ثقافة پازيريك
| النطاق الجغرافي | South Siberia |
|---|---|
| التواريخ | 6th to 3rd centuries BC |
| سبقها | Arzhan culture, Karakol culture |
| تلاها | Xiongnu, Tashtyk culture |
The Pazyryk culture (روسية: Пазырыкская культура Pazyrykskaya kul'tura) is a Saka (Central Asian Scythian)[1] nomadic Iron Age archaeological culture (6th to 3rd centuries BC) identified by excavated artifacts and mummified humans found in the Siberian permafrost, in the Altay Mountains, Kazakhstan and nearby Mongolia. The mummies are buried in long barrows (or kurgans) similar to the tomb mounds of Scythian culture in Ukraine. The type site are the Pazyryk burials of the Ukok Plateau.[2] Many artifacts and human remains have been found at this location, including the Siberian Ice Princess, indicating a flourishing culture at this location that benefited from the many trade routes and caravans of merchants passing through the area.[3] The Pazyryk are considered to have had a war-like life.[4] The Pazyryk culture was preceded by the "Arzhan culture" (Initial Scythian period, 8th - 7th century BC).[5]
الآثار
Other kurgan cemeteries associated with the culture include those of Bashadar, Tuekta, Ulandryk, Polosmak, or Berel. There are so far no known sites of settlements associated with the burials, suggesting a purely nomadic lifestyle.
Because of a freak climatic freeze, some of the Altai burials, notably those of the 5th century BC at Pazyryk and neighbouring sites, such as Katanda, Shibe, and Tuekta, were isolated from external climatic variations by a protective layer of ice that conserved the organic substances buried in them. At Pazyryk these included the bodies of horses and an embalmed man whose body was covered with tattoos of animal motifs. The remarkable textiles recovered from the Pazyryk burials include the oldest woollen knotted-pile carpet known, the oldest embroidered Chinese silk, and two pieces of woven Persian fabric (State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg). Red and ochre predominate in the carpet, the main design of which is of riders, stags, and griffins. Many of the Pazyryk felt hangings, saddlecloths, and cushions were covered with elaborate designs executed in appliqué feltwork, dyed furs, and embroidery. Of exceptional interest are those with animal and human figural compositions, the most notable of which are the repeat design of an investiture scene on a felt hanging and that of a semihuman, semibird creature on another (both in the State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg). Clothing, whether of felt, leather, or fur, was also lavishly ornamented.
Horse reins either had animal designs cut out on them or were studded with wooden ones covered in gold foil. Their tail sheaths were ornamented, as were their headpieces and breastpieces. Some horses were provided with leather or felt masks made to resemble animals, with stag antlers or rams’ horns often incorporated in them. Many of the trappings took the form of iron, bronze, and gilt wood animal motifs either applied or suspended from them; and bits had animal-shaped terminal ornaments. Altai-Sayan animals frequently display muscles delineated with dot and comma markings, a formal convention that may have derived from appliqué needlework. Such markings are sometimes included in Assyrian, Achaemenian, and even Urartian animal representations of the ancient Middle East. Roundels containing a dot serve the same purpose on the stag and other animal renderings executed by contemporary Śaka metalworkers. Animal processions of the Assyro-Achaemenian type also appealed to many Central Asian tribesmen and are featured in their arts.
Certain geometric designs and sun symbols, such as the circle and rosette, recur at Pazyryk but are completely outnumbered by animal motifs. The stag and its relatives figure as prominently as in Altai-Sayan. Combat scenes between carnivores and herbivores are exceedingly numerous in Pazyryk work; the Pazyryk beasts are locked in such bitter fights that the victim's hindquarters become inverted.[6]
Tatooes of the warrior excavated at Pazyryk, with zoomorphic symbols, 5th-4th century BCE.[7]
Scene of torment, burial mound Berel (V. - III. BCE) Kazakhstan, Pazyryk culture.[8]
Frontal decoration (harness), burial mound Berel (IV.-III. B.C.) Kazakhstan, Pazyryk culture.[8]
الجينات
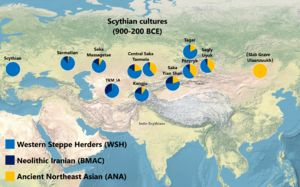
The Pazyryk population is associated with the Eastern Scythian horizon, which emerged out of Western Steppe Herders (WSH or Steppe_MLBA) and local groups of Southern Siberia. Genetic data revealed that the Iron Age Pazyryk people were not identical with the WSH but substantially shifted towards East Eurasians. The eastern Eurasian geneflow can largely be explained through Khövsgöl LBA groups, themselves a combination of primarily Ancient Northeast Asians and components associated with Ancient North Eurasians and the Sintashta culture. Some outlier samples need additional geneflow from an Ancient Northeast Asian source, best represented by Neolithic groups from the Devil’s Gate Cave site in the Russian Far East.[9] Overall, the Pazyryk population could be modeled to derive between c. 50% from the Khövsgöl LBA source, c. 36% from WSH (Steppe_MLBA), and c. 14% from a BMAC-like source. One outlier specimen (Pazyryk_Berel_50BCE) could be modeled as c. 18% Pazyryk_IA and c. 82% additional Northeast Asian admixture, suggesting that this individual represents a migrant who arrived from further East.[10][11]
Maternal haplogroups
Two individuals were found to belong to the East Eurasian maternal haplogroup C4.[12]
Paternal haplogroups
Two closely related males from the Pazyryk culture were found to belong to the East Eurasian paternal haplogroup N.[13][14]
Another Pazyryk specimen was found to belong to the West Eurasian paternal haplogroup R1a-Z93.[15]
Pazyryk man (reconstruction from burials, Anokhin Museum).[16]
Siberian Ice Maiden inside her wooden sarcophagus (reconstruction from burial, Anokhin Museum).[16]
Mummy of the Siberian Ice Maiden
See also
References
Citations
- ^ The Editors (2001-09-11). "Pazyryk | archaeological site, Kazakhstan". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2019-03-05.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ (NOVA 2007)
- ^ (State Hermitage Museum 2007)
- ^ (Jordana 2009)
- ^ Murphy, Eileen M. (2003). "Iron Age Archaeology and Trauma from Aymyrlyg South Siberia: An examination of the health diet and lifestyles of the two Iron Age populations buried at the cemetery complex of Aymyrlyg". BAR International Series.
- ^ "Altaic Tribes". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved December 5, 2016.
- ^ "Siberian Princess reveals her 2,500 year old tattoos". The Siberian Times. 2012.
- ^ أ ب ت "International exhibition of original artifacts «Scythian gold»" (PDF). 2017: 92–97.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Gnecchi-Ruscone, Guido Alberto; Khussainova, Elmira; Kahbatkyzy, Nurzhibek; Musralina, Lyazzat; Spyrou, Maria A.; Bianco, Raffaela A.; Radzeviciute, Rita; Martins, Nuno Filipe Gomes; Freund, Caecilia; Iksan, Olzhas; Garshin, Alexander; Zhaniyazov, Zhassulan; Bekmanov, Bakhytzhan; Kitov, Egor; Samashev, Zainolla (2021-03-26). "Ancient genomic time transect from the Central Asian Steppe unravels the history of the Scythians". Science Advances (in الإنجليزية). 7 (13). doi:10.1126/sciadv.abe4414. ISSN 2375-2548. PMC 7997506. PMID 33771866.
- ^ Gnecchi-Ruscone, Guido Alberto; Khussainova, Elmira; Kahbatkyzy, Nurzhibek; Musralina, Lyazzat; Spyrou, Maria A.; Bianco, Raffaela A.; Radzeviciute, Rita; Martins, Nuno Filipe Gomes; Freund, Caecilia; Iksan, Olzhas; Garshin, Alexander; Zhaniyazov, Zhassulan; Bekmanov, Bakhytzhan; Kitov, Egor; Samashev, Zainolla (2021-03-26). "Ancient genomic time transect from the Central Asian Steppe unravels the history of the Scythians". Science Advances (in الإنجليزية). 7 (13). doi:10.1126/sciadv.abe4414. ISSN 2375-2548. PMC 7997506. PMID 33771866.
- ^ Unterländer 2017
- ^ Pilipenko, Trapezov & Polosmak 2015, p. 148
- ^ Pilipenko, A. S.; Trapezov, R. O.; Polosmak, N. V (2015). "A PALEOGENETIC STUDY OF PAZYRYK PEOPLE BURIED AT AK-ALAKHA-1, THE ALTAI MOUNTAINS". Archaeology, Ethnology and Anthropology of Eurasia (Russian-language). 43 (4): 144–150. doi:10.17746/1563-0102.2015.43.4.144-150.
- ^ Pilipenko, Trapezov & Polosmak 2015, p. 148
- ^ Unterländer 2017
- ^ أ ب "Legal bid fails to rebury remains of 2,500 year old tattooed 'ice princess'". The Siberian Times. 2016.
Sources
- Jordana, Xavier (2009). "The warriors of the steppes: osteological evidence of warfare and violence from Pazyryk tumuli in the Mongolian Altai". Journal of Archaeological Science. 36 (7): 1319–1327. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2009.01.008.
- NOVA (2007). "Ice Mummies: Siberian Ice Maiden". PBS - NOVA. Retrieved 2007-07-31.
- State Hermitage Museum (2007). "Prehistoric Art - Early Nomads of the Altaic Region". The Hermitage Museum. Archived from the original on 2007-06-22. Retrieved 2007-07-31.
- Сергей Иванович Руденко (Sergei I. Rudenko) (1970). Frozen Tombs of Siberia: The Pazyryk Burials of Iron Age Horsemen. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0520013957.
External links
- Nomadic Art of the Eastern Eurasian Steppes, an exhibition catalog from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (fully available online as PDF), which contains material on Pazyryk culture
- CS1 errors: generic name
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles containing روسية-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Pages using multiple image with auto scaled images
- Archaeological cultures of Siberia
- Animals in art
- جماعات بدوية في أوراسيا
- Iranian archaeological cultures
- Saka
- Scytho-Siberian world
- 6th-century BC establishments





![Tatooes of the warrior excavated at Pazyryk, with zoomorphic symbols, 5th-4th century BCE.[7]](/w/images/thumb/c/cd/Pazyryk_tatoo_design_with_zoomorphic_symbols%2C_4th_century_BCE.jpg/200px-Pazyryk_tatoo_design_with_zoomorphic_symbols%2C_4th_century_BCE.jpg)


![Catlike predator with protomas of two elk, burial mound Berel (IV.-III. BCE) Kazakhstan, Pazyryk culture.[8]](/w/images/thumb/f/ff/31._Catlike_predator_with_protomas_of_two_elk_burial_mound_Berel_%28IV.-III._B.C.%29_Kazakhstan.JPG/163px-31._Catlike_predator_with_protomas_of_two_elk_burial_mound_Berel_%28IV.-III._B.C.%29_Kazakhstan.JPG)
![Scene of torment, burial mound Berel (V. - III. BCE) Kazakhstan, Pazyryk culture.[8]](/w/images/thumb/0/05/25._Scene_of_torment_burial_mound_Berel_%28V._-_III._B._C.%29_Kazakhstan.JPG/200px-25._Scene_of_torment_burial_mound_Berel_%28V._-_III._B._C.%29_Kazakhstan.JPG)
![Frontal decoration (harness), burial mound Berel (IV.-III. B.C.) Kazakhstan, Pazyryk culture.[8]](/w/images/thumb/2/2f/34._Frontal_decoration_%28harness%29_burial_mound_Berel_%28IV.-III._B.C.%29_Kazakhstan.JPG/116px-34._Frontal_decoration_%28harness%29_burial_mound_Berel_%28IV.-III._B.C.%29_Kazakhstan.JPG)

![Pazyryk man (reconstruction from burials, Anokhin Museum).[16]](/w/images/thumb/c/ce/Pazyryk_man_%28reconstruction%2C_Anokhin_Museum%29.jpg/128px-Pazyryk_man_%28reconstruction%2C_Anokhin_Museum%29.jpg)
![Siberian Ice Maiden inside her wooden sarcophagus (reconstruction from burial, Anokhin Museum).[16]](/w/images/thumb/2/26/Siberian_Ice_Maiden_in_her_wooden_sarcophagus.jpg/157px-Siberian_Ice_Maiden_in_her_wooden_sarcophagus.jpg)

