زوهاي
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
زوهاي أو النطق الصحيح: ژوهاي Zhuhai ( /ˈdʒuːˈhaɪ/،[3] Chinese: 珠海; pinyin: Zhūhǎi; يـِل: Jyūhói؛ حرفياً: "بحر اللؤلؤ")، هي مدينة بمستوى محافظة على الساحل الجنوبي لمقاطعة گوانگدونگ في الصين. تقع مدينة ژوهاي في دلتا نهر اللؤلؤ، وتحدها جيانگمن من الشمال الغربي، ژونگشان من الشمال، ومكاو من الجنوب. كانت ژوهاي واحدة من المناطق الاقتصادية الخاصة الأصلية التي تأسست في الثمانينيات. كما كانت ژوهاي واحدة من الوحجات السياحية الرئيسية في الصين، حيث كان يطلق عليها الريڤييرا الصينية. ولكون المدينة واقعة في المنطقة الناطقة بالكانتونية التقليدية في مقاطعة گوانگدونگ، فإنها تضم نسبة كبيرة من السكان يشكلون الآن المهاجرين الاقتصاديين الناطقين بالماندرين والذين يرجع أصلهم إلى المحافظات الواقعة في البر الرئيسي.
يقع مركز مدينة ژوهاي في المنطقة الشمالية الشرقية من التقسيم الاداري، وهو جزء من منطقة گوانگژو-شنژن العمرانية على مصب دلتا نهر اللؤلؤ، التي هي أكبر منطقة عمرانية في العالم بعدد سكان يفوق 44.478.513 نسمة حسب تعداد 2010، وتضم شنژن، دونگگوان، فوشان، ژونگشان، مكاو، والجزء الرئيسي من گوانگژو، مناطق صغيرة من مدينتي جيانگمن وهويژو.
تبعاً للتقرير الصادر في 2014 من الأكاديمية الصينية للعلوم الاجتماعية، فإن ژوهاي تعتبر المدينة الأكثر ملاءمة للعيش في الصين.[4]
الجغرافيا
تقع ژوهاي على حدود منطقة مكاو الادارية الخاصة (من الشمال والغرب)، وتبعد 140 كم جنوب غرب گوانگژو. وتشمل أراضيها 146 جزيرة وشريط ساحلي يمتد بطول 690 كم.
The islands within the prefecture-level city of Zhuhai include a number of near-shore islands, often connected to the mainland by bridges or causeways (such as Hengqin, Qi'ao, or Yeli Islands), as well as some islands in the open South China Sea (the Wanshan Archipelago). Some of the latter are actually geographically closer to Hong Kong than to the Zhuhai mainland. The jurisdiction of Nei Lingding Island, located in the Pearl River estuary was transferred from Zhuhai to Shenzhen in 2009.[5]
الاقتصاد
أصبحت ژوهاي مدينة في 1979، قبل عام من تخصيصها كواحدة من أوائل المناطق الاقتصادية الخالصة في الصين، مثل جارتها شنژن، والتي أصبحت أول منطقة اقتصادية خاصة عام 1978، ويرجع جعل ژوهاي منطقة اقتصادية خالصة إلى موقعها الاستراتيجي مواجهة لمكاو، كونها مركز للتجارة الرأسمالية كما هو الحال مع شنژن قبالة هونگ كونگ.
The establishment of Zhuhai as an SEZ allowed the Chinese Central Government and economy to have easier access to the Macau and consequently, global market. As a result, Zhuhai is now a major city in the Pearl River Delta region according to the new general urban plan approved by the State Council. The implementation of Special Economy Zone intended for the city to become a key port city, science and education city, scenic and tourism city, and as a regional hub for transportation.
The outstanding geographic location, a wide range of supporting infrastructure and a deep-water port serve as a major attraction for foreign capital. Utilized foreign investment reached US$10.344 billion in 2008. Among the top 500 enterprises worldwide, 19 of them have investment projects in Zhuhai such as ExxonMobil, BP, Siemens, Carrefour and Matsushita.
التصنيع
Industrial development in Zhuhai focuses on five new high-tech and heavy industries including electronics, computer software, biotechnology and pharmacy, machinery and equipment as well as petrochemical industries. Aiming to strengthen the existing industrial base as well as to provide a better environment for the development of new high-tech industries, the local government has taken the initiative in developing five economic zones:
- Zhuhai High-Tech Industrial Development Zone
As one of the four earliest Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in China, Zhuhai SEZ was set up in the year 1980 and granted with a local legislative right. Zhuhai hi-tech zone is located in the north of Zhuhai, which is very close to downtown. Furthermore, technological resources are centralized in our zone; there is also a huge development in hi-tech industries led by the software and IC industries. The hi-tech zone is the showcase for Zhuhai's scientific development.[6] Meizu is one high tech product headquartered in Zhuhai.
- Zhuhai Free Trade Zone[7]
Zhuhai Free Trade Zone (Zhuhai FTZ) was founded in 1996 with the State Council's approval, occupying 3 km2 (1.2 sq mi). A Zhuhai FTZ Administrative Committee was set up in June 1997. By the end of 2006, there had been over 200 companies registered in the Free Trade Zone, including more than 150 foreign-funded enterprises, and the total investment amount was one billion US dollars. Industries encouraged in the zone include electronics assembly & manufacturing, telecommunications equipment, building/construction materials, instruments & industrial equipment production, medical equipment and supplies, raw material processing, research & development, shipping/warehousing/logistics, and heavy industry.[8]
- Harbour industrial zone (provincial level)
- Wanshan ocean development testing zone (provincial level)
The Wanshan archipelago is located in one of the major fishing areas of China and is core to the Wanshan ocean development testing zone. However, Perna viridis, a species of green mussel, was found to be contaminated by HCHs, DDTs, and PCBs.[9][10]
- Hengqin economic development zone (provincial level)[11]
- Global printer consumables manufacturing centre
Zhuhai manufactured and supplied 70% of the world's ribbons, 60% of the world's aftermarket inkjet cartridges and 20% of the world's third-party laser toner cartridges. Their combined sales were worth more than 1.3 billion US dollars or 10% of all the sales in the world. Zhuhai owns a comprehensive supply chain and almost any of the raw materials needed by the printer consumables industry can be provided locally.
المناخ
Despite being located within the tropics, Zhuhai has a humid subtropical climate affected by the East Asian Monsoon (Koppen classification Cwa) and moderated by the South China Sea, with long, hot and humid summers with frequent thunderstorms, and short, mild and dry winters. Average highs in January and July are 18 and 32 °C (64 and 90 °F) respectively. Snowfalls are unknown and a frost has never been recorded in the city centre. Conversely, extreme heat waves do not occur as they do further inland. Being named one of the most liveable cities in China, real estate is robust here. Residents from the mainland, especially those from the North, will buy homes and spend their winters in Zhuhai.
| Climate data for ژوهاي (1981−2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 27.0 (80.6) |
28.3 (82.9) |
29.9 (85.8) |
33.2 (91.8) |
35.3 (95.5) |
36.5 (97.7) |
38.7 (101.7) |
36.9 (98.4) |
36.3 (97.3) |
34.8 (94.6) |
31.1 (88.0) |
28.5 (83.3) |
38.7 (101.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 18.6 (65.5) |
18.9 (66.0) |
21.5 (70.7) |
25.4 (77.7) |
28.9 (84.0) |
30.8 (87.4) |
32.0 (89.6) |
31.9 (89.4) |
30.6 (87.1) |
28.4 (83.1) |
24.4 (75.9) |
20.2 (68.4) |
26.0 (78.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 15.1 (59.2) |
15.8 (60.4) |
18.4 (65.1) |
22.3 (72.1) |
25.7 (78.3) |
27.7 (81.9) |
28.5 (83.3) |
28.3 (82.9) |
27.3 (81.1) |
25.0 (77.0) |
21.0 (69.8) |
16.6 (61.9) |
22.6 (72.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 12.6 (54.7) |
13.7 (56.7) |
16.3 (61.3) |
20.4 (68.7) |
23.5 (74.3) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.9 (78.6) |
25.8 (78.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
22.5 (72.5) |
18.4 (65.1) |
13.9 (57.0) |
20.3 (68.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 3.2 (37.8) |
3.0 (37.4) |
2.9 (37.2) |
9.7 (49.5) |
15.2 (59.4) |
19.0 (66.2) |
20.9 (69.6) |
21.0 (69.8) |
17.6 (63.7) |
10.5 (50.9) |
5.2 (41.4) |
2.8 (37.0) |
2.8 (37.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 27.0 (1.06) |
57.0 (2.24) |
83.1 (3.27) |
197.7 (7.78) |
298.3 (11.74) |
347.1 (13.67) |
278.6 (10.97) |
337.4 (13.28) |
223.2 (8.79) |
75.1 (2.96) |
43.8 (1.72) |
31.0 (1.22) |
1٬999٫3 (78.7) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74 | 81 | 85 | 86 | 85 | 85 | 83 | 84 | 80 | 74 | 71 | 69 | 80 |
| Source: مركز خدمة بيانات الأرصاد الجوية في الصين | |||||||||||||
الإدارة
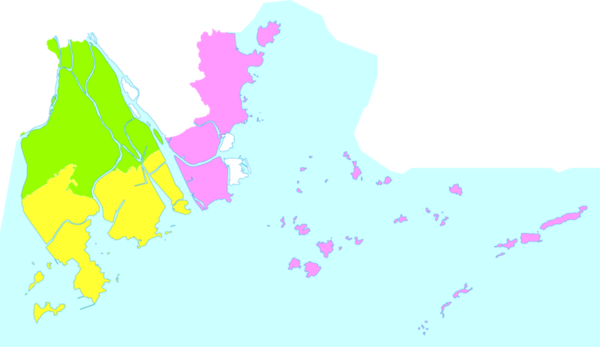
ژوهاي كمدينة بمستوى محافظة، تنقسم إلى 3 تقسيمات على مستوى مقاطعة و4 مناطق اقتصادية خاصة، وتعتبر جميعها مديريات.
| التقسيمات الادارية في ژوهاي | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| رمز التقسيم[12] | الاسم بالعربية | بالصينية | پنين | المساحة كم²[13] | Population 2010[14] | المقر | Postal code | التقسيمات[15] | |||
| تحت-مديريات | البلدات | الأحياء السكنية | القرى الادارية | ||||||||
| 440400 | مدينة ژوهاي | 珠海市 | Zhūhǎi Shì | 1724.32 | 1,562,530 | مديرية شيانگژوو | 519000 | 9 | 15 | 189 | 122 |
| 440402 | Xiangzhou District * | 香洲区 | Xiāngzhōu Qū | 550.84 | 892,685 | Meihua Subdistrict | 519000 | 8 | 6 | 141 | 7 |
| 440403 | Doumen District | 斗门区 | Dǒumén Qū | 613.88 | 415,882 | بلدة جينگآن | 519100 | 1 | 5 | 23 | 101 |
| 440404 | Jinwan District * | 金湾区 | Jīnwān Qū | 559.60 | 253,963 | بلدة هونگتشي | 519100 | 4 | 25 | 14 | |
| منطقة هونگتشين الجديدة | 横琴新区 | Héngqín Xīnqū | 106.46 | بلدة هونگتشي | 519030 | ||||||
| منطقة وانشان التجريبية التنموية البحرية |
万山海洋开发试验区 | Wànshān Hǎiyáng Kāifā Shìyànqū | 80.00 | بلدة وانشان | 519000 | ||||||
| Zhuhai National Hi-Tech Industrial Development District |
珠海国家高新技术产业开发区 | Zhūhǎi Guójiā Gāoxīn Jìshù Chǎnyè Kāifāqū | 130.00 | Tangjiawan Town | 519080 | ||||||
| Zhuhai Gaolanggang Port Economic Zone |
珠海经济技术开发区 | Zhūhǎi Jīngjì Jìshù Kāifāqū | 380.00 | بلدة نانشوي | 519050 | ||||||
| |||||||||||
السياحة
Zhuhai and the surrounding landscapes have a reputation within China of being a garden city with a high quality of life. In 2002, the city attracted 1.3 million international tourists and 3.64 million domestic tourists. Following Guangzhou and Shenzhen, Zhuhai has the third largest amount of foreign tourism in the Guangdong province.[when?][بحاجة لمصدر]
Zhuhai hosts the China International Aviation & Aerospace Exhibition biannually in November. It is the largest Air Show in China and a huge tourist attraction.
Realizing the benefits brought by tourism, the local government is expanding tourist destinations and is developing new spots such as Hengqin (横琴岛), Dong'ao (东澳), Hebao (荷包), Qi'ao (淇澳岛) and Yeli (野狸).
قصر يوان مينگ الجديد
قصر يوان مينگ الجديد (simplified Chinese: 圆明新园; traditional Chinese: 圓明新園) هو منتزه مساحته 1.39 كم²، يضم بحيرة مساحتها 80,000 م². ويضم نموذج لـالقصر الصيفي القديم في بكين التي تدمر أثناء حرب الأفيون الثانية ولم يعاد بناؤه في موقعه الأصلي.[16]
- قصر يوان مينگ الجديد في ژوهاي
ساحل خليج شيانگلو — تمثال الفتاة الصيادة
The coast of Xianglu Bay is considered the "symbol" of Zhuhai, offering a scenic view of Pearl River Delta with silt-rich water, rocks, and a beach. The famous landmark of the city, the Fisher Girl Statue, stands elegantly on a boulder in Xianglu Bay; the statue is draped by a fishnet and holds a pearl high in the air with both hands up to the sky, symbolizing a vigorous and lively Zhuhai welcoming visitors from all over the world. It was erected in 1982 by a professor from the Guangzhou Academy of Fine Arts and is 8.7 meters tall, composed of 70 pieces of granite. Visitors can view the statue up close from a boardwalk on the shore.[17][18]
The statue was based on a local legend, in which the daughter of the celestial Dragon King visited the Pearl River delta. Enamored by the beauty of the Zhuhai region, she disguised herself as a fisher girl and lived among the people there, weaving baskets and healing locals with her powers until she fell in love with a fellow fisherman named Haipeng. The romance between Haipeng and the fisher girl was interrupted by vicious rumors among the people about the latter's true origins. Haipeng eventually confronted the fisher girl about this and demanded she give her magical pearl bracelets to him as proof of her love. She confirmed the rumors and explained that if she removed even one of the pearls, she would die. As Haipeng refused to believe her story and turned to leave, the fisher girl took off her bracelets, dying in Haipeng's arms. Heartbroken and guilt-ridden, Haipeng set out to find a cure, eventually discovering from a local elder that he would need to cultivate a special grass with his own blood. After years of toiling, Haipeng finally harvested enough to revive the fisher girl, turning her into a mortal. The two later married and the fisher girl found a large pearl, which she gifted to the elder in gratitude on the day of the wedding.[19]
المدن الشقيقة
انظر المدن الشقيقة لژوهاي
انظر أيضاً
- قائمة البلدات التوأم والمدن الشقيقة في الصين
- هنگتشين
- وانشان چونداو، أرخبيل مكون من 104 جزيرة في بحر الصين الجنوبي
الهامش
- ^ "China: Guăngdōng (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) – Population Statistics, Charts and Map". citypopulation.de (in الإنجليزية).
- ^ أ ب "2016年珠海市国民经济和社会发展统计公报".
- ^ "Zhuhai pronunciation". thefreedictionary.com. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ^ 社科院:珠海取代香港成为最宜居城市 网易新闻,2014-05-09
- ^ "Nèi língdīng dǎo guīshǔ shēnzhèn shì guǎnxiá" 内伶仃岛归属深圳市管辖. sznews.com (in الصينية المبسطة). 2009-09-26. Archived from the original on 29 September 2009. Retrieved 1 September 2014.
- ^ "Zhuhai High-Tech Industrial Zone". RightSite.asia (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2021-06-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Zhūhǎi bǎoshuìqū, zhū ào kuà jìng gōngyè qū" 珠海保税区、珠澳跨境工业区. Zhōngguó bǎoshuìqū chūkǒu jiāgōng qū xiéhu 中国保税区出口加工区协会 (in الصينية).
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Zhuhai Free Trade Zone". RightSite.asia (in الإنجليزية).
- ^ Huang, Shao-hui 黄少辉; Wang, Wei-chen 王伟臣 (2000). "Zhūhǎi wàn shān qúndǎo hǎishàng shēngtài gōngyuán jiànshè guīhuà gòuxiǎng" 珠海万山群岛海上生态公园建设规划构想 [A Conception of Constructing the Marine Ecological Park in Wanshan Islands, Zhuhai]. Rèdài dìlǐ / Tropical Geography (in الصينية). 20 (13): 228–232.
- ^ Fang, Zhanqiang 方展强; Zhang, Runxing 张润兴; Huang, Minghong 黄铭洪 (2001). "Zhūjiāng hékǒu qū fěicuì yí bèi zhōng yǒujī lǜ nóngyào hé duō lǜ lián běn hánliàng jí fēnbù" 珠江河口区翡翠贻贝中有机氯农药和多氯联苯含量及分布. Huánjìng kēxué xuébào 环境科学学报 [Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae] (in الصينية) (1). doi:10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2001.01.022.
- ^ "Why Zhuhai?". Recycling Times (in الإنجليزية). Archived from the original on 8 May 2013.
- ^ "中华人民共和国县以上行政区划代码". 中华人民共和国民政部.
- ^ 广东省统计局、国家统计局广东调查总队 (2014.09). 《广东统计年鉴2014》. 中国统计出版社. ISBN 978-7-5037-7174-3.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|year=(help),数字为第二次全国土地调查数据 - ^ shi, Guo wu yuan ren kou pu cha ban gong; council, Guo jia tong ji ju ren kou he jiu ye tong ji si bian = Tabulation on the 2010 population census of the people's republic of China by township / compiled by Population census office under the state; population, Department of; statistics, employment statistics national bureau of (2012). Zhongguo 2010 nian ren kou pu cha fen xiang, zhen, jie dao zi liao (Di 1 ban. ed.). Beijing Shi: Zhongguo tong ji chu ban she. ISBN 978-7-5037-6660-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ 中华人民共和国民政部 (2014.08). 《中国民政统计年鉴2014》. 中国统计出版社. ISBN 978-7-5037-7130-9.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - ^ "New Yuanming Palace". TravelChinaGuide.com (in الإنجليزية).
- ^ "Walking along the Coast of Xianglu Bay: Zhuhai Things to Do Tip by Minosuke". VirtualTourist (in الإنجليزية).
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Statue of Fisher Girl in Zhuhai: The Landmark of Zhuhai City". Top China Travel (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2019-06-16.
- ^ Faulhaber, Pia (2013-11-29). "The Love Story Behind the Zhuhai Fisher Girl". InternChina (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2019-06-16.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)
وصلات خارجية
- الموقع الرسمي لمدينة ژوهاي (متاح بالإنگليزية، الپرتغالية والإسپانية)
- الموقع الحكومي الرسمي (متاح بالصينيةوالإنگليزية)
- الموقع الرسمي للمستثمرين (متاح بالصينية والإنگليزية)
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- CS1 uses الصينية-language script (zh)
- CS1 الصينية المبسطة-language sources (zh-hans)
- CS1 maint: url-status
- CS1 الصينية-language sources (zh)
- CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Pages using multiple image with auto scaled images
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Articles containing صينية-language text
- Pages using infobox settlement with image map1 but not image map
- Articles containing traditional Chinese-language text
- Vague or ambiguous time from August 2020
- Articles with unsourced statements from August 2020
- Articles containing simplified Chinese-language text
- Articles containing Chinese-language text
- ژوهاي
- Prefecture-level divisions of Guangdong