Company Limited. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
وصلات خارجية
- Office of the President, Republic of Guyana (official website).
- Petroleum exploration in Guyana
- Parliament of the Cooperative Republic of Guyana (official website).
 Wikimedia Atlas of Guyana
Wikimedia Atlas of Guyana- Outsourcing in Guyana from news publication, Nearshore Americas.
 Geographic data related to غيانا at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to غيانا at OpenStreetMap- Guyana entry at The World Factbook
- Country Profile from the BBC News.
- Guyana from the Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Guyana at UCB Libraries GovPubs.
- (بالإسپانية) Derechos Venezolanos de Soberania en el Esequibo, Ministerio del Poder Popular para Relaciones Exteriores.
- Venezuelan rights of sovereignty in the Essequibo, Ministry of Popular Power for Foreign Affairs (translated by Google).
- غيانا at the Open Directory Project
- The State of the World's Midwifery, Guyana Country Profile.
- Key Development Forecasts for Guyana from International Futures.
- CS1 errors: unsupported parameter
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles needing additional references from December 2008
- All articles needing additional references
- Articles with unsourced statements from December 2009
- Pages with empty portal template
- Guyana
- Commonwealth republics
- بلدان أمريكا الجنوبية
- Countries in the Caribbean
- بلدان وأراضي ناطقة بالإنگليزية
- Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas
- Former monarchies of South America
- Member states of the Caribbean Community
- الدول الأعضاء في كومنولث الأمم
- دول أعضاء في اتحاد أمم أمريكا الجنوبية
- الدول الأعضاء في الأمم المتحدة
- دول وأقاليم تأسست في 1966
- 1966 establishments in South America
- Small Island Developing States
- Former countries in South America
- غويانا