الاستعمار اليوناني
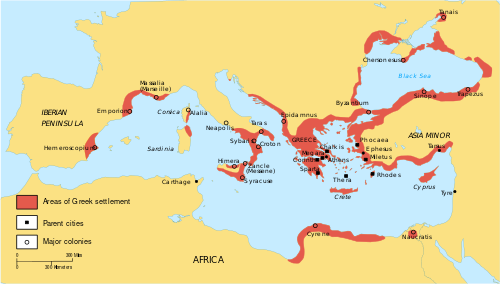
الاستعمار اليوناني refers to the expansion of Archaic Greeks, particularly during the 8th–6th centuries BC, across the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.
The Archaic expansion differed from the Iron Age migrations of the Greek Dark Ages, in that it consisted of organized direction (see oikistes) away from the originating metropolis rather than the simplistic movement of tribes, which characterized the aforementioned earlier migrations. Many colonies, or apoikia (باليونانية قديمة: ἀποικία, تر. "home away from home"), that were founded during this period eventually evolved into strong Greek city-states, functioning independently of their metropolis.
الدوافع

Reasons that the Greeks would establish colonies was the strong economic growth with the consequent overpopulation of the motherland.[1] The terrain that some of these Greek city states were in could not support a large city. Because of the capacity, famine and drought were common in these cities. The areas that the Greeks would try to colonize were areas that were hospitable and fertile. Also the demand for more raw materials that weren't native to the region meant that sending settlers to the area with said materials that came from that area. This meant that settlers could stay in the region full time without continuous travel between city states. With the travel between city states also meant that trade and economic reasons had a part to play in colonization. Politics were also reason as refugees from Greek city states tended to settle away from these cities in the colonies.[2]
السمات

The founding of the colonies was consistently an organized enterprise. The launch was organized by the metropolis, although in many cases they collaborated with other cities. The place to be colonized was selected in advance with the goal of offering business advantages, but also security from raiders. In order to create a feeling of security and confidence in relation to the new colony, the choice of place was decided according to its usefulness.[3] The mission always included a leader nominated by the colonists. In the new cities, the colonists parceled out the land, including farms. The system of governance usually took a form reminiscent of that which prevailed in the metropolis.
التاريخ
The Greeks started colonizing around the beginning of the 8th century BCE. The first Greek colonies were founded by the Euboeans, who founded colonies in Southern Italy and Chalcidice. The two most powerful states on Euboea, Chalcis and Eretria founded numerous colonies in Chalcidice, the most important of which was Olynthus, and they were the first to found colonies in Southern Italy (the so-called "Magna Graecia"). The first colony that they founded there was Pithecusae on the Isle of Ischia. Subsequently, they founded the colonies of Cumae, Zancle, Rhegium and Naxos.[3]
At the end of the 8th century, Euboea fell into decline with the outbreak of the Lelantine War and the baton of colonial foundation was passed to other Greek cities. Due to the decline of the Euboeans, other Greeks such as the Ionians and Corinthians took place.[2] The Ionians started to colonize the Mediterranean world around the 7th century as their first colonies were founded in Southern Italy, Thrace and on the Black Sea. Other Greek city states such as Thera, which founded Cyrene and Andros and Samos, which founded multiple colonies in the Northern Aegean.[4]
المواقع
مقدونيا وتراقيا
Numerous colonies were founded in Northern Greece, chiefly in the region of Chalcidice but also in the region of Thrace.
Chalcidice was settled by Euboeans, chiefly from Chalcis, who lent their name to these colonies. The most important settlements of the Euboeans in Chalcidice were Olynthos (which colony was settled in collaboration with the Athenians), Torone, Mende, Sermyle, Aphytis and Cleonae in the peninsula of Athos. Other important colonies in Chalcidice were Acanthus, a colony which was founded by colonists from Andros[5] and Potidaea, a colony of Corinth. Thasians with the help of the Athenian Callistratus of Aphidnae founded the city of Datus. During the Peloponnesian War, the Athenians with the Hagnon, son of Nikias founded the city of Ennea Hodoi (Ἐννέα ὁδοὶ), meaning nine roads, at the place were now is the 'Hill 133' north of Amphipolis in Serres.[6]
Numerous other colonies were founded in the region of Thrace by the Ionians from the coast of Asia Minor. Important colonies were Maroneia, and Abdera. The Milesians also founded Abydos and Cardia on the Hellespont and رايدستوس in Propontis. The Samians colonized the island of Samothrace, becoming the source of its name. Finally, the Parians colonised Thasos under the leadership of the oecist and father of the poet Archilochus, Telesicles.
In 340 BCE, while Alexander the Great was regent of Macedon, he founded the city of Alexandropolis Maedica after defeating a local Thracian tribe.[7]
ماگنا گريشيا: البر الرئيسي لإيطاليا وصقلية
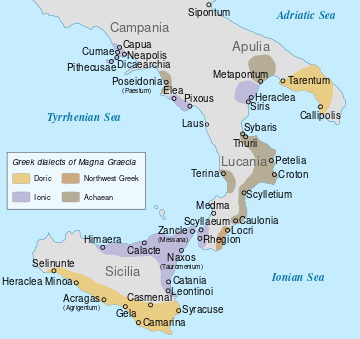
Magna Graecia[8] was the name given by the Romans to the coastal areas of Southern Italy in the present-day Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania and Sicily; these regions were extensively populated by Greek settlers.[9]
The first to colonize Southern Italy were the Euboeans, who with the move to Pithecusae (on the isle of Ischia), founded a series of cities in that region. The second city that they founded was Cumae, nearly opposite Ischia. The colonists from Cumae founded Zancle in on Sicily, and nearby on the opposite coast, Rhegium. Further, the Euboeans founded Naxos, which became the base for the founding of the cities of Leontini, Tauromenion and Catania. In this effort they were accompanied by small numbers of Dorians and Ionians; the Athenians had notably refused to take part in the colonization.[quotes 1]
The strongest of the Sicilian colonies was Syracuse, an 8th-century B.C. colony of the Corinthians. Colonists of that same period from Achaea founded the cities of Sybaris and Croton in the Gulf of Taranto but also in the Metapontum in the same district. In the same area, refugees from Sparta founded Taranto which evolved into one of the most powerful cities in the area. Other Greek states that founded cities in Southern Italy were Megara, which founded Megara Hyblaea, and Selinous; Phocaea, which founded Elea; Rhodes, which founded Gela together with the Cretans and Lipari together with Cnidus, even as the Locrians founded Epizephyrean Locris.[3] According to legend, Lagaria which was between Thurii and the river Sinni River was founded by Phocians.
Many cities in the region became in turn metropolia for new colonies such as the Syracusans, who founded the city of Camarina in the south of Sicily; or the Zancleans, who led the founding of the colony of Himera. Likewise, Naxos, which we see taking further part in the founding of many colonies while the city of Sybaris founded the colony of Poseidonia to its north. The city of Gela which was a colony of Rhodes and Crete founded its own colony, Acragas.[quotes 2]
There is evidence to suggest that there was frequent contact between the Greek settlers and the indigenous people's of Southern Italy. The evidence shown of these interactions comes from the Ionian coast in which the settlements of Timpone Della Motta which shows influence of Greek style in Oneotroian pottery. There is also evidence of Greek influence in architecture in the Oneotroian site that are similar to the construction of houses in nearby Greek colonies such as the colony of Sybaris.[12] Down south in Sicily when the settling of the Corinthians near Syracuse the native Sicels began attacking the Syracusans ultimately leading to the eviction of the Sicels from the area. The burials that are first discovered at Syracuse from early Greek colonists are buried not in a way that the Greeks would have buried their deceased.[2]
The areas of settlement in Southern Italy became so thoroughly Hellenised that Roman writers such as Ovid and Polybius referred to the region as Magna Graecia ("Great Greece"). To this day, some of the Griko people in Southern Italy still speak Griko and Calabrian Greek, Doric Greek-influenced dialects with a substantial Latin adstrate, and worship in the Greek Byzantine Catholic Church instead of the Latin rite more usual among other Italians. In Modern Greek, Southern Italy is referred to as Kato Italia (lit. "Lower Italy") and the relict Greek dialects there as Katoitalika.
Some of these Greek colonies in Italy still stand today such as Neàpolis ("New City", now Naples), Syrakousai (Syracuse), Akragas (Agrigento), Taras (Taranto), Rhegion (Reggio Calabria), or Kroton (Crotone). The type of government was in the form of "city-states" (poleis) administered by the aristocracy.[1] The most populous city of Magna Graecia was Sybaris (now Sibari), with an estimated population, from 600 BC to 510 BC, between 300,000 and 500,000 inhabitants.[13] The names of the inhabitants of Magna Graecia are Italiotes and Siceliotes.
From the motherland Greece, art, literature and philosophy decisively influenced the life of the colonies. Noteworthy was the South Italian ancient Greek pottery, fabricated in Magna Graecia largely during the 4th century BC. In Magna Graecia much impetus was given to culture, especially in some cities, such as Taras (now Taranto).[1] Among the illustrious characters born in Magna Graecia we mention: the philosophers Parmenides of Elea, Zeno of Elea, Gorgias of Lentini and Empedocles of Agrigento; the Pythagoreans Philolaus of Crotone, Archytas of Taranto, Lysis of Taranto, Echecrates and Timaeus of Locri; the mathematician Archimedes of Syracuse; the poets Theocritus of Syracuse, Stesichorus, Ibycus of Reggio Calabria, Nossis of Locri, Alexis of Thuri and Leonidas of Taranto; the doctors Alcmeon of Crotone and Democedes of Crotone; the sculptor from Reggio Clearchus; the painter Zeuxis, the musicologist Aristoxenus of Taranto and the legislator Zaleucus of Locri.
The Greek colonists of Magna Graecia elaborated a civilization of the highest level,[14] which had peculiar characteristics, due to the distance from the motherland and the influence of the indigenous peoples of southern Italy.[14] Magna Graecia, in some fields such as architecture and urban planning, sometimes surpassed the mother country and the other Greek colonies.[15] The settlers of Magna Graecia had great successes in the Ancient Olympic Games in their homeland. Crotone's athletes won 18 titles in 25 Olympics.[16] Although many of the Greek inhabitants of Magna Graecia were entirely Latinized during the Middle Ages,[17] pockets of Greek culture and language remained and have survived to the present day. One example is the Griko people in Calabria (Bovesia) and Salento (Grecìa Salentina), some of whom still maintain their Greek language (Griko language) and customs.[18] The Griko language is the last living trace of the Greek elements that once formed Magna Graecia.[19]
البحر الأيوني والبحر الأدرياتي وإليريا
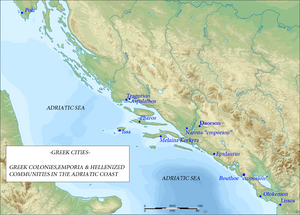
The region of the Ionian Sea and that of Illyria were colonized strictly by Corinth. The Corinthians founded important overseas colonies on the sea lanes to Southern Italy and the west which succeeded in making them the foremost emporia of the western side of the Mediterranean. Important colonies of Corinth included Leucada, Astacus, Anactoreum, Actium, Ambracia, and Corcyra. The Corinthians also founded important colonies in Illyria, which evolved into important cities, Apollonia and Epidamnus. The fact that about the 6th century BC the citizens of Epidamnus constructed a Doric-style treasury at Olympia confirms that the city was among the richest of the Ancient Greek world. An ancient account describes Epidamnos as ‘a great power and very populated’ city.[20] Nymphaeum was another Greek colony in Illyria.[21] The Abantes of Euboea founded the city of Thronion at the Illyria.[22] The island of Paros founded the colony Pharos on the island of Hvar in the Adriatic.[4]
In 1877, archaeologists discovered in Lumbarda on the island of Korčula, in modern-day Croatia, a Greek inscription that writes about the founding of an Ancient Greek settlement on the island. The artifact is known as Lumbarda Psephisma.[23] Evidence of coinage on the Illyrian coast can be dated back to around the 4th cent. BCE. The locations of these coins were founded to minted in Adriatic colonies such as Issa and Pharos. These coins were used for trade between the Illyrians and the Greeks.[24]
البحر الأسود و Propontis

The Greeks had at one point called the Black Sea shore "inhospitable". According to ancient sources, they eventually created 70 to 90 colonies.[25] The colonization of the Black Sea was led by the Megarans and some of the Ionian cities such as Miletus, Phocaea and Teos. The majority of colonies in the region of the Black Sea and Propontis were founded in the 7th century B.C. In the area of Propontis, the Megarans founded the cities of Astacus in Bithynia, Chalcedonia and Byzantium in which they occupied a privileged position. Miletus founded Cyzicus and the Phocaeans Lampsacus.[26]
On the western shore of the Black Sea region the Megarans founded the cities of Selymbria and a little later, Nesebar. A little farther north in the region of today's Romania the Milesians founded the cities of Istria and Orgame. And Miletus also founded a city on the western shore of the Black Sea, Apollonia. In the south of the Black Sea the most important colony was Sinope which according to prevailing opinion was founded by Miletus. The precise chronology of its foundation is not known at present but it appears that it was founded some time around the middle of the 7th century B.C.[26] Sinope was founded with a series of other colonies in the Pontic region: Trebizond, Cerasus, Cytorus, Cotyora, Cromne, Pteria, Tium, et al. The most important colony founded on the southern shore of the Black Sea was likewise a Megaran foundation: Heraclea Pontica, which was founded in the 6th century B.C.
On the north shore of the Black Sea Miletus was the first to start. The colonies of Miletus in this region of the Black Sea were Pontic Olbia and Panticapaeum (modern Kerch.) Later in the 6th century B.C. the Milesians founded Odessa in the region of modern Ukraine.[26] Further north from the Danube delta the Greeks colonized an islet, modern Berezan (probably then a peninsula). That location is found at the confluence of the Bug estuary (the River Hypanis to the Ancient Greeks) and the Dnieper (the Barysthenes to the Ancient Greeks) The islet or peninsula itself was called by the ancients Barythmenis; across from this, they found the site that would be settled later as Olbia. Next to Olbia was another Greek colony that had Istria as its mother city.
On the Crimean peninsula (the Greeks then called it Tauric Chersonese or "Peninsula of the Bulls") they founded likewise the cities of Sympheropolis, and Nymphaeum and Hermonassa. On the Sea of Azov (Lake Maiotis to the ancients) they founded Tanais (in Rostov), Tyritace, Myrmeceum, Cecrine and Phanagoria—the last being a colony of the Teians. In 2018, archaeologists discovered a previously unknown ancient Greek settlement of the 4th-3rd centuries BC near the town of Baherove in Crimea. According to the researchers, the settlement was called Manitra.[27]
On the eastern shore, which was known in ancient times as Colchis and in which today for the greater part is in Georgia and the autonomous region of Abkhazia, the Greeks founded the cities of Phasis and Dioscouris. The latter was called Sebastopolis by the Romans and Byzantines and is known today as Sukhumi—the ruins of the ancient and Byzantine foundations are now found principally below the waterline.
البحر المتوسط الأوسع
The Greek colonies expanded as far as the Iberian Peninsula and North Africa. In North Africa, on the peninsula of Kyrenaika, colonists from Thera founded Kyrene, which evolved into a very powerful city in the region.[3] Other colonies in Kyrenaika later included Barca, Euesperides (modern Benghazi), Taucheira, and Apollonia.
On the north side of the Mediterranean, the Phokaians founded Massalia on the coast of Gaul. Massalia became the base for a series of further foundations farther away in the region of Spain. Phokaia also founded Alalia in Corsica and Olbia in Sardinia. The Phokaians arrived next on the coast of the Iberian peninsula. As related by Herodotus, a local king summoned the Phokaians to found a colony in the region and rendered meaningful aid in the fortification of the city. The Phokaians founded Empuries in this region and later the even more distant Hemeroskopeion.
By the middle of the 7th century, the lone Greek colony in Egypt had been founded, Naukratis.[28] The pharaoh Psammitecus I gave a trade concession to Milesian merchants for one establishment on the banks of the Nile, founding a trading post which evolved into a prosperous city by the time of the Persian expedition to Egypt in 525 B.C.
Similar to the emporion established in the Nile Delta it is possible there was a Greek trading colony established by the Euboians along the Syrian coast on the mouth of the Orontes river at the site Al-Mina in the early 8th century BC. The Greek colony of Posideion on the promontory Ras al-Bassit was colonised just to the south of the Orontes estuary later in the 7th century BC.[29]
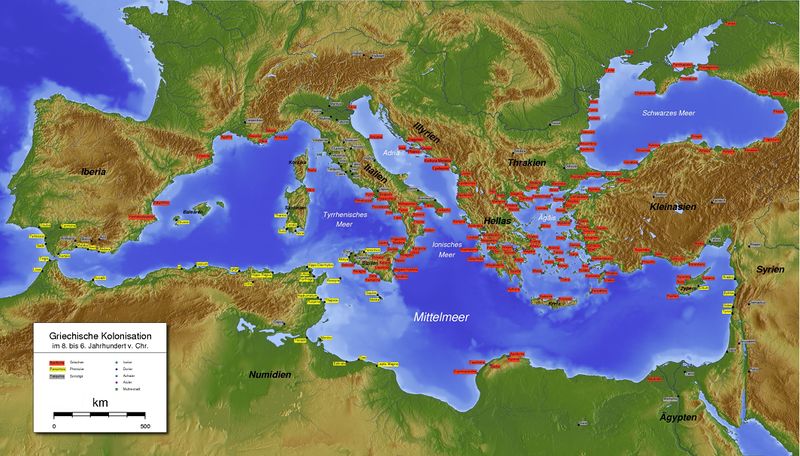
المستعمرات اليونانية قبل الإسكندر الأكبر (قبل 336 ق.م.)
ألبانيا الحديثة
AL1. Nymphaeum AL2. Epidamnos AL3. Apollonia AL4. Aulon AL5. Chimara AL6. Bouthroton AL7. Oricum AL8. Thronion
Modern Bulgaria
* Pseudo-Scymnus writes that some say that the city of Bizone belongs to the barbarians, while others to be a Greek colony of Mesembria.
BUL1. Mesembria BUL2. Odessos BUL3. Apollonia / Antheia BUL4. Agathopolis BUL5. Kavarna BUL6. Pomorie BUL7. Naulochos BUL8. Krounoi BUL9. Pistiros BUL10. Anchialos BUL11. Bizone * BUL12. Develtos BUL13. Heraclea Sintica BUL14. Beroe
Modern Crimea * Russia annexed Crimea in 2014 and unofficially it is no longer part of Ukraine.
CR1. Panticapaeum CR2. Nymphaion CR3. Tyritake CR4. Theodosia CR5. Chersonesus CR6. Charax CR7. Myrmekion CR8. Kerkinitis CR9. Kimmerikon CR10. Kalos Limen CR11. Yalita CR12. Akra
Modern Croatia
C1. Salona C2. Tragyrion C3. Aspálathos C4. Epidaurus C5. Issa C6. Dimos C7. Pharos C8. Kórkyra Mélaina C9. Epidaurum C10. Narona C11. Lumbarda
Modern Cyprus
مصر الحديثة
E1. Naucratis
Modern France
F1. Agde F2. Massalia F3. Tauroention F4. Olbia F5. Nicaea F6. Monoikos F7. Antipolis F8. Alalia F9. Rhodanousia F10. Athenopolis
Modern Georgia/ Abkhazia * Abkhazia is recognised only by Russia and a small number of other countries.
G1. Bathys G2. Triglite G3. Pityus G4. Dioscurias G5. Phasis G6. Gyenos
Modern Greece
GR1. Potidaea GR2. Stageira GR3. Acanthus GR4. Mende GR5. Ambracia GR6. Corcyra GR7. Maroneia GR8. Krinides GR9. Olynthus GR10. Abdera GR11. Therma GR12. Arethusa GR13. Leucas GR14. Eion GR15. Sane GR16. Amphipolis GR17. Argilus GR18. Sane GR19. Akanthos GR20. Astacus GR21. Galepsus GR22. Oesyme GR23. Phagres GR24. Datus GR25. Stryme GR26. Pistyrus GR27. Rhaecelus GR28. Dicaea GR29. Methoni GR30. Heraclea in Trachis GR31. Heraclea in Acarnania GR32. Anactorium GR33. Sale GR34. Drys GR35. Toroni GR36. Amorgos GR37. Actium GR38. Scabala GR39. Philippi GR40. Colonides GR41. Oliarus GR42. Potidaea
Modern Italy
* According to ancient writers Scylletium was a Greek colony, but there are no other evidence other than that.
I1. Olbia I2. Adria I3. Ancona I4. Parthenope I5. Cumae I6. Procida I7. Dicaearchia I8. Neapolis I9. Poseidonia I10. Metapontum I11. Sybaris I12. Thurii I13. Taras I14. Siris I15. Crotona I16. Gallipoli I17. Elea I18. Messina I19. Kale Akte I21. Syracuse I22. Didyme I23. Hycesia I24. Phoenicusa I26. Therassía I27. Lipara/Meligounis I28. Epizepherean Locris I29. Rhegium I30. Lentini I31. Selinountas I32. Megara Hyblaea I33. Naxos I34. Tauromenion I35. Acragas I36. Himera I37. Gela I38. Catania I39. Leontini I40. Ereikousa I41. Euonymos I42. Kamarina I43. Medma I44. Hipponion I45. Heraclea Minoa I46. Caulonia I47. Trotilon I48. Pyxous I49. Mylae I50. Laüs I51. Terina I52. Rhegion I53. Tindari I54. Macalla I55. Temesa I56. Metauros I57. Krimisa I58. Chone I59. Saturo I60. Heraclea Lucania, Siris I61. Scylletium * I62. Agathyrnum I63. Adranon I64. Akrillai I65. Casmenae I66. Akrai I67. Engyon I68. Thapsos I69. Pithekoussai I70. Castelmezzano I71. Licata I72. Avella I73. Ortygia
Modern Libya
L1. Barce L2. Cyrene L3. Balagrae L4. Taucheira L5. Ptolemais L6. Euesperides L7. Antipyrgus L8. Apollonia L9. Cinyps
Modern Montenegro
M1. Bouthoe
Modern North Macedonia * Some historians believe that it was near the modern Resen (North Macedonia) while others believe that it was near the modern Vranje (Serbia).
MA1. Damastion * MA2. Heraclea Lyncestis
Modern Romania
RO1. Tomis RO2. Histria/Istros RO3. Aegyssus RO4. Stratonis RO5. Axiopolis RO6. Kallatis
Modern Russia
RU1. Tanais RU2. Kepoi RU3. Phanagoria RU4. Bata RU5. Gorgippia RU6. Hermonassa RU7. Korokondame RU8. Taganrog RU9. Tyramba RU10. Patraeus RU11. Toricos
Modern Serbia * Some historians believe that it was near the modern Resen (North Macedonia) while others believe that it was near the modern Vranje (Serbia).
SE1. Damastion *
Modern Spain
S1. Portus Illicitanus S2. Akra Leuke S3. Alonis S4. Hemeroscopeum S5. Zakynthos S6. Salauris S7. Rhode S8. Emporion S9. Kalathousa S10. Mainake S11. Menestheus's Limin S12. Kypsela S13. Helike
Modern Turkey
TR1. Selymbria TR2. Heraclea Pontica TR3. Cius TR4. Ephesus TR5. Dios Hieron TR6. Iasos TR7. Myndus TR8. Selge TR9. Priene TR10. Halicarnassus TR11. Miletus TR12. Tralles TR13. Phaselis TR14. Aspendos TR15. Side TR16. Sillyon TR17. Zephyrion TR18. Kelenderis TR19. Mallus TR20. Amos TR21. Byzantium TR22. Amaseia TR23. Amastris TR24. Ainos TR25. Berge TR26. Perinthos TR27. Cardia TR28. Chalcedon TR29. Nicomedia TR30. Abydos TR31. Sestos TR32. Lampsacus TR33. Panormos TR34. Cyzicus TR35. Ilion TR36. Sigeion TR37. Sinope TR38. Tirebolu TR39. Amisos TR40. Tripolis TR41. Cotyora TR42. Polemonion TR43. Pharnakia TR44. Kerasous TR45. Trapezous TR46. Themiscyra TR47. Astacus in Bithynia TR48. Assos TR49. Pitane TR50. Phocaea TR51. Smyrna TR52. Pergamon TR53. Teos TR55. Colophon TR56. Patara TR57. Canae TR58. Bargylia TR59. Madytus TR60. Elaeus TR61. Tieion TR62. Apamea Myrlea TR63. Klazomenai TR64. Notion TR65. Parion TR66. Heraion Teichos TR67. Bisanthe TR68. Erythrae TR69. Priapus TR70. Alopeconnesus TR71. Limnae TR73. Crithote TR74. Pactya TR75. Perinthus TR76. Tium TR77. Teichiussa TR78. Triopium TR79. Placia TR80. Scylace TR81. Arisba TR82. Apollonia TR83. Apollonia ad Rhyndacum TR84. Myrina TR85. Pythopolis TR86. Cytorus TR87. Armene TR88. Kolonai TR89. Paesus TR90. Scepsis TR91. Myus TR92. Mallus TR93. Mopsus TR94. Caryanda TR95. Athenae TR96. Syrna TR97. Cyme TR98. Marathesium TR99. Chrysopolis TR100. Neonteikhos TR101. Artace TR102. Semystra TR103. Cobrys TR104. Cypasis TR105. Kydonies TR106. Coryphas TR107. Heraclea (Aeolis) TR108. Gargara TR109. Lamponeia TR110. Elaea TR111. Mariandyn TR112. Claros TR113. Knidos TR114. Prusias ad Hypium TR115. Dardanus TR116. Pygela TR117. Temnos TR118. Gryneium TR119. Aigai TR120. Rhoiteion TR121. Cadrema
Modern Ukraine
U1. Borysthenes U2. Tyras U3. Olbia U4. Nikonion U5. Odessa
ملاحظات
- ^
...and on this coast are the outlets of the Symaethus and all rivers that flow down from Aetna and have good harbors at their mouths; and here too is the promontory of Xiphonia. According to Ephorus these were the earliest Greek cities to be founded in Sicily, that is, in the tenth generation after the Trojan war; for before that time men were so afraid of the bands of Tyrrhenian pirates and the savagery of the barbarians in this region that they would not so much as sail thither for trafficking; but though Theocles, the Athenian, borne out of his course by the winds to Sicily, clearly perceived both the weakness of the peoples and the excellence of the soil, yet, when he went back, he could not persuade the Athenians, and hence took as partners a considerable number of Euboean Chalcidians and some Ionians and also some Dorians (most of whom were Megarians) and made the voyage; so the Chalcidians founded Naxus, whereas the Dorians founded Megara, which in earlier times had been called Hybla. The cities no longer exist, it is true, but the name of Hybla still endures, because of the excellence of the Hyblaean honey.[10]
- ^
But the rest of the settlements, as well as most of the interior, have come into the possession of shepherds; for I do not know of any settled population still living in either Himera, or Gela, or Callipolis or Selinus or Euboea or several other places. Of these cities, Himera was founded by the Zanclaeans of Mylae, Callipolis by the Naxians, Selinus by the Megarians of the Sicilian Megara, and Euboea by the Leontines. Many of the barbarian cities, also, have been wiped out; for example Camici, the royal residence of Cocalus at which Minos is said to have been murdered by treachery.[11]
المراجع
- ^ أ ب ت "Magna Grecia" (in الإيطالية). Retrieved 9 July 2023.
- ^ أ ب ت Descœudres, Jean‐Paul (2013-02-04). "Greek colonization movement, 8th–6th centuries". The Encyclopedia of Global Human Migration. doi:10.1002/9781444351071.wbeghm260.
- ^ أ ب ت ث Nikolaos Papahatzis; et al. (1971). Ιστορία του ελληνικού έθνους [History of the Greek Nation]. Vol. 2. Ekdotike Athenon.
- ^ أ ب Lombardo, Mario (June 2012). "Greek colonization: small and large islands". Mediterranean Historical Review. 27 (1): 73–85. doi:10.1080/09518967.2012.669150. ISSN 0951-8967.
- ^ Eleni Triakoupoulou-Salakidou (June 1997). "Ακάνθος-Εριίσσος-Ιερίσσος" [Acanthus-Erissus-Hierissus] (PDF). Αρχαιολογία και Τέχνες (Archaeology & Art) (in اليونانية). Vol. 63.
- ^ Thucydides, The Peloponnesian War, 4.102
- ^ Plutarch, Alexander, 9
- ^ UK /ˌmæɡnə ˈɡriːsiə,_ʔ ˈɡriːʃə/ MAG-nə GREE-see-ə, - GREE-shə, الأمريكي /ʔ ˈɡreɪʃə/ - GRAY-shə, لاتينية: [ˈmaŋna ˈɡrae̯ki.a]; حرفياً 'Great[er] Greece'; باليونانية قديمة: Μεγάλη Ἑλλάς, Megálē Hellás, IPA: [meɡálɛː hellás], with the same meaning; إيطالية: Magna Grecia, النطق بالإيطالية: [ˈmaɲɲa ˈɡrɛːtʃa].
- ^ Henry Fanshawe Tozer (30 October 2014). A History of Ancient Geography. Cambridge University Press. p. 43. ISBN 978-1-108-07875-7.
- ^ Strabo (1903). "6.2.2". Geographica. Translated by W. Falconer. in قالب:Perseus
- ^ Strabo (1903). "6.2.6". Geographica. Translated by W. Falconer. in قالب:Perseus
- ^ Allen, Peter S. (October 2010). "Book Review of Meetings of Cultures: Between Conflict and Coexistence, edited by Pia Guldager Bilde and Jane Hjarl Petersen". American Journal of Archaeology. 114 (4). doi:10.3764/ajaonline1144.allen. ISSN 1939-828X.
- ^ "Sybaris: la storia della più ricca città della Magna Grecia" (in الإيطالية). Retrieved 10 July 2023.
- ^ أ ب (in it)Magna Grecia, VII, Treccani, 1970, p. 259
- ^ "L'architettura in Grecia e nelle colonie" (in الإيطالية). Retrieved 21 July 2023.
- ^ "Olimpiadi antiche" (in الإيطالية). Retrieved 11 July 2023.
- ^ "Multilinguismo in Sicilia ea Napoli nel primo Medioevo" (PDF) (in الإيطالية). Retrieved 15 July 2023.
- ^ "Per la difesa e la valorizzazione della Lingua e Cultura Greco-Calabra" (PDF) (in الإيطالية). Retrieved 15 July 2023.
- ^ "Una lingua, un'identità: alla scoperta del griko salentino" (in الإيطالية). Retrieved 15 July 2023.
- ^ Cabanes, Pierre (2008). "Greek Colonisation in the Adriatic". In Tsetskhladze, Gocha R. (ed.). Greek Colonisation: An Account of Greek Colonies and Other Settlements Overseas. Vol. 2. Brill. p. 271. ISBN 9789047442448.
- ^ Cabanes 2008, p. 175.
- ^ Pausanias, Description of Greece, 5.22.4
- ^ J. J. Wilkes/The Journal of Hellenic Studies, Vol. 123, (2003), pp. 251-253-Jstor Archives
- ^ "Keria". Studia Latina et Graeca. 20 (3). 2019-01-28. doi:10.4312/keria.20.3. ISSN 2350-4234.
- ^ "Ancient Europe 8000 B.C-A.D 1000" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-01-09. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ أ ب ت *Demetriadou, Daphne (May 9, 2003). "Αποικισμός του Εύξεινου Πόντου" [The Colonisation of the Black Sea]. Encyclopaedia of the Hellenic World, Asia Minor. Translated by Kalogeropoulou, Georgia.
- ^ "Russian archaeologists said they discovered an ancient Greek settlement in Crimea". Archived from the original on 16 November 2018. Retrieved 16 November 2018.
- ^ Strabo, Geographia 17.1.18, cited in "The Archaic Period:Economy:Trade Station". Hellenic History on the Web. The Foundation for the Hellenic World.
- ^ Adkins, Lesley & Roy (1997). Handbook to life in ancient Greece. New York: Facts On File. ISBN 0816031118.
للاستزادة
- Zuchtriegel, Gabriel (2020). Colonization and Subalternity in Classical Greece: Experience of the Nonelite Population. Cambridge University Press; Reprint edition. ISBN 978-1108409223.
- Lucas, Jason; Murray, Carrie Ann; Owen, Sara (2019). Greek Colonization in Local Context: Case Studies Exploring the Dynamics among Locals and Colonizers. University of Cambridge Museum of Classical Archaeology Monographs. Oxbow Books. ISBN 978-1789251326.
- Tsetskhladze, Gocha R.; Atasoy, Sümer; Temür, Akın; Yiğitpaşa, Davut (2019). Settlements and Necropoleis of the Black Sea and Its Hinterland in Antiquity: Select Papers from the Third International Conference 'The Black Sea in Antiquity and Tekkeköy: An Ancient Settlement on the Southern Black Sea Coast', 27-29 October 2017, Tekkeköy, Samsun. Archaeopress. doi:10.2307/j.ctvwh8bw7. S2CID 241412939.
- Bosher, Kathryn (2016). Theater outside Athens: Drama in Greek Sicily and South Italy. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1107527508.
- Irad, Malkin (2013). A Small Greek World: Networks in the Ancient Mediterranean. Oxford University Press; Reprint edition. ISBN 978-0199315727.
- Tsetskhladze, Gocha (2011). The Black Sea, Greece, Anatolia and Europe in the First Millennium BC. Peeters Publishers. ISBN 978-9042923249.
- Rhodes, P. J. (2010). A History of the Classical Greek World: 478 - 323 BC. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1405192866.
- Dietler, Michael; López-Ruiz, Carolina (2009). Colonial Encounters in Ancient Iberia: Phoenician, Greek, and Indigenous Relations. University Of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0226148472.
- Tsetskhladze, Gocha (2008). Greek Colonisation: An Account Of Greek Colonies and Other Settlements Overseas: Volume 2. Brill Academic Publishers. ISBN 978-9004155763.
- Tsetskhladze, Gocha (2006). Greek Colonisation: An Account Of Greek Colonies and Other Settlements Overseas: Volume 1. Brill Academic Publishers. ISBN 978-9004122048.
- Kirigin, Branko (2006). Pharos. The Parian Settlement in Dalmatia: A study of a Greek colony in the Adriatic. British Archaeological Reports. ISBN 978-1841719917.
- Hall, Jonathan M. (2006). A History of the Archaic Greek World: ca. 1200-479 BCE. Wiley-Blackwel. ISBN 978-0631226680.
- Cerchiai, Luca; Janelli, Lorena; Longo, Fausto; Edward Smith, Mark (2004). The Greek Cities of Magna Graecia and Sicily. J. Paul Getty Museum. ISBN 978-0892367511.
- Tsetskhladze, Gocha (2004). The Archaeology of Greek Colonisation: Essays Dedicated to Sir John Boardman. Oxford University School of Archaeology; 2nd Revised edition. ISBN 978-0947816612.
- Tsetskhladze, Gocha; Snodgrass, A. M. (2002). Greek Settlements in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea. British Archaeological Reports. ISBN 978-1841714424.
- Graham (2001). Collected Papers on Greek Colonization. Brill Academic Publishers. ISBN 978-9004116344.
- Dominguez, Adolfo; Sanchez, Carmen (2001). Greek Pottery from the Iberian Peninsula: Archaic and Classical Periods. Brill Academic Publishers. ISBN 978-9004116047.
- Boardman, John; Solovyov, Sergei; Tsetskhladze, Gocha (2001). Northern Pontic Antiquities in the State Hermitage Museum. Brill Academic Publishers. ISBN 978-9004121461.
- Boardman, John (1999). The Greeks Overseas: Their Early Colonies and Trade. Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0500281093.
- Tsetskhladze, Gocha R. (1998). The Greek Colonisation of the Black Sea Area. Franz Steiner Verlag. ISBN 978-3515073028.
- Isaac, Benjamin H. (1997). The Greek Settlements in Thrace Until the Macedonian Conquest. Studies of the Dutch Archaeological and Historical Society, Vol 10. Brill Academic Pub. ISBN 978-9004069213.
- Treister, M Yu (1997). The Role of Metals in Ancient Greek History. Brill. ISBN 978-9004104730.
- Cohen, Getzel M. (1996). The Hellenistic Settlements in Europe, the Islands, and Asia Minor. Hellenistic Culture and Society. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0520083295.
- Irad, Malkin (1987). Religion and Colonization in Ancient Greece. Brill Academic Publishers. ISBN 978-9004071193.
- Sealey, Raphæl (1976). A History of the Greek City States, 700-338 B. C. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0520031777.
وصلات خارجية
- CS1 الإيطالية-language sources (it)
- CS1 اليونانية-language sources (el)
- Articles containing Ancient Greek (to 1453)-language text
- Articles containing إيطالية-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Greek colonies
- Archaic Greece