العلاقات الخارجية للهند
|
هذا القالب جزء مقالات عن: |
|
حكومات المحليات والولايات
|
|
|
تعتبر جمهورية الهند من أكثر بلدان العالم الانتخابية الديموقراطية إكتظاظا بالسكان ولديها واحدا من أسرع معدلات النمو الاقتصادي في العالم (8.9 % زيادة إجمالي الناتج المحلي في عام 2007، ثاني أسرع اقتصادات العالم الكبرى بعد الصين).[1] وهي ثالث أكبر بلدان العالم من حيث عدد القوات المسلحة،[2] ورابع اقتصاد الهند|اقتصاد من حيث تعادل القوة الشرائية، ومن المتوقع أن تصبح قوة عالمية،[3][4] اقليمية[5][6] وأوسطية.[7][8][9][10] وأدى تزايد النفوذ الدولي للهند إلى إعطائه صوتا أكثر نفوذا في الشؤون العالمية.[11][12][13][14]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التاريخ
السياسة
دور رئيس الوزراء

وزارة الشؤون الخارجية
نظرة عامة

الهند، في عهد حكومة حزب المؤتمر, وريثة غاندي ونهرو, تدير ظهرها لسياسة الدبلوماسية الأخلاقية التي ورثتها من روادها وتتحول إلي قاعدة عسكرية استراتيجية هجومية في صعود مطرد, وهنا لابد من فتح ملف لم يهتم به الخبراء في عالمنا العربي, بينما ارتفع عدد الدراسات المتخصصة في كبري مجلات دول حلف شمال الأطلنطي.
- الوثائق شبه الرسمية تشير إلي أن المناطق التي تري الهند أنها تمثل أهمية كبيرة لأمنها القومي تشمل: شرق إفريقيا الجنوبية, ومناطق مهمة في إفريقيا الشرقية( أوغندا ـ كينيا ـ تنزانيا), وكذا الجزيرة والخليج, ثم سيريلانكا, نيبال, بورما, ماليزيا وسنغافورة, أي مفاتيح طريق إمداد آسيا الشرقية بالطاقة القادمة من الشرق الأوسط في المقام الأول.[15]
- ميزانية الدفاع في الهند لعام2009 بلغت29 مليار دولار, وذلك لتمويل قوات مسلحة تعدادها1,3 مليون. الوحدات البرية تشمل تعدادها1,1 مليون تعتمد علي4 آلاف دبابة,2800 مركبة مدرعة,12 ألف قطعة مدفعية,150 مروحية للنقل,3500 صاروخ أرض جو,2300 مدفع مضاد للطائرات.. القوات الجوية تشمل170 ألف رجل يعتمدون علي852 طائرة حربية و280 طائرة نقل هذا بينما تشرع الهند لشراء196 طائرة حربية من ستة مصانع أمريكية, أوروبية, إسرائيلية. والملفت أن البحرية تحظي بالمكانة الأولي فسوف تشمل قريبا حاملتي طائرات ومعها63 سفينة حربية كبيرة و16 غواصة.
وقد بدا الأمر وكأن الجيش الهندي ينسي غاندي ويحلم بالجبروت علي حد تعبير مجلة الموند الدبلوماسي( سبتمبر2009). عند هذا الحد نتساءل: ما الهدف من هذا الصعود الخارق للقوة الاستراتيجية الهندية؟ الإجابة التقليدية هي: باكستان ـ ولكن الواضح أن القوات البرية الهندية متفوقة بشكل هائل علي قو ات باكستان, وكذا من المعروف أن التسلح النووي الهندي يكفي لردع قدرات باكستان. ويري بعض المحللين أن الصراع علي كشمير يساعد علي فهم التصعيد الهندي ولكن الواقع أن القوات الهندية التقليدية تكفي بجميع المقاييس. وهناك رأي يتجه إلي الاهتمام بنمو الوجود الهندي في أفغانستان: هناك مثلا خمس قنصليات للهند علي مساحة الحدود بين أفغانستان وباكستان ومن ورائها عشرات الآلاف من الخبراء العسكريين ينتشرون, يدربون, يوجهون قوات إدارة أفغانستان الموالية للولايات المتحدة وبديهي ان الاهتمام بالحدود الافغانية, الباكستانية يلبي احتياجات حصار الحركة الإسلامية الاستقلالية في كشمير.
حسنا, ولكن: كيف يمكن تفسير الاتفاق حول الطاقة الذرية السلمية الذي أبرمه كل من الرئيسين جورج دبليو بوش ومانموهان سنغ عام2005 والذي وافق عليه كونجرس الولايات المتحدة عام2005 ؟ الولايات المتحدة ضربت بقواعد معاهدة عدم الانتشار النووي عرض الحائط وسمحت للهند أن تصبح دولة نووية عسكرية مسئولة وهي ثاني حالة في العالم, بعد أن تفردت إسرائيل بهدا الوضع دون تصريح أمريكي بطبيعة الأمر.
ما الهدف من هذه الترسانة النووية في قلب التعبئة العسكرية الهائلة, خاصة فيما يتعلق بسلاح البحرية؟ مجرد الضغط علي كشمير؟ أو صيانة حكم كرزاي في افغانستان؟ أم أن جوهر الموضوع حسب جميع الخبراء والمحللين في معظم أنحاء العالم هو ان هذه الخطة تهدف الي تحقيق هدفين: السيطرة الكاملة علي مضايق وخطوط الملاحة عبر المحيط الهندي أي السيطرة علي خط حياة الاقتصاد الصيني والآسيوي الشرقي من ناحية, وهي الناحية الرئيسية. أما الهدف الثاني, المواكب وليس الثانوي, فإنما هو دعم الطاقة الاستراتيجية الأمريكية في آسيا الوسطي التي تهدف الي قطع شرايين امداد الطاقة من غرب آسيا وروسيا الي الصين وكذا اليابان وكوريا عبر سيبيريا. ولو تصورنا لحظة مع أدعياء الخبرة الجيوسياسية الحاقدين ان هذا المخطط يمكن أن ينجح في يوم من الأيام, فإن هذا النجاح قد يعني ـ في نظر الواهمين بطبيعة الأمر ـ خنق الصين وآسيا الشرقية والقضاء نهائيا ودون رجعة لظهور أقطاب جديدة للنظام العالمي الجديد, ليس فقط الصين وشرق آسيا وإنما كذلك روسيا ـ بحيث تنفرد الولايات المتحدة وكوكبة حلف شمال الأطلنطي بالسيطرة علي قارة آسيا كلها, مستندة إلي الهند الحليفة الجديدة الصاعدة يدا في يد مع إسرائيل>


الشركاء الاستراتيجيون
العلاقات الثنائية والاقليمية
دور الجوار
"الهندي القبيح"[16]
أفغانستان
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
بنگلادش
بوتان

بورما
المالديڤ
نيپال
پاكستان
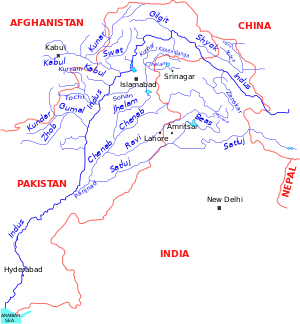
- مشكلة كشمير العالقة.
- خلافات حدودية حول فيروزپور وپاثانكوت
- خلاف حول خور كوري والحدود البحرية في ران كچ في الهند.
- تقاسم مياه نهر الإندوس (قناطر ولار) (معاهدة نهر الإندوس).
سريلانكا
آسيا-المحيط الهادي
أستراليا
الصين

فيجي
اليابان

لاوس
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
اندونسيا
ماليزيا
India has a high commission in Kuala Lumpur, and Malaysia has a high commission in New Delhi. Both countries are full members of the Commonwealth of Nations, and the Asian Union. India and Malaysia are also connected by various cultural and historical ties that date back to antiquity. The two countries are on excellently friendly terms with each other seeing as Malaysia is home to a strong concentration of Indian immigrants.
سنغافورة

كوريا الجنوبية


تايوان
تايلاند
ڤتنام
الأمريكتين
الأرجنتين
البرازيل
كندا
كولومبيا
المكسيك
انظر أيضا الهندوسية في المكسيك
پاراگواي
الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية
فترة الحرب الباردة

إختبارات پوخران
بعد هجمات 11 سبتمبر

الشراكة الاستراتيجية الهندية الأمريكية
اوروپا
الاتحاد الاوروپي
المملكة المتحدة
فرنسا
ايطاليا
ألمانيا

تركيا
بلدان اوروپية أخرى
| البلد | بدء العلاقات الرسمية | الهوامش |
|---|---|---|
| انظر العلاقات الخارجية لبلاروس | ||
| 1954 | انظر العلاقات الهندية البلغارية | |
| انظر العلاقات الخارجية لكرواتيا | ||
| انظر العلاقات الخارجية لقبرص | ||
| انظر العلاقات الخارجية للدنمارك | ||
| 1991-09-09 | انظر العلاقات الهندية الاستونية
India's first recognition of Estonia came on 22 September 1921 when the former had just acquired membership in the League of Nations. India re-recognised Estonia on September 9, 1991 and diplomatic relations were established on December 2 of the same year in Helsinki. Neither country has a resident ambassador. Estonia is represented in India by 2 honorary consulates (in Mumbai and New Delhi). India is represented in Estonia through its embassy in Helsinki (Finland) and through an honorary consulate in Tallinn. | |
| انظر العلاقات الخارجية لفنلندا | ||
| انظر العلاقات الخارجية لجورجيا | ||
| انظر العلاقات الخارجية لليونان | ||
| انظر Foreign relations of the Holy See | ||
| انظر العلاقات الهندية الآيسلندية
Iceland and India established diplomatic relations in 1972. The Embassy of Iceland in لندن was accredited to India and the Embassy of India in Oslo, Norway, was accredited to Iceland. However, it was only after 2003 that the two countries have began close diplomatic and economic relationships.[20] In 2003, President of Iceland Ólafur Ragnar Grímsson visited India on diplomatic mission. This was the first visit by an Icelandic President to India. During the visit, Iceland pledged support to New Delhi's candidature for a permanent seat in the United Nation Security Council thus becoming the first Nordic country to do so. This was followed by an official visit of President of India A. P. J. Abdul Kalam to Iceland in May 2005.[21] Following this a new embassy of Iceland was opened in New Delhi on 26 February 2006.[20] Soon, a Indian Navy team visited Iceland on friendly mission.[22] Gunnar Pálsson is the ambassador of Iceland to India. The Embassy's area of accreditation, apart from India includes Bangladesh, Indonesia, the Seychelles, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Maldives, Mauritius and Nepal.[23] India appointed S. Swaminathan as the first resident ambassador to Iceland in March 2008.[24] | ||
| انظر العلاقات الهندية الايرلندية
Indo-Irish relations picked up steam during the freedom struggles of the respective countries against a common imperial empire in the المملكة المتحدة. Political relations between the two states have largely been based on socio-cultural ties, although political and economic ties have also helped build relations. Indo-Irish relations were greatly strengthened by the such luminaries as the likes of Pandit Nehru, Éamon de Valera, Rabindranath Tagore, W. B. Yeats, James Joyce, and, above all, Annie Besant. Politically relations have not been cold nor warm. Mutual benefit has led to economic ties that are fruitful for both states.[بحاجة لمصدر] Visits by government leaders have kept relations cordial at regular intervals. | ||
| انظر العلاقات الهندية المالطية
Malta opened a High Commission in New Delhi in 2007. Malta also has an honourary consulate in Bombay. India is represented in Malta through its embassy in Tripoli, Libya and an honorary consulate in Valletta. | ||
| انظر العلاقات الخارجية البولندية
Historically, relations have generally been close and friendly, characterized by understanding and cooperation on international front.[25] | ||
| انظر العلاقات الهندية الروسية
During the Cold War, India and the الاتحاد السوڤيتي enjoyed a strong strategic, military, economic and diplomatic relationship. After the collapse of the USSR, India improved its relations with the West but it continued its close relations with Russia. India is the second largest market for Russian arms industry. In 2004, more than 70% on Indian Military's hardware came from Russia, making Russia the chief supplier of arms.[28] India has an embassy in Moscow and 2 Consulates-General (in Saint Petersburg and Vladivostok). Russia has an embassy in New Delhi and 3 Consulates-General (in Chennai, Kolkata, Mumbai). Since 2000 and the visit of Vladimir Putin in India there have been an Indo-Russian Strategic Partnership. | ||
| ||
| ||
| انظر العلاقات الهندية الاوكرانية
Diplomatic relations between الهند and Ukraine were established in January 1992. Indian Embassy in Kiev was opened in May 1992 and Ukraine opened its Mission in New Delhi in February 1993. The Consulate General of India in Odessa functioned from 1962 till its closure in March 1999. |
الشرق الأوسط
دول الخليج العربي
البحرين
مصر
إيران
العراق
إسرائيل
لبنان
عمان
السعودية
روسيا ووسط آسيا
روسيا

أرمنيا
كزاخستان
منغوليا
طاجيكستان
اوزبكستان
أفريقيا

ساحل العاج
ليبريا
نيجريا
جنوب أفريقيا
السودان
المنظمات الدولية
الهند عضو في المنظمات الدولية التالية:[32]
ADB-Asian Development Bank, AfDB-African Development Bank (nonregional members), ASEAN Regional Forum, ASEAN (dialogue partner), BIMSTEC-Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multisectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation , BIS-Bank for International Settlements, Commonwealth of Nations, CERN-European Organization for Nuclear Research (observer), CP-Colombo Plan, EAS, FAO-Food and Agriculture Organization, G-15, G-24, G-77, IAEA-International Atomic Energy Agency, IBRD-International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (World Bank), ICAO-International Civil Aviation Organization, ICC-International Chamber of Commerce, ICRM-International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, IDA-International Development Association, IFAD-International Fund for Agricultural Development, IFC-International Finance Corporation, IFRCS-International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, IHO-International Hydrographic Organization, ILO-International Labor Organization, IMF-International Monetary Fund, IMO-International Maritime Organization, IMSO-International Mobile Satellite Organization, Interpol-International Criminal Police Organization, IOC-International Olympic Committee, IOM-International Organization for Migration (observer), IPU-Inter-parliamentary Union, ISO-International Organization for Standardization, ITSO-International Telecommunications Satellite Organization, ITU-International Telecommunication Union, ITUC-International Trade Union Confederation (the successor to ICFTU (International Confederation of Free Trade Unions) and the WCL (World Confederation of Labor)), LAS-League of Arab States (observer), MIGA-Multilateral Investment Geographic Agency, MONUC-United Nations Organization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, NAM-Nonaligned Movement, OAS-Organization of American States (observer), OPCW-Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons, PCA-Permanent Court of Arbitration, PIF-Pacific Islands Forum (partner), SAARC-South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, SACEP-South Asia Co-opeative Environment Programme, SCO-Shanghai Cooperation Organization (observer), UN-United Nations, UNCTAD-United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, UNDOF-United Nations Disengagement Observer Force, UNESCO-United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization, UNHCR-United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, UNIDO-United Nations Industrial Development Organization, UNIFIL-United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, UNMEE-United Nations Mission in Ethiopia and Eritrea, UNMIS, UNOCI-United Nations Operation in Cote d'Ivoire, UNWTO-World Tourism Organization, UPU-Universal Postal Union, WCL-World Confederation of Labor, WCO-World Customs Organization, WFTU-World Federation of Trade Unions, WHO-World Health Organization, WIPO-World Intellectual Property Organization, WMO-World Meteorological Organization, WTO-World Trade Organization
حركة عدم الإنحياز
الأمم المتحدة
منظمة التجارة العالمية
SAARC
النزاعات الدولية
بنگلادش
نيپال
Anglo Indian Ocean Territories
المالديڤ
پاكستان
الصين
سياسة نحو الشرق
الهند-آسيان
انظر أيضا
- قائمة البعثات الدبلوماسية في الهند
- قائمة البعثات الدبلوماسية للهند
- Research and Analysis Wing
- Role of India in nonaligned movement
المصادر
- ^ "Indian economic growth rate eases". BBC. 2007-11-30. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- ^ World Almanac: Nation's with Largest Armed Forces
- ^ "US President Barack Obama hails India as global power". Reuters. 2009-04-02. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- ^ Ruth David (2006-07-13). "India As A Global Power". Forbes. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- ^ Indian Navy tsunami aid highlights country's role as 'super regional power
- ^ India As a Regional Power
- ^ India: Asia's Other Superpower Breaks Out
- ^ The Coverage of Three International Newspapers on India's Super Power Capabilities in the Region: A Content Analysis of The Times of India, New York Times and London Times
- ^ India: A Superpower in the making
- ^ "India set to become an economic superpower: Chidambaram". The Economic Times. 2008-07-22. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- ^ US Today on NIC report
- ^ The New Great Game: Why the Bush administration has embraced India
- ^ E.U. India relations
- ^ US-India relations
- ^ أنور عبد الملك (09-03-2010). جريدة الأهرام http://www.ahram.org.eg/100/2010/03/09/4/10591.aspx. Retrieved 09-03-2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ "Ugly Indian debate sets scene for election". BBC. 2008-07-22. Retrieved 2010-03-09.
- ^ "Indo-China trade to surpass $60 bn before 2010". Business-standard.com. 2008-06-06. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- ^ Bulgarian embassy in New Delhi
- ^ Indian embassy in Sofia
- ^ أ ب "Inauguration of the Embassy of Iceland in New Delhi". Icelandic Foreign Service. 2006-02-26. Retrieved 2008-09-28.
- ^ "My background helps me: Kalam". The Hindu. 2005-05-30. Retrieved 2008-09-28.
{{cite news}}:|first=missing|last=(help) - ^ "About the Embassy". Icelandic Foreign Service. Retrieved 2008-09-28.
- ^ "Shri S. Swaminathan to be India's first resident Ambassador to Iceland". NIC India Ministry of External Affairs, New Delhi. September 3, 2008. Retrieved 2008-09-28.
- ^ "Indo-Polish relations". Embassy of India in Poland. Retrieved 2008-10-10.
- ^ Indian embassy in Bucharest
- ^ Romanian embassy in New Delhi
- ^ VOA News Report
- ^ Indian embassy in Belgrade
- ^ Serbian embassy in New Delhi
- ^ Embassy of India in Ljubljana
- ^ CIA World Fact Book https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html
وصلات خارجية
- Foreign Relations: Ministry of external affairs, Government of India
- India-China Relations[dead link]
- Harvard University homepage India's Foreign Policy, Xenia Dormandy
- Russia-India relations