تشنهوانغداو
39°53′18″N 119°31′13″E / 39.8882°N 119.5202°E
Qinhuangdao
秦皇岛市 | |
|---|---|
Clockwise from the top: Aerial view of the city, Shanhai Pass, Longtan Falls, Yan Mountains, Old Dragon Head, Habitat Apartments | |
| الكنية: Back Garden of Beijing and Tianjin (京津后花园) | |
 | |
 Location of Qinhuangdao City jurisdiction in Hebei | |
| الإحداثيات (People's Square): 39°56′26″N 119°35′42″E / 39.9406°N 119.5951°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Hebei |
| Settled | 1737 |
| Established | March 3, 1983 |
| Municipal seat | Haigang District |
| الحكومة | |
| • Party Secretary | Meng Xiangwei |
| • Mayor | Zhang Ruishu |
| المساحة | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 7٬791٫57 كم² (3٬008٫34 ميل²) |
| • الحضر | 2٬122٫9 كم² (819٫7 ميل²) |
| • العمران | 2٬122٫9 كم² (819٫7 ميل²) |
| التعداد (2020 census)[1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 3٬136٬879 |
| • الكثافة | 400/km2 (1٬000/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1٬881٬047 |
| • الكثافة الحضرية | 890/km2 (2٬300/sq mi) |
| • العمرانية | 1٬881٬047 |
| • الكثافة العمرانية | 890/km2 (2٬300/sq mi) |
| منطقة التوقيت | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 066000 |
| مفتاح الهاتف | (0)335 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HE-03 |
| Licence Plate Prefix | 冀C |
| الموقع الإلكتروني | http://www.qhd.gov.cn/ |
| تشنهوانغداو | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Qinhuangdao", as written in Simplified Chinese (top) and Traditional Chinese (bottom) | |||||||||
| الصينية المبسطة | 秦皇岛 | ||||||||
| الصينية التقليدية | 秦皇島 | ||||||||
| المعنى الحرفي | Qin Shi Huang Island | ||||||||
| |||||||||
تشنهوانگداو (صينية مبسطة: 秦皇岛; صينية تقليدية: 秦皇島; پنين: Qínhuángdǎo; ويد-گايلز: Ch'in Huang Tao; Postal map spelling: Chinwangtao; أصد: [´tɕʰɪn´hwɒŋ`´taʊ]) هي مدينة في مقاطعة خـِبـِيْ، الصين، تبعد حوالي 300 كم شرق بكين، على بحر بوهاي أكثر الخلجان عمقاً في البحر الأصفر، وتعتبر الميناء الرئيسي في خبي. بلغ عدد سكان تشنهوانگداو في عام 2020، 3,136,879 نسمة موزعين على مساحة 7.812،4 كم مربع.
قيل أن الامبراطور من أسرة تشين تشين شي هوانگ نشد الخلود في جزيرة في منطقة هايگانگ، إلا أنه لم يعثر عليها.
وتضم تشنهوانگداو ثلاث مناطق عمرانية:
- بـِيْدايخه Beidaihe: المنتجع الساحلي الصيفي لكبار المسئولين الحكوميين. العديد من القرارت السياسية الهامة التي تؤثر على الصين تتخذ هنا، مما يجعله مشابهاً للمنتجعات الرئاسية الأمريكية مثل كامپ ديڤيد في مريلاند في الولايات المتحدة.[3]
- منطقة هايگانگ: المدينة الميناء. وهي المقصودة إذا قيل "تشنهوانگداو". وهي مقر جامعة يان شان، من أهم جامعات شمال شرق مقاطعة خبـِيْ.
- شانهايگوان Shanhaiguan: مقصد سياحي شهير، لأنه الطرف الشرقي لسور الصين العظيم.
وقد استعمل الاستاد مركز الرياضات الاولمبية في تشنهوانگداو كمقر لتصفيات كرة القدم الاولمبية أثناء الألعاب الاولمبية الصيفية 2008.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Climate
Qinhuangdao has a monsoon-influenced humid continental climate (Köppen Dwa), with four distinct seasons. Winters are cold and dry due to the Siberian high, which often causes winds to blow in from the northwest, minimising the oceanic influence: the monthly daily average temperature in January is −4.8 °C (23.4 °F), colder than Beijing's −3.7 °C (25.3 °F).[4] Summers are hot and humid due to the East Asian Monsoon, often allowing onshore flows; summer is also when the coast moderates the weather the most: the average high temperature in July here is 28.1 °C (83 °F), as compared to 30.9 °C (88 °F) in Beijing.[4] As measured by daily mean temperature, July and August are equally warm, averaging 24.7 °C (76.5 °F). The annual mean is 11.0 °C (51.8 °F), and 70% of the annual precipitation falls from June to August.
| Climate data for Qinhuangdao (1981–2010 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12.7 (54.9) |
18.3 (64.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
28.6 (83.5) |
37.1 (98.8) |
39.2 (102.6) |
39.2 (102.6) |
35.2 (95.4) |
34.2 (93.6) |
29.5 (85.1) |
21.6 (70.9) |
14.0 (57.2) |
39.2 (102.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −0.1 (31.8) |
3.1 (37.6) |
8.6 (47.5) |
16.0 (60.8) |
22.2 (72.0) |
25.5 (77.9) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.2 (82.8) |
25.3 (77.5) |
18.5 (65.3) |
9.7 (49.5) |
2.2 (36.0) |
15.6 (60.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −5.6 (21.9) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
3.5 (38.3) |
10.8 (51.4) |
17.1 (62.8) |
21.3 (70.3) |
24.7 (76.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
19.9 (67.8) |
12.5 (54.5) |
3.8 (38.8) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
10.6 (51.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −10.6 (12.9) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
6.1 (43.0) |
12.4 (54.3) |
17.5 (63.5) |
21.5 (70.7) |
20.5 (68.9) |
14.9 (58.8) |
7.1 (44.8) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −26.0 (−14.8) |
−18.6 (−1.5) |
−13.1 (8.4) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
3.0 (37.4) |
9.9 (49.8) |
14.2 (57.6) |
11.4 (52.5) |
4.4 (39.9) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
−17.7 (0.1) |
−26.0 (−14.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 3.0 (0.12) |
3.9 (0.15) |
10.3 (0.41) |
26.8 (1.06) |
54.0 (2.13) |
87.3 (3.44) |
168.2 (6.62) |
155.8 (6.13) |
51.5 (2.03) |
26.2 (1.03) |
9.5 (0.37) |
3.7 (0.15) |
600.2 (23.64) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 2.1 | 2.2 | 3.3 | 5.1 | 7.3 | 10.6 | 12.8 | 9.9 | 7.1 | 4.6 | 3.3 | 1.7 | 60.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 57 | 59 | 58 | 61 | 67 | 78 | 84 | 82 | 75 | 66 | 59 | 56 | 67 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Data Service Center[5] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China (precipitation days 1971–2000)[6] | |||||||||||||
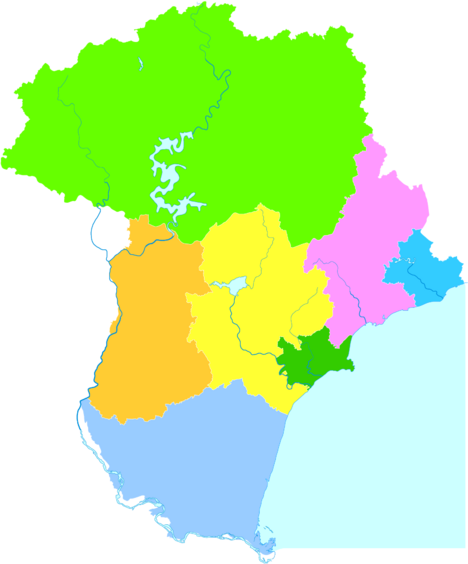
التقسيمات الإدارية
| الخريطة | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| الاسم | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010) |
Area (km2) | Density (/km2) |
| City proper | |||||
| Haigang District | 海港区 | Hǎigǎng Qū | 765,254 | 246 | 3,110 |
| Suburban | |||||
| Shanhaiguan District | 山海关区 | Shānhǎiguān Qū | 178,879 | 193 | 926 |
| Beidaihe District | 北戴河区 | Běidàihé Qū | 85,647 | 73 | 1,173 |
| Funing District | 抚宁区 | Fǔníng Qū | 517,073 | 1,618 | 319 |
| Rural | |||||
| Changli County | 昌黎县 | Chānglí Xiàn | 559,687 | 1,212 | 461 |
| Lulong County | 卢龙县 | Lúlóng Xiàn | 384,439 | 961 | 400 |
| Qinglong Manchu Autonomous County | 青龙满族自治县 | Qīnglóng Mǎnzú Zìzhìxiàn | 496,726 | 3,510 | 141 |
منطقة تنمية
The Qinhuangdao Economic & Technology Development Zone was approved by the State Council of the People's Republic of China in 1984 to become one of China's first state-level economic and technological development zones. Qinhuangdao is in the heart of the rapidly growing "Bohai-Rim Economic Circle", in easy reach of Beijing (280 km (170 mi)) and Tianjin (245 km (152 mi)).[7] It covers a sea area of 23.81 km2 (9.19 sq mi) and has a coastline of 6 km (3.7 mi). The planned and controlled area of the development zone has reached 56.72 km2 (21.90 sq mi). By the end of 2006, the number of approved projects reached 4,546, in which 647 projects were foreign-invested, with a total investment of US$4.73 billion.
Qinhuangdao Export Processing Zone is the first export processing zone in Hebei Province. It passed joint appraisal held by the General Administration of Customs, the State Development Planning Commission, and other six departments in 2003. Industries encouraged in the zone include electronics assembly and manufacturing, building/construction materials, computer software, trading and distribution.[8]
الاقتصاد
Qinhuangdao Port is a strategically important port and is the largest coal shipping port in the country, much of which is shipped to power plants elsewhere in China. With recent expansion, its capacity has reached 209 million metric tons. The harbor is adding a further six berths to add capacity and is increasingly being invested in by other port operators, such as South Africa's Port of Richards Bay, who have announced plans to invest US$150 million to increase capacity by at least 28 percent.
China is the world's third largest coal exporter, and Qinhuangdao is expected to handle much of the nation's coal exports. Rail links from Shanxi (China's largest coal producer) to Qinhuangdao Port are being upgraded, which should allow for Qinhuangdao to ultimately increase its throughput to 400 million tonnes of coal per annum from its current level of about 250 million tons by 2015.[بحاجة لمصدر]
Other Chinese and foreign service suppliers are moving to Qinhuangdao to support this. China Ocean Shipping (Group) Co, China's biggest shipping company, expects US$49 billion of spending on ports over the next five years as the industry tackles bottlenecks created by the nation's unprecedented economic boom.[9]
Qinhuangdao is on the Jingshen Expressway which links Beijing with Shenyang, Liaoning.
The city is served by Qinhuangdao Beidaihe Airport.
السياحة
The Qinhuangdao Wildlife Park was opened in 1995 and is China's second largest wildlife park.[بحاجة لمصدر]
Red Ribbon
Qinhuangdao is home to the Tanghe River Park, which features the Red Ribbon, a knee-high steel sculpture that runs the length of the park, providing seating, environmental interpretation, lighting, and the display of native plants. The project has won an honor award from the American Society of Landscape Architects and was selected by readers of Condé Nast Traveler magazine as one of the seven new wonders of the architecture world.[10]
التعليم
- Yanshan University
- Northeastern University at Qinhuangdao
- Hebei Institute of International Business and Economics
- Hebei Normal University of Science and Technology
- Northeastern Petroleum University at Qinhuangdao
المدن التوأم
تشنهوانگداو متوأمة مع:
 Gangdong, كوريا الجنوبية
Gangdong, كوريا الجنوبية ميازو, اليابان
ميازو, اليابان پسارو، إيطاليا
پسارو، إيطاليا سيوسان, كوريا الجنوبية
سيوسان, كوريا الجنوبية توليدو, الولايات المتحدة
توليدو, الولايات المتحدة Toyama, اليابان
Toyama, اليابان لوگو, اسبانيا
لوگو, اسبانيا
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
المدن الشقيقة
المصادر
- ^ "China: Hébĕi (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- ^ Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, ed. (2019). China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2017. Beijing: China Statistics Press. p. 46. Archived from the original on June 18, 2019. Retrieved January 11, 2020.
- ^ "China Expat City Guide". Asia Briefing. 2009. Retrieved 2009-02-08.
- ^ أ ب 中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1971-2000年) (in الصينية المبسطة). China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved May 28, 2011.
- ^ 中国地面气候标准值月值(1981-2010) (in الصينية المبسطة). China Meteorological Data Service Center. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ 秦皇岛 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 (in الصينية). Weather China. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ "Qinhuangdao Economic & Technology Development Zone". RightSite.asia. Archived from the original on August 1, 2012. Retrieved December 24, 2012.
- ^ "Qinhuangdao Export Processing Zone". RightSite.asia. Archived from the original on August 1, 2012. Retrieved December 24, 2012.
- ^ "China Briefing Business Guide" (PDF). China Briefing. 2009. Retrieved February 8, 2009.[dead link]
- ^ "Red Ribbon in Tanghe River Park". Contemporist. March 27, 2008. Archived from the original on January 20, 2009. Retrieved December 19, 2008.
وصلات خارجية
- الموقع الرسمي للمدينة
- Official website of Qinhuangdao Travel Administration
- China Travel Guide - Qinhuangdao
- China Briefing Business Reports
- China Expat City Guide: Qinghuangdao
للاستزادة
China Briefing: Business Guide to Beijing and Northeast China (2nd ed.). 2008. Retrieved 2008-02-17.
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- CS1 uses الصينية-language script (zh)
- CS1 الصينية المبسطة-language sources (zh-hans)
- CS1 الصينية-language sources (zh)
- Articles with dead external links from November 2021
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles containing صينية-language text
- Articles containing Pinyin-language text
- Articles with unsourced statements from May 2022
- مقالات ذات عبارات بحاجة لمصادر
- تشنهوانگداو
- مدن في خبي
- Prefecture-level divisions of Hebei
- صفحات مع الخرائط