المملكة الكوشانو-ساسانية
Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom Kushanshahr | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ح. 230 CE–ح. 365 CE | |||||||||||
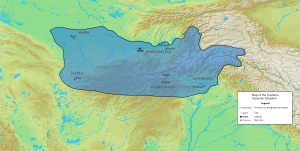 Map of the domains governed by the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom | |||||||||||
| العاصمة | بلخ | ||||||||||
| اللغات الشائعة | Middle Persian Bactrian | ||||||||||
| الدين | البوذية الزرادشتية الهندوسية | ||||||||||
| الحكومة | ملكية إقطاعية | ||||||||||
| الحقبة التاريخية | القِدم المتأخر | ||||||||||
• تأسست | ح. 230 CE | ||||||||||
• انحلت | ح. 365 CE | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom (also called Kushanshahs, KΟÞANΟ ÞAΟ or Koshano Shao in Bactrian,[1] or Indo-Sasanians) is a historiographic term used by modern scholars[2] to refer to a branch of the Sasanian Persians who established their rule in Bactria during the 3rd and 4th centuries CE at the expense of the declining Kushans. They captured the provinces of Sogdiana, Bactria and Gandhara from the Kushans in 225 CE.[3] The Sasanians established governors for the Sasanian Empire, who minted their own coinage and took the title of Kushanshas, i.e. "Kings of the Kushans".[3] They are sometimes considered as forming a "sub-kingdom" inside the Sasanian Empire.[4] This administration continued until 360-370 CE,[3] when the Kushano-Sasanians lost much of its domains to the invading Kidarite Huns, whilst the rest was incorporated into the imperial Sasanian Empire.[5] Later, the Kidarites were in turn displaced by the Hephthalites.[6] The Sasanians were able to re-establish some authority after they destroyed the Hephthalites with the help of the Turks in 565, but their rule collapsed under Arab attacks in the mid 7th century.
The Kushanshas are mainly known through their coins. Their coins were minted at Kabul, Balkh, Herat, و مرو، attesting the extent of their realm.[7]
A rebellion of Hormizd I Kushanshah (277–286 CE), who issued coins with the title Kushanshahanshah ("ملك ملوك الكوشان"), seems to have occurred against contemporary emperor Bahram II (276–293 CE) of the Sasanian Empire, but failed.[3]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التاريخ
الفترة الكوشانو-ساسانية الأولى (230-365 CE)
The Sassanids, shortly after victory over the Parthians, extended their dominion into Bactria during the reign of Ardashir I around 230 CE, then further to the eastern parts of their empire in western Pakistan during the reign of his son Shapur I (240–270). Thus the Kushans lost their western territory (including Bactria and Gandhara) to the rule of Sassanid nobles named Kushanshahs or "Kings of the Kushans". The farthest extent of the Kushano-Sasanians to the east appears to have been Gandhara, and they apparently did not cross the Indus river, since almost none of their coinage has been found in the city of Taxila just beyond the Indus.[8]
The Kushano-Sasanians under Hormizd I Kushanshah seem to have led a rebellion against contemporary emperor Bahram II (276-293 CE) of the Sasanian Empire, but failed.[3] According to the Panegyrici Latini (3rd-4th century CE), there was a rebellion of a certain Ormis (Ormisdas) against his brother Bahram II, and Ormis was supported the people of Saccis (Sakastan).[7] Hormizd I Kushanshah issued coins with the title Kushanshahanshah ("King of kings of the Kushans"),[9] probably in defiance of imperial Sasanian rule.[3]
Around 325, Shapur II was directly in charge of the southern part of the territory, while in the north the Kushanshahs maintained their rule. Important finds of Sasanian coinage beyond the Indus in the city of Taxila only start with the reigns of Shapur II (r.309-379) and Shapur III (r.383-388), suggesting that the expansion of Sasanian control beyond the Indus was the result of the wars of Shapur II "with the Chionites and Kushans" in 350-358 as described by Ammianus Marcellinus.[8] They probably maintained control until the rise of the Kidarites under their ruler Kidara.[8]
قالب:South Asia in 350 CE The decline of the Kushans and their defeat by the Kushano-Sasanians and the Sasanians, was followed by the rise of the Kidarites and then the Hephthalites (Alchon Huns) who in turn conquered Bactria and Gandhara and went as far as central India. They were later followed by Turk Shahi and then the Hindu Shahi, until the arrival of Muslims to north-western parts of India.
الفترة الساسانية الثانية (565-651 CE)
The Hephthalites dominated the area until they were defeated in 565 CE by an alliance between the First Turkic Khaganate and the Sasanian Empire, and some Sassanid authority was re-established in eastern lands. According to al-Tabari, Khosrow I managed, through his expansionist policy, to take control of "Sind, Bust, Al-Rukkhaj, Zabulistan, Tukharistan, Dardistan, and Kabulistan".[10]
The Hephthalites were able to set up rival states in Kapisa, Bamiyan, and Kabul, before being overrun by the Tokhara Yabghus and the Turk Shahi. The Sasanians may also have expelled by the Nezak-Alchons.[11] The 2nd Indo-Sassanid period ended with the collapse of Sassanids to the Rashidun Caliphate in the mid 7th century. Sind remained independent until the Arab invasions of India in the early 8th century.[بحاجة لمصدر]
التأثيرات الدينية

Obv: King Varhran I with characteristic head-dress.
Rev: Shiva with bull Nandi, in Kushan style.
Coins depicting Shiva and the Nandi bull have been discovered, indicating a strong influence of Shaivite Hinduism.
The prophet Mani (210–276 CE), founder of Manichaeism, followed the Sassanids' expansion to the east, which exposed him to the thriving Buddhist culture of Gandhara. He is said to have visited Bamiyan, where several religious paintings are attributed to him, and is believed to have lived and taught for some time. He is also related to have sailed to the Indus valley area now in modern-day Pakistan in 240 or 241 AD, and to have converted a Buddhist King, the Turan Shah of India.[12]
On that occasion, various Buddhist influences seem to have permeated Manichaeism: "Buddhist influences were significant in the formation of Mani's religious thought. The transmigration of souls became a Manichaean belief, and the quadripartite structure of the Manichaean community, divided between male and female monks (the 'elect') and lay follower (the 'hearers') who supported them, appears to be based on that of the Buddhist sangha"[12]
العملات
The Kushano-Sassanids created an extensive coinage with legend in Brahmi, Pahlavi or Bactrian, sometimes inspired from Kushan coinage, and sometimes more clearly Sassanid.
The obverse of the coin usually depicts the ruler with elaborate headdress and on the reverse either a Zoroastrian fire altar, or Shiva with the bull Nandi.
Kushano-Sasanian ruler Ardashir I Kushanshah, circa 230-250 CE. Merv mint.
Ardashir I Kushanshah in the name of Kushan ruler Vasudeva I, circa 230-245 CE.[13]
Hormizd I Kushanshah with mention of Mazda and Anahita. Merv mint.[9]
الحكام الكوشانو-ساسانيون الرئيسيون
The following Kushanshahs were:[14]
- Ardashir I Kushanshah (230–245)
- Peroz I Kushanshah (245–275)
- Hormizd I Kushanshah (275–300)
- Hormizd II Kushanshah (300–303)
- Peroz II Kushanshah (303–330)
- Varahran Kushanshah (330-365)
الفن الكوشانو-ساسانية
The Indo-Sassanids traded goods such as silverware and textiles depicting the Sassanid emperors engaged in hunting or administering justice.
Kushano-Sasanian footed cup with medallion, 3rd-4th century CE, Bactria, Metropolitan Museum of Art.[15]
Possible Kushano-Sasanian plate, excavated in Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 350-400 CE.[16] British Museum 124093.[17][18]
التأثيرات الفنية
The example of Sassanid art was influential on Kushan art, and this influence remained active for several centuries in the northwest South Asia. Plates seemingly belonging to the art of the Kushano-Sasanians have also been found in Northern Wei tombs in China, such as a plate depicting a boar hunt found in the 504 CE tomb of Feng Hetu.[22]
Vishnu Nicolo Seal: Kushano-Sasanian or Kidarite prince worshipping Vishnu or Vāsudeva, with Bactrian inscription. Found in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. 4th century CE. British Museum.[23][24][25]
Sasanian dignitary drinking wine, on ceiling of Cave 1, at Ajanta Caves, India, end of the 5th century.[26]
انظر أيضاً
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
المراجع
- ^ Rezakhani, Khodadad. From the Kushans to the Western Turks (in الإنجليزية). p. 204.
- ^ Rezakhani 2017b, p. 72.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 3, E. Yarshater p.209 ff
- ^ The Cambridge Companion to the Age of Attila, Michael Maas, Cambridge University Press, 2014 p.284 ff
- ^ Rezakhani 2017b, p. 83.
- ^ Sasanian Seals and Sealings, Rika Gyselen, Peeters Publishers, 2007, p.1
- ^ أ ب Encyclopedia Iranica
- ^ أ ب ت Ghosh, Amalananda (1965). Taxila (in الإنجليزية). CUP Archive. pp. 790–791.
- ^ أ ب CNG Coins
- ^ Rezakhani, Khodadad (2017). ReOrienting the Sasanians: East Iran in Late Antiquity (in الإنجليزية). Edinburgh University Press. pp. 125–156. ISBN 9781474400312.
- ^ ALRAM, MICHAEL (2014). "From the Sasanians to the Huns New Numismatic Evidence from the Hindu Kush". The Numismatic Chronicle. 174: 282. ISSN 0078-2696.
- ^ أ ب Richard Foltz, Religions of the Silk Road, New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010
- ^ CNG Coins
- ^ Rezakhani 2017b, p. 78.
- ^ "Metropolitan Museum of Art". www.metmuseum.org.
- ^ For the precise date: Sundermann, Werner; Hintze, Almut; Blois, François de. Exegisti Monumenta: Festschrift in Honour of Nicholas Sims-Williams (in الإنجليزية). Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. p. 284, note 14. ISBN 978-3-447-05937-4.
- ^ "Plate British Museum". The British Museum (in الإنجليزية).
- ^ Sims, Vice-President Eleanor G.; Sims, Eleanor; Marshak, Boris Ilʹich; Grube, Ernst J.; I, Boris Marshak. Peerless Images: Persian Painting and Its Sources (in الإنجليزية). Yale University Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-300-09038-3.
- ^ Carter, M.L. "Encyclopaedia Iranica". iranicaonline.org.
A gilt silver plate depicting a princely boar hunt, excavated from a tomb near Datong dated to 504 CE, is close to early Sasanian royal hunting plates in style and technical aspects, but diverges enough to suggest a Bactrian origin dating from the era of the Kushano-Sasanian rule (ca. 275-350 CE)
- ^ HARPER, PRUDENCE O. (1990). "An Iranian Silver Vessel from the Tomb of Feng Hetu". Bulletin of the Asia Institute. 4: 51–59. ISSN 0890-4464.
- ^ Watt, James C. Y. (2004). China: Dawn of a Golden Age, 200-750 AD (in الإنجليزية). Metropolitan Museum of Art. pp. 152–153. ISBN 978-1-58839-126-1.
- ^ Carter, M.L. "Encyclopaedia Iranica". iranicaonline.org.
A gilt silver plate depicting a princely boar hunt, excavated from a tomb near Datong dated to 504 CE, is close to early Sasanian royal hunting plates in style and technical aspects, but diverges enough to suggest a Bactrian origin dating from the era of the Kushano-Sasanian rule (ca. 275-350 CE)
- ^ "Seal British Museum". The British Museum (in الإنجليزية).
- ^ "a Sasanian prince is represented adoring before the Indian god Vishnu" in Herzfeld, Ernst. Kushano-Sasanian Coins (in الإنجليزية). Government of India central publication branch. p. 16.
- ^ "South Asia Bulletin: Volume 27, Issue 2". South Asia Bulletin. University of California, Los Angeles. 2007. p. 478:
A seal inscribed in Bactrian , fourth to fifth century AD , shows a Kushano - Sasanian or Kidarite official worshipping Vishnu : Pierfrancesco Callieri , Seals and Sealings from the North - West of the Indian Subcontinent and Afghanistan.
- ^ The Buddhist Caves at Aurangabad: Transformations in Art and Religion, Pia Brancaccio, BRILL, 2010 p.82
المصادر
- Cribb, Joe (2018). Rienjang, Wannaporn; Stewart, Peter (eds.). Problems of Chronology in Gandhāran Art: Proceedings of the First International Workshop of the Gandhāra Connections Project, University of Oxford, 23rd-24th March, 2017. University of Oxford The Classical Art Research Centre Archaeopress. ISBN 978-1-78491-855-2. قالب:Free access
- Cribb, Joe (2010). Alram, M. (ed.). "The Kidarites, the numismatic evidence.pdf". Coins, Art and Chronology Ii, Edited by M. Alram et al. Coins, Art and Chronology II: 91–146. قالب:Free access
- Daryaee, Touraj; Rezakhani, Khodadad (2017a). "The Sasanian Empire". In Daryaee, Touraj (ed.). King of the Seven Climes: A History of the Ancient Iranian World (3000 BCE - 651 CE). UCI Jordan Center for Persian Studies. pp. 1–236. ISBN 978-0-692-86440-1.
- Payne, Richard (2016). "The Making of Turan: The Fall and Transformation of the Iranian East in Late Antiquity". Journal of Late Antiquity. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. 9: 4–41. doi:10.1353/jla.2016.0011. S2CID 156673274. قالب:Free access
- Rapp, Stephen H. (2014). The Sasanian World through Georgian Eyes: Caucasia and the Iranian Commonwealth in Late Antique Georgian Literature. London: Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 978-1-4724-2552-2.
- Rezakhani, Khodadad (2017b). "East Iran in Late Antiquity". ReOrienting the Sasanians: East Iran in Late Antiquity. Edinburgh University Press. pp. 1–256. ISBN 978-1-4744-0030-5. JSTOR 10.3366/j.ctt1g04zr8. قالب:Registration required
- Rypka, Jan; Jahn, Karl (1968). History of Iranian literature (in الإنجليزية). D. Reidel.
- Sastri, Nilakanta (1957). A Comprehensive History of India: The Mauryas & Satavahanas (in الإنجليزية). Orient Longmans. p. 246.
- Vaissière, Étienne de La (2016). "Kushanshahs i. History". Encyclopaedia Iranica.
- Wiesehöfer, Joseph (1986). "Ardašīr I i. History". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. II, Fasc. 4. pp. 371–376.
وصلات خارجية
قالب:Rulers of Ancient Central Asia
| الممالك الوسطى في الهند | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| خط زمني والفترة التاريخية |
Northwestern India | Indo-Gangetic Plain | الهند الوسطى | الهند الجنوبية | ||
| Upper Gangetic Plain | Middle Gangetic Plain
|
Lower Gangetic Plain
| ||||
| العصر الحديدي | ||||||
| الثقافة | فترة الڤديك المتأخرة | فترة الڤديك المتأخرة (Brahmin ideology)[أ] |
فترة الڤديك المتأخرة (Kshatriya/Shramanic culture)[ب] |
ما قبل التاريخ | ||
| القرن 6 ق.م. | گاندارا | كورو-Panchala | ماگادا | أديڤاسي (قبائل) | ||
| الثقافة | التأثير الفارسي-اليوناني | "التمدن الثاني" | ما قبل الهند | |||
| القرن 5 ق.م. | (الحكم الفارسي) | Shishunaga dynasty | أديڤاسي (قبائل) | |||
| القرن 4 ق.م. | (الغزوات اليونانية) | امبراطورية ناندا | ||||
| العصر التاريخي | ||||||
| الثقافة | انتشار البوذية | ما قبل التاريخ | Sangam period (300 ق.م. – 200 م) | |||
| القرن 3 ق.م. | امبراطورية مورايا | Early Cholas 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | ||||
| الثقافة | الهندوسية ما قبل الكلاسيكية[ت] - "Hindu Synthesis"[ث] (ca. 200 BC - 300 AD)[ج][ح] الملاحم - Puranas - Ramayana - Mahabharata - Bhagavad Gita - Brahma Sutras - Smarta Tradition Mahayana Buddhism |
Sangam period (استمرت) | ||||
| القرن 2 ق.م. | المملكة الهندو-يونانية | امبراطورية شونگا | Early Cholas 46 ممالك أخرى صغيرة في Ancient Thamizhagam | |||
| القرن 1 ق.م. | ||||||
| القرن 1 م | مملكة كونيندا | |||||
| القرن 2 | امبراطورية كوشان | |||||
| القرن 2 | المملكة الكوشانية الساسانية | امبراطورية كوشان | Western Satraps | Kamarupa kingdom | Kalabhra dynasty | |
| الثقافة | "العصر الذهبي للهندوسية"(ح. 320-650 م)[خ] Puranas Co-existence of Hinduism and Buddhism | |||||
| القرن 4 | Kidarites | Gupta Empire | Kalabhra dynasty | |||
| القرن 5 | Hephthalite Empire | Alchon Huns | Kalabhra dynasty | |||
| القرن 6 | Nezak Huns | Maitraka | Adivasi (tribes) | Badami Chalukyas | ||
| الثقافة | Late-Classical Hinduism (ح. 650-1100 م)[د] Advaita Vedanta - Tantra Decline of Buddhism in India | |||||
| القرن 7 | Indo-Sassanids | Vakataka dynasty Empire of Harsha |
Mlechchha dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | |
| القرن 8 | Kabul Shahi | Pala Empire | Pandyan Kingdom | |||
| القرن 9 | Gurjara-Pratihara | Rashtrakuta dynasty | ||||
| القرن 10 | Ghaznavids | Pala dynasty | Kalyani Chalukyas | |||
مصادر ومراجع الجدول المصادر Sources
| ||||||
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- مقالات ذات عبارات بحاجة لمصادر
- Portal-inline template with redlinked portals
- Pages with empty portal template
- Asia articles missing geocoordinate data
- All articles needing coordinates
- Ancient history of Pakistan
- Ancient history of Afghanistan
- الامبراطورية الساسانية




![Ardashir I Kushanshah in the name of Kushan ruler Vasudeva I, circa 230-245 CE.[13]](/w/images/thumb/9/9a/Ardashir_I_Kushanshah_in_the_name_of_Vasudeva_circa_230-245_CE.jpg/150px-Ardashir_I_Kushanshah_in_the_name_of_Vasudeva_circa_230-245_CE.jpg)
![Hormizd I Kushanshah with mention of Mazda and Anahita. Merv mint.[9]](/w/images/thumb/8/83/Hormizd_I_Kushanshah_Merv_mint.jpg/150px-Hormizd_I_Kushanshah_Merv_mint.jpg)


![Kushano-Sasanian footed cup with medallion, 3rd-4th century CE, Bactria, Metropolitan Museum of Art.[15]](/w/images/thumb/1/12/Kushano-Sasanian_footed_cup_with_medallion_3rd-4th_century_CE_Bactria_Metropolitan_Museum_of_Art.jpg/200px-Kushano-Sasanian_footed_cup_with_medallion_3rd-4th_century_CE_Bactria_Metropolitan_Museum_of_Art.jpg)
![Possible Kushano-Sasanian plate, excavated in Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 350-400 CE.[16] British Museum 124093.[17][18]](/w/images/thumb/9/9a/Silverplate_with_investiture_scene._Sasanian_4th_century_CE%2C_possibly_Afghanistan._Middle_East%2C_52_Ancient_Iran_-_28174064678.jpg/200px-Silverplate_with_investiture_scene._Sasanian_4th_century_CE%2C_possibly_Afghanistan._Middle_East%2C_52_Ancient_Iran_-_28174064678.jpg)

![A probable Kushano-Sasanian plate with hunting scene, found in the 504 CE tomb of Feng Hetu in China. Shanxi Museum. It is dated the 3rd-4th century CE, and was probably manufactured in northern Afghanistan.[19][20][21]](/w/images/thumb/8/82/Sasanian_Gilt_Silver_Plate%2C_from_Northern_Wei_504_CE_tomb.jpg/200px-Sasanian_Gilt_Silver_Plate%2C_from_Northern_Wei_504_CE_tomb.jpg)
![Vishnu Nicolo Seal: Kushano-Sasanian or Kidarite prince worshipping Vishnu or Vāsudeva, with Bactrian inscription. Found in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. 4th century CE. British Museum.[23][24][25]](/w/images/thumb/0/08/VishnuGandhara.JPG/147px-VishnuGandhara.JPG)
![Sasanian dignitary drinking wine, on ceiling of Cave 1, at Ajanta Caves, India, end of the 5th century.[26]](/w/images/thumb/b/ba/Ajanta_Cave_1_Group_of_foreigners.jpg/200px-Ajanta_Cave_1_Group_of_foreigners.jpg)

