اليونان الكلاسيكية
Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years (the 5th and 4th centuries BC) in Ancient Greece,[1] marked by much of the eastern Aegean and northern regions of Greek culture (such as Ionia and Macedonia) gaining increased autonomy from the Persian Empire; the peak flourishing of democratic Athens; the First and Second Peloponnesian Wars; the Spartan and then Theban hegemonies; and the expansion of Macedonia under Philip II. Much of the early defining politics, artistic thought (architecture, sculpture), scientific thought, theatre, literature and philosophy of Western civilization derives from this period of Greek history, which had a powerful influence on the later Roman Empire. The Classical era ended after Philip II's unification of most of the Greek world against the common enemy of the Persian Empire, which was conquered within 13 years during the wars of Alexander the Great, Philip's son.
In the context of the art, architecture, and culture of Ancient Greece, the Classical period corresponds to most of the 5th and 4th centuries BC (the most common dates being the fall of the last Athenian tyrant in 510 BC to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC). The Classical period in this sense follows the Greek Dark Ages and Archaic period and is in turn succeeded by the Hellenistic period.
القرن الخامس ق.م.

Athens under Cleisthenes
The Persian wars
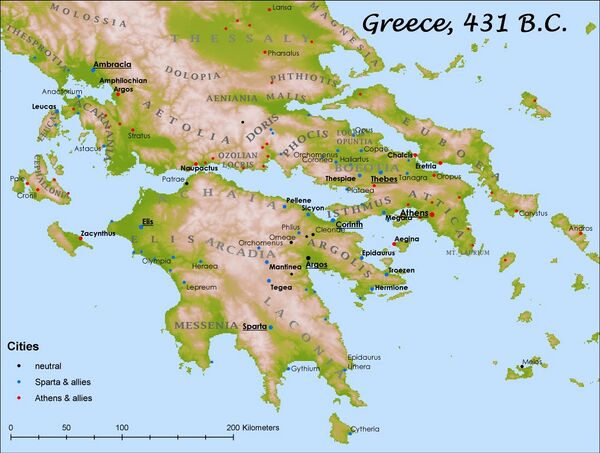
The Peloponnesian war
Origins of the Delian League and the Peloponnesian League
Delian league
Peloponnesian (or Spartan) league
The thirty years peace
Causes of the Peloponnesian war
The Peloponnesian war: Opening stages (431–421 BC)

The Peloponnesian war: Second phase (418–404 BC)
The Melian expedition (416 BC)
The Sicilian expedition (415–413 BC)


Alcibiades in Sparta
Persia intervenes
Lysander and the end of the war
4th century BC
The fall of Sparta
Foundation of a Spartan empire

The peace of Antalcidas
Spartan interventionism
Clash with Thebes
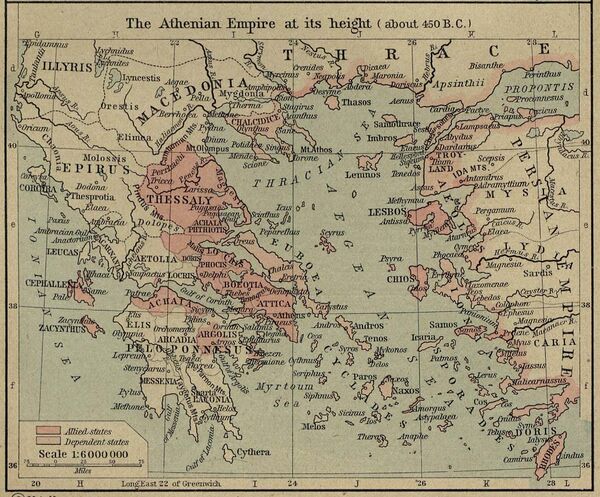
The rise of Athens
Financing the league
Athenian hegemony halted
Theban hegemony – tentative and with no future
5th century BC Boeotian confederacy (447–386 BC)
Theban reconstruction
Confrontation between Athens and Thebes
Rise of Macedon

Legacy of Classical Greece
انظر أيضاً
الهوامش
المصادر
- ^ The "Classical Age" is "the modern designation of the period from about 500 B.C. to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C." (Thomas R. Martin, Ancient Greece, Yale University Press, 1996, p. 94).