ثلاثي أكسيد ثنائي النتروجين
| |

| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك
N-oxonitramide[1]
| |
| أسماء أخرى
Nitrous anhydride, nitrogen sesquioxide
| |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.013 |
| رقم EC |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2421 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | N2O3 |
| كتلة مولية | 76.01 g/mol |
| المظهر | deep blue tinted liquid |
| الكثافة | 1.447 g/cm3, liquid 1.783 g/cm3 (gas) |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| نقطة الغليان | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | very soluble |
| قابلية الذوبان | soluble in ether |
| القابلية المغناطيسية | −16.0·10−6 cm3/mol |
| البنية | |
| الشكل الجزيئي | planar, Cs |
| Dipole moment | 2.122 D |
| الكيمياء الحرارية | |
| الإنتالپية المعيارية للتشكل ΔfH |
+91.20 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy S |
314.63 J K−1 mol−1 |
| سعة الحرارة النوعية، C | 65.3 J/mol K |
| المخاطر | |
| ن.م.ع. مخطط تصويري |    
|
| ن.م.ع. كلمة الاشارة | Danger |
| H270, H280, H310, H310+H330, H314, H330 | |
| P220, P244, P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P330+P331, P302+P350, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P320, P321, P322, P361, P363, P370+P376, P403, P403+P233, P405, P410+P403, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |
| نقطة الوميض | Non-flammable |
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |
| Nitrous oxide Nitric oxide Nitrogen dioxide Dinitrogen tetroxide Dinitrogen pentoxide Nitrogen trioxide | |
مركـّبات ذات علاقة
|
Nitrous acid |
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
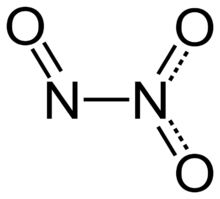
Dinitrogen trioxide (also known as nitrous anhydride) is the chemical compound with the formula N2O3. It is one of the simple nitrogen oxides. It forms upon mixing equal parts of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide and cooling the mixture below −21 °C (−6 °F):[4]
- NO + NO2
 N2O3
N2O3
Dinitrogen trioxide is only isolable at low temperatures, i.e. in the liquid and solid phases. In liquid and solid states, it has a deep blue color.[2] At higher temperatures the equilibrium favors the constituent gases, with Kdiss = 193 kPa (25 °C).[5]
This compound is sometimes called "nitrogen trioxide", but this name properly refers to another compound, the (uncharged) nitrate radical NO 3.
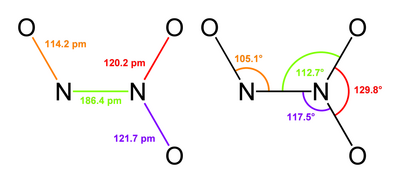
Structure and bonding
Typically, N–N bonds are similar in length to that in hydrazine (145 pm). Dinitrogen trioxide, however, has an unusually long N–N bond at 186 pm. Some other nitrogen oxides also possess long N–N bonds, including dinitrogen tetroxide (175 pm). The N2O3 molecule is planar and exhibits Cs symmetry. The dimensions displayed below come from microwave spectroscopy of low-temperature, gaseous N2O3:[4]
It is the anhydride of the unstable nitrous acid (HNO2), and produces it when mixed into water. An alternative structure might be anticipated for the true anhydride, i.e. O=N–O–N=O, but this isomer is not observed. If the nitrous acid is not then used up quickly, it decomposes into nitric oxide and nitric acid. Nitrite salts are sometimes produced by adding N2O3 to solutions of bases:
- N2O3 + 2 NaOH → 2 NaNO2 + H2O
Here the oxidation state of one nitrogen is +3.
References
- ^ "Dinitrogen trioxide".
- ^ أ ب Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 444. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ "Dinitrogen trioxide". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ أ ب Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1984). Chemistry of the Elements. Oxford: Pergamon Press. pp. 521–22. ISBN 978-0-08-022057-4.
- ^ قالب:Holleman&Wiberg