مجلس أوروپا
مجلس اوروپا Council of Europe Conseil de l'Europe | |
|---|---|
النشيد: Ode to Joy (orchestral) | |
 الأعضاء المؤسسون العشرة Joined subsequently المرشحون رسمياً مراقب في المجلس البرلماني مراقب في لجنة الوزراء مراقب في لجنة الوزراء والمجلس البرلماني | |
| المقر | ستراسبورگ, فرنسا |
| العضوية | 47 دولة اوروبية 5 مراقبون (اللجنة) 3 مراقبين (المجلس) |
| الزعماء | |
| Thorbjørn Jagland | |
• Deputy Secretary General | Maud de Boer-Buquicchio |
• President of the Parliamentary Assembly | مولود جاڤوشاوغلو |
• President of the لجنة الوزراء | The Minister of Foreign Affairs of the state chairing the Committee of Ministers |
| Thomas Hammarberg | |
| التأسيس | |
| 5 May 1949 | |
الموقع الإلكتروني www.coe.int | |
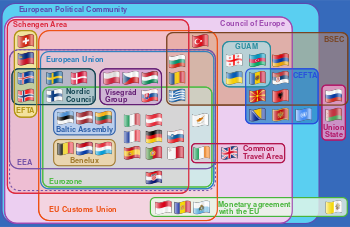
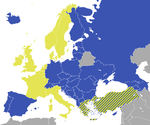
مجلس اوروپا هو منظمة دولية مكونة من 47 دولة أوروبية تأسست في عام 1949. يقع المجلس في مدينة ستراسبورگ على الحدود الفرنسية الألمانية. أول اجتماع تم في جامعة ستراسبورگ. لاحقاً، أصبح قصر أوروبا (Palais de l'Europe) المقر الرئيسي للمجلس، ويبعد عن وسط المدينة بحوالي كيلومترين. العضوية في المجلس مفتوحة لجميع دول أوروبا الديمقراطية التي تقبل قانون القضاء والتي تضمن حقوق الإنسان والحريات لجميع المواطنين. من أبرز إنجازات المجلس: الميثاق الأوروبي لحقوق الإنسان في عام 1950 والذي يمثل أساس المحكمة الأوروبية لحقوق الإنسان.
مجلس أوروبا هو منظمة منفصلة وليس جزء من الاتحاد الاوروبي، مع ملاحظة أنه مختلف عن مجلس الاتحاد الأوروبي والمجلس الأوروبي.
المؤسسات
المقر الرئيسي والمباني

الرموز
العضوية
| ملاحظات على الجدول; aتعبر كل من تركيا وإيران مؤسسو المنظمة. bIn 1950, the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany), est. 23 May 1949, and then French-occupied Saar (protectorate) became associate members. (West) Germany became a full member in 1951, while the Saarland withdrew from its associate membership in 1956 after acceding to the Federal Republic after a referendum in 1955. The Soviet-occupied eastern part of Germany and later East German Democratic Republic never became a member of the Council of Europe. Through German reunification in 1990, the five Länder (i.e. states/regions) of East Germany acceded to the Federal Republic of Germany and thus gained representation in the Council of Europe. |
| الدولة | تاريخ الانضمام |
|---|---|
| مؤسس | |
| مؤسس | |
| مؤسس | |
| مؤسس | |
| مؤسس | |
| مؤسس | |
| مؤسس | |
| مؤسس | |
| مؤسس | |
| مؤسس | |
| 9 أغسطس 1949 | |
| 9 أغسطس 1949 | |
| 7 مارس 1950 | |
| 13 يوليو 1950 | |
| 16 أبريل 1956 | |
| 24 مايو 1961 | |
| 6 مايو 1963 | |
| 29 أبريل 1965 | |
| 22 سبتمبر 1976 | |
| 24 نوفمبر 1977 | |
| 23 نوفمبر 1978 | |
| 16 نوفمبر 1988 | |
| 5 مايو 1989 | |
| 6 نوفمبر 1990 | |
| 26 نوفمبر 1991 | |
| 7 مايو 1992 | |
| 14 مايو 1993 | |
| 14 مايو 1993 | |
| 14 مايو 1993 | |
| 30 مايو 1993 | |
| 30 يونيو 1993 | |
| 7 اكتوبر 1993 | |
| 10 نوفمبر 1994 | |
| 10 فبراير 1995 | |
| 13 يوليو 1995 | |
| 13 يوليو 1995 | |
| 9 نوفمبر 1995 | |
| 9 نوفمبر 1995 | |
| 28 فبراير 1996 | |
| 6 نوفمبر 1996 | |
| 27 أبريل 1999 | |
| 25 يناير 2001 | |
| 25 يناير 2001 | |
| 24 أبريل 2002 | |
| 3 أبريل 2003 | |
| 5 اكتوبر 2004 | |
| 11 مايو 2007 |

التعاون
الدول غير الأعضاء
Invitations to sign and ratify relevant conventions of the Council of Europe on a case-by-case basis are sent to three groups of non-member entities[2]:
- Non-European states: Algeria, الأرجنتين, Australia, Bahamas, Bolivia, Brasil, Burkina Faso, Chile, China, Colombia, Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Honduras, South Korea, Kyrgystan, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mauritius, Morocco, New Zealand, Panama, Peru, Philippines, Senegal, South Africa, Syria, Tajikistan, Tonga, Trinidad and Tobago, Tunisia, Uruguay, Venezuela and the observers كندا, Israel, Japan, Mexico, الولايات المتحدة.
- European states: Kazakhstan, Kosovo, Belarus and the observer Vatican City.
- the European Community and later the European Union after its legal personality was established by the ratification of the EU's Lisbon Treaty.
الاتحاد الاوروبي
العلاقات عموماً بين مجلس اوروبا والاتحاد الاوروبي
انظر أيضاً
- CAHDI
- CODEXTER
- Common European Framework of Reference for Languages
- Conference of Specialised Ministers
- Co-ordinated organisations
- Council of Europe Film Award (FACE)
- Council of Europe Archives
- اوروبا
- European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages
- الاتحاد الاوروبي
- Group of States Against Corruption
- المنظمات الدولية في اوروبا
- مركز الشمال-الجنوب of the Council of Europe
- منظمة الأمن والتعاون في اوروبا
- OSCE countries statistics
- WADA
الهامش
- ^ "Statute of the Council of Europe". Council of Europe. 5 May 1949. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
- ^ CoE Conventions
وصلات خارجية
| Council of Europe
]].- Official site
- Statute of the Council of Europe
- Eurominority map of minorities, native peoples and ethnic groups
- European NAvigator Council of Europe
- Armenia, Azerbaijan join Council of Europe
- European Movement
- European Audiovisual Observatory
وصلات فيديو
- UK.YouTube.com, Council of Europe YouTube channel