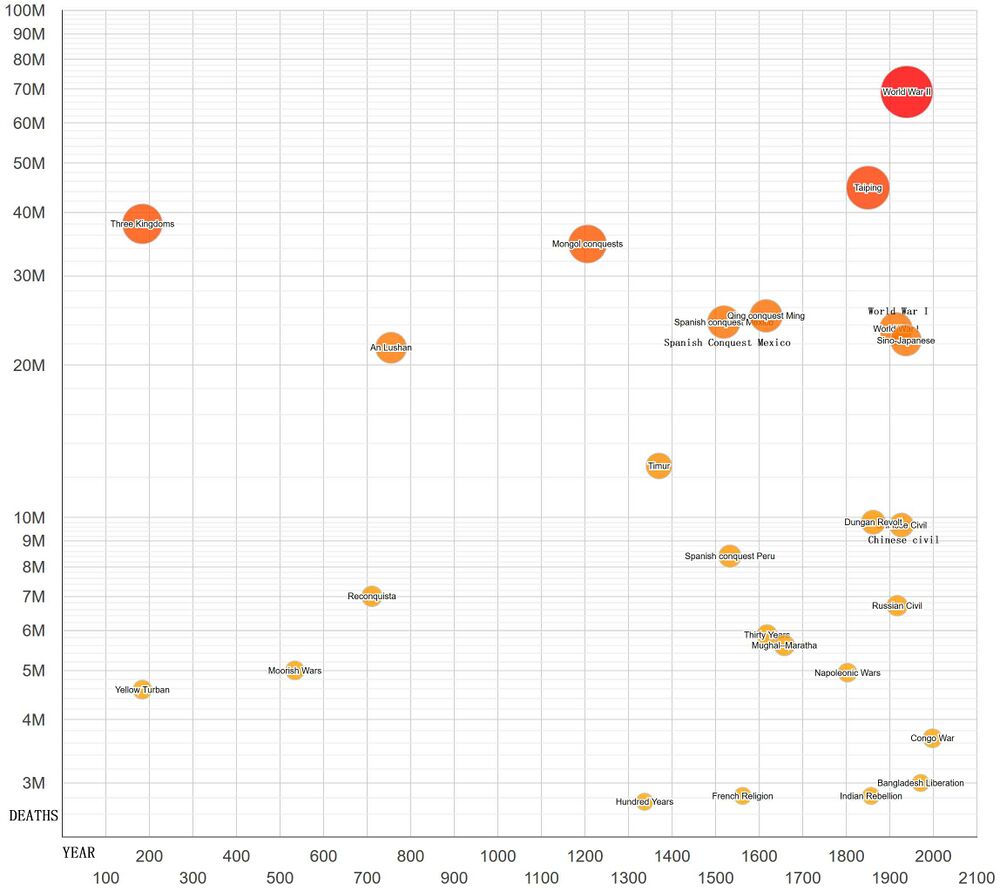
قائمة الحروب حسب عدد القتلى
قائمة الحروب حسب عدد القتلى، تتضمن جميع الوفيات الناجمة عن الحرب بشكل مباشر أو غير مباشر. تشمل هذه الأرقام عادةً وفيات الأفراد العسكريين التي تكون نتيجة مباشرة للمعركة أو غيرها من الأعمال العسكرية في وقت الحرب، بالإضافة إلى وفيات المدنيين في وقت الحرب/المرتبطة بالحرب والتي تكون نتيجة للأوبئة والمجاعات والفظائع والإبادة الجماعية والحرب وغيرها.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الحروب قبل المعاصرة (قبل 1500)
الحروب القديمة (قبل 500)
| الحرب | نطاق القتلى |
التاريخ | الأطراف المتحاربة | المكان | الهوامش |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| غزوات قورش الكبير | 100.000+ | 549 ق.م.–530 ق.م. | الإمبراطورية الفارسية ضد الدويلات المختلفة | الشرق الأوسط | الرقم الموضح هو مجموع جميع الوفيات في المعركة التي سجلها الكتاب الفرس خلال هذه الفترة الزمنية، ولا يأخذ في الاعتبار الوفيات بين المدنيين، وقد يكون العدد الفعلي أكبر من ذلك بكثير. |
| الحروب اليونانية الفارسية | 300.000+ | 499 ق.م.–449 ق.م. | الدوليلات-المدن اليونانية ضد الإمبراطورية الفارسية | اليونان | |
| الدويلات المتناحرة الصينية | 1.500.000+ | ح. 475 ق.م. - 221 ق.م. | القوى العظمى السبع الصينية | الصين | يقدر بـ 1.500.000 قبل حروب تشين التوحيدية[1] |
| الحروب السمنية | 33.500+ | 343 ق.م. –290 ق.م. | Roman Republic vs. Samnites | Italy | Number given is the sum of all deaths in battle recorded by Roman writers during this time period, does not take into account civilian deaths, the actual number may be much greater. |
| حروب الإسكندر الأكبر | 142.000+ | 336 ق.م.–323 ق.م. | Macedonian Empire and other Greek City-States vs. Persian Empire and various other states | Middle East / North Africa / Central Asia / India | Number given is the sum of all deaths in battle during these wars recorded by Greek writers, does not take into account civilian deaths, the actual number may be much greater. |
| الحروب الپونيقية | 1,620,000–1,920,000+ | 264 BC–146 BC | Roman Republic vs. Carthaginian Empire | Western Europe / North Africa | |
| الحرب الپونيقية الأولى | 400,000+ | 264 BC–241 BC | Roman Republic vs. Carthaginian Empire | Southern Europe / North Africa | Part of the Punic Wars |
| الحرب الپونيقية الثانية | 770,000+ | 218 BC–201 BC | Roman Republic vs. Carthaginian Empire | Western Europe / North Africa | [2] – Part of the Punic Wars |
| الحرب الپونيقية الثالثة | 450,000-750,000+ | 149 BC–146 BC | Roman Republic vs. Carthaginian Empire | Tunisia | Part of the Punic Wars |
| حروب توحيد تشين | 700,000+[بحاجة لمصدر] | 230 BC–221 BC | Qin state vs. Han, Zhao, Yan, Wei, Chu, Qi States | China | Part of Warring States period |
| Cimbrian War | 410,000–650,000 | 113 BC–101 BC | Roman Republic vs. Cimbri and Teutones | Western Europe | Part of the Germanic Wars |
| Roman civil wars from Social War (91–87 BC) to War of Actium | 3,000,000+[3] | 91 BC - 30 BC | Roman civil wars | Europe/North Africa/Middle East | Fall of the Roman Republic |
| Gallic Wars | 1,000,000+ | 58 BC–50 BC | Roman Republic vs. Gallic tribes | France | |
| Iceni Revolt | 150,000+[4] | 60–61 | Roman Empire vs. Celtic tribes | England | Year is uncertain – Part of the Roman Conquest of Britain |
| الحروب اليهودية الرومانية | 1,270,000–2,000,000[5] | 66–136 | Roman Empire vs. Jews | Middle East/North Africa | Deaths caused by Roman attempt to permanently root out Judaism included. |
| الحرب اليهودية الرومانية الأولى | 250,000–1,100,000[5] | 66–73 | Roman Empire vs. Jews | Middle East | – Part of Jewish–Roman Wars |
| Kitos War | 440,000+ | 115–117 | Roman Empire vs. Jews | Southern Europe / North Africa | – Also known as the Second Jewish–Roman War – Part of Jewish–Roman Wars |
| ثورة بار كوخبا | 580,000 | 132–136 | Roman Empire vs. Jews | Middle East | – Also known as the Third Jewish–Roman War – Part of Jewish–Roman Wars |
| حرب الممالك الثلاثة | 36,000,000–40,000,000 | 184–280 | Wei vs. Shu vs. Wu | China | [6][7] – Academically, the period of the Three Kingdoms refers to the period between the foundation of the state of Wei in 220 and the conquest of the state of Wu by the Jin dynasty in 280. The earlier, "unofficial" part of the period, from 184 to 220, was marked by chaotic infighting between warlords in various parts of China.
See: End of the Han dynasty - Also, note that the death range provided is actually the amount the population declined according to the census data and is likely an overestimation of actual combat fatalities. |
| Yellow Turban Rebellion | 3,000,000–7,000,000 | 184–205 | Peasants vs. Eastern Han China | China | – Part of Three Kingdoms War |
| Wars of the Sixteen Kingdoms | 150,000+ [بحاجة لمصدر] |
304–439 | Northern Chinese States | Northern China | Number given is the sum of all deaths in battle recorded in this time period in battles between armies of the Sixteen Kingdoms, does not take into account civilian deaths, the actual number may be much greater. |
| Hunnic Reclaims | 165,000+ [بحاجة لمصدر] |
395–453 | Roman Empire vs. Hunnic Empire | Europe | Number given is the sum of all deaths in battle recorded by Roman writers during this time period; does not take into account civilian deaths; the actual number may be much greater. |
Note 1: The geometric mean is the middle of the quoted range, taken by multiplying together the endpoints and then taking the square root.
حروب العصور الوسطى (500–1500 م)
Note: the identity of a single "war" cannot be reliably given in some cases, and some "wars" can be taken to last over more than a human lifetime, e.g. "Reconquista" (711–1492, 781 years) "Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent" (12th to 16th c., 500 years) "Crusades" (ten or more campaigns during the period 1095–1291, 196 years), "Mongol invasions and conquests" (1206–1368, 162 years), "early Muslim conquests" (622–750, 128 years), "Hundred Years' War" (1337–1453, 116 years).
| War | Death range |
Date | Combatants | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arab–Byzantine Wars | 2,000,000+[بحاجة لمصدر] | 629–1050 | Byzantine Empire and allies vs. Islamic Empire and allies | Middle East / North Africa / Southern Europe | Number given is the sum of all deaths in battle recorded by writers during this time period, does not take into account civilian deaths, the actual number may be much greater. |
| Reconquista | 7,000,000 | 711–1492 | Spanish and Portuguese Christian states vs. Spanish and Portuguese Muslim states | Iberian Peninsula | [8] |
| Goguryeo–Sui War | 300,000+ | 598–614 | Sui dynasty China and Goguryeo Kingdom Korea | China, Korea | [9] |
| An Lushan Rebellion | 13,000,000–36,000,000 | 755–763 | Tang dynasty China and Islamic Empire vs. Yan state | China | [10] – Also known as the An–Shi Rebellion |
| Goryeo–Khitan Wars | 90,000+ | 993–1019 | Liao Empire vs. Goryeo Kingdom | Korea | [11] |
| Song–Đại Việt war | 600,000+ | 1075–1077 | Song Empire vs. Dai Viet Kingdom under Lý dynasty | China, Vietnam | [12][13] |
| Crusades | 1,000,000–3,000,000 | 1095–1291 | Originally Byzantine Empire vs. Seljuq Empire, but evolved into Christians vs. Muslims. | Europe / Middle East ("Holy Land") | [14] |
| Albigensian Crusade | 200,000–1,000,000 | 1208–1229 | Papal States and France vs. Cathar States | France | [15][16] – Also known as the Cathar Crusade
– Part of the Crusades |
| Mongol invasions and conquests | 30,000,000–40,000,000 | 1206–1368 | Mongol Empire vs. Several Eurasian states | Eurasia | [17][18][19] – Excludes the (up to) 200,000,000 deaths from the Black Death migration that may have been associated with the Mongol expansion |
| Wars of Scottish Independence | 60,000–150,000 | 1296–1357 | Scotland vs. England | Scotland / England | |
| Hundred Years' War | 2,300,000–3,500,000 | 1337–1453 | House of Valois vs. House of Plantagenet | Western Europe | [20] |
| Conquests of Timur | 8,000,000–20,000,000 | 1370–1405 | Timurid Empire vs. several middle eastern states | Eurasia | [21][22] |
| Wars of the Roses | 35,000–105,000 | 1455–1487 | House of Lancaster, House of Tudor, and allies vs. House of York and allies | England / Wales | [23][مطلوب مصدر أفضل] |
التاريخ المعاصر
الحروب المعاصرة (1500 م–الحاضر) حروب بأكثر من 25.000 قتيل
| الحرب | نطاق القتلى |
التاريخ | الأطراف المتحاربة | المكان | ملاحظات | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| حرب المتوسط | 900,000–1,000,000 | 1470–1574 | Republic of Venice, Spain, Republic of Genoa, Papal States, Duchy of Savoy, and Order of Saint John vs. Ottoman Empire | Mediterranean | [24] | |
| الحروب الإيطالية | 300,000–400,000 | 1494–1559 | Holy Roman Empire, Spain, and some Italian states vs. France, Ottoman Empire, and some Italian states | Southern Europe (primarily) | [24] – Also known as the Great Wars of Italy | |
| Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire | 24,300,000+ | 1519–1632 | Spanish Empire vs. Aztec Empire | Mexico | [24] – Part of the European colonization of the Americas, includes the cocoliztli plagues | |
| Spanish conquest of Yucatán | 1,460,000+ | 1519–1595 | Spanish Empire vs. Mayan states | North America | [24] – Part of the European colonisation of the Americas, includes deaths due to European disease | |
| الغزو الإسپاني لنيكاراگوا | 575,000+ | 1522–1536 | Spanish Empire vs. Indigenous peoples of Nicaragua | نيكاراگوا | [24] – Part of the European colonization of the Americas, includes deaths due to European diseases | |
| Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire | 8,400,000+ | 1533–1572 | Spanish Empire vs. Inca Empire | Peru | [24] – Part of the European colonization of the Americas, includes deaths due to European diseases | |
| Campaigns of Suleiman the Magnificent | 200,000+ | 1521–1566 | Ottoman Empire vs. several Balkan, African, and Arabian states | Eastern Europe / Middle East / North Africa | [25] | |
| German Peasants' War | 100,000+ | 1524–1525 | German Peasants vs. Swabian League | Germany | [26] – Also known as the Great Peasants War | |
| Arauco War | 125,000–142,000 | 1550–1790 | Spanish Empire vs. Mapuches | Chile | [24] – Part of the European colonization of the Americas, includes deaths due to European diseases | |
| حروب الأديان الفرنسية | 2,000,000–4,000,000 | 1562–1598 | Protestants vs. France vs. Catholics | France | [27] – Also known as the Huguenot Wars | |
| Eighty Years' War | 600,000–700,000 | 1568–1648 | Dutch Republic, England, and France vs. Spanish Empire | Northern Europe (primarily) | [24] – Also known as the Dutch War of Independence | |
| Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604) | 106,285+ | 1585–1604 | Spanish Empire and allies vs. Kingdom of England and allies | Americas, Netherlands, Belgium, France, Portugal, Spain, England, Ireland, Atlantic Ocean | English 88,285[28][29] Spanish 18,000 during the Spanish Armada[29] | |
| الغزوات اليابانية لكوريا | 1,000,000+ | 1592–1598 | Kingdom of Great Joseon and Ming China vs. Japan | Korea | [30][24] | |
| Nine Years' War (Ireland) | 130,000+ | 1593–1603 | Irish rebels vs. Kingdom of England | Ireland | [24] | |
| Transition from Ming to Qing | 25,000,000+ | 1616–1683 | Qing China vs. Ming China vs. peasant rebels like the Shun dynasty (led by Li Zicheng) and Xi dynasty (led by Zhang Xianzhong) vs. Kingdom of Shu (She-An Rebellion) vs. Evenk-Daur federation (Bombogor) | China | [31] – Also known as the Ming–Qing transition | |
| Thirty Years' War | 4,000,000–12,000,000 | 1618–1648 | Austria and Spain vs. Anti-Habsburg states | Europe | [32] | |
| Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659) | 200,000+ | 1635–1659 | France and allies vs. Spain and allies | Western Europe | [25][29] | |
| Wars of the Three Kingdoms | 876,000+ | 1639–1651 | Royalists vs. Covenanters vs.Union of the Irish vs. Scottish Protestants vs. Parliamentarians | British Isles | [33][34][35] – Also known as the British Civil Wars | |
| Portuguese Restoration War | 80,000 | 1640–1668 | Portugal, France, and England vs. Spain | Iberian Peninsula | ||
| الحرب الأهلية الإنگليزية | 211,830+ | 1642–1651 | Royalists vs. Parliamentarians | England, Scotland, and Ireland | Part of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms | |
| Fifth Ottoman–Venetian War | 72,000 | 1645–1669 | Republic of Venice vs. Ottoman Empire | Candia, Crete, Dalmatia and Aegean Sea | ||
| Deluge | 3,000,000 | 1655–1660 or 1648-1667 | Primarily Poland vs. Sweden and Russia | Poland | [36] | |
| Mughal–Maratha Wars | 5,000,000+ | 1658–1707 | Maratha empire vs. Mughal Empire | India-Bangladesh | [37][38] | |
| Franco-Dutch War | 342,000 | 1672–1678 | France and allies vs. Dutch Republic and allies | Western Europe | Also known as the Dutch War | |
| الحرب التركية الكبرى | 380,000+ | 1683–1699 | Ottoman Empire vs. European Holy League | Eastern Europe | [25] – Also known as the War of the Holy League | |
| Nine Years' War | 680,000+ | 1688–1697 | France vs. League of Augsburg (Dutch, Habsburgs, England, Scotland, Spain and others) | Global (mainly Europe) | [39] | |
| Great Northern War | 350,000+ | 1700–1721 | Russia and allies vs. Swedish Empire | Eastern Europe | Sweden, the Swedish Baltic provinces, and Finland, together, with a population of only 2.5 million, lost some 350,000 dead during the war from all causes.[40] | |
| War of the Spanish Succession | 400,000–1,250,000 | 1701–1714 | Grand Alliance vs. Bourbon Alliance | Europe / Americas | [25] | |
| War of Jenkins' Ear | 30,000+ | 1739–1748 | Spanish Empire vs. British Empire | American South, Caribbean, Pacific and Atlantic | [41] | |
| Maratha expeditions in Bengal | 400,000+ | 1741–1751 | Maratha Empire vs. Nawab of Bengal | India, Bangladesh | [42][43] | |
| Seven Years' War | 868,000–1,400,000 | 1756–1763 | Great Britain and allies vs. France and allies | Worldwide | ||
| الحرب البورمية الصينية | 70,000+ | 1765–1769 | Burma vs. Qing China | Southeast Asia | – Also known as the Qing invasions of Burma | |
| Tây Sơn rebellion | 1,200,000–2,000,000+ | 1771–1802 | Tây Sơn rebels then dynasty (British supports) and Chinese pirates vs Nguyễn lords, Trịnh lords, Lê dynasty of Vietnam; Siam; Qing dynasty of China; Kingdom of Vientiane; French army. | Southeast Asia | ||
| الحرب الثورية الأمريكية | 70,000-116,000 | 1775–1783 | United States and allies vs. British Empire and German Mercenaries | Worldwide | 37,324 battle dead, all sides, all theaters.[25][44][45][46][47] – Also known as the American War of Independence | |
| تمرد اللوتس الأبيض | 100,000+ | 1794–1804 | Qing China vs. White Lotus rebels | China | ||
| الحملة الفرنسية على مصر وسوريا | 65,000+ | 1798–1801 | France vs. Ottoman Empire and Great Britain | Middle East / North Africa | [25] | |
| Saint-Domingue expedition | 135,000+ | 1802–1803 | France vs. Haiti and UK | Haiti | [29] – Part of the Haitian Revolution | |
| الحروب الناپوليونية | 3,500,000–7,000,000 | 1803–1815 | Coalition powers vs. French empire and allies | Worldwide | See: Napoleonic Wars casualties | |
| Peninsular War | 1,000,000+ | 1808–1814 | Spain, Portugal and United Kingdom vs. France, Kingdom of Italy and Duchy of Warsaw | Iberian Peninsula | [29] – Part of the Napoleonic Wars | |
| Spanish American wars of independence | 600,000+ | 1808–1833 | Spain vs. American Independentists | Americas | [48] | |
| Venezuelan War of Independence | 228,000+ | 1810–1823 | Spain vs. Venezuelan states | Venezuela | – Part of Spanish American Wars of Independence | |
| Mfecane | 1,000,000–2,000,000 | 1810s–1840s | Ethnic communities in southern Africa | Modern day South Africa | [49][50][51][52] | |
| الغزو الفرنسي لسوريا | 540,000+ | 1812 | French Empire vs. Russia | Russia | [25] – Part of the Napoleonic Wars | |
| Carlist Wars | 200,000+ | 1820–1876 | Carlist Insurgents vs. Spain | Spain | [48] | |
| حرب الاستقلال اليونانية | 170,000+ | 1821–1831 | Greek Revolutionaries vs. Ottoman Empire | Greece | ||
| الغزو الفرنسي للجزائر | 595,665–1,095,665 | 1830–1903 | France vs. Algerian resistance | Algeria | Between 500,000 and 1,000,000, from approximately 3 million Algerians, were killed in the first three decades of the conquest.[53][54] French losses from 1830 to 1851 were 92,329 dead from disease and only 3,336 killed in action.[29][55][56] | |
| الحملات الاستعمارية الفرنسية | 110,000+ | 1830–1895 | France vs. Local forces | Algeria, Tunisia, Morocco, French Indochina (Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos), Mexico, Madagascar, West Africa | In all colonial campaigns, France suffered 10,000 killed and 35,000 wounded, primarily in Algeria. From this number, a few thousand soldiers died in Mexico and Vietnam. Disease further compounded the toll, resulting in an estimated total of 110,000 deaths among French and Foreign Legion forces due to battles and disease throughout the entire 19th century.[29] | |
| تمرد تايپنگ | 20,000,000–70,000,000 | 1850–1864 | Qing China vs. Taiping Heavenly Kingdom | China | [57][58][59] – Also known as the Taiping Civil War | |
| حرب القرم | 356,000–615,000 | 1853–1856 | Ottoman Empire and allies vs. Russia | Crimean Peninsula | ||
| Red Turban Rebellion (1854–1856) | 1,000,000+ | 1854–1856 | Qing China vs. Red Turban rebels | China | ||
| تمرد مياو | 4,900,000 [بحاجة لمصدر] | 1854–1873 | Qing China vs. Miao | China | Also known as the Qian rebellion | |
| Punti–Hakka Clan Wars | 500,000–1,000,000+ | 1855-1868 | Hakka vs. Punti | China | ||
| تمرد الپانثاي | 890,000–1,000,000 | 1856–1873 | Qing China vs. Hui | China | – Also known as the Du Wenxiu Rebellion | |
| التمرد الهندي 1857 | 800,000–1,000,000 | 1857–1858 | Sepoy Mutineers vs. British East India Company | India | [60] – Also known as the Sepoy Mutiny or the Indian First War of Independence | |
| الحرب الأهلية الأمريكية | 650,000–1,000,000 | 1861–1865 | Union States vs. Confederate States | USA | [61][62][63] | |
| Dungan Revolt | 8,000,000–20,000,000 | 1862–1877 | Qing China vs. Hui vs. Kashgaria | China | – Also known as the Tongzhi Hui Revolt | |
| French intervention in Mexico | 49,287+ | 1862–1867 | Mexican Republicans vs. France and Mexican Empire | Mexico | [29] | |
| Paraguayan War | 300,000–1,200,000 | 1864–1870 | Triple alliance vs. Paraguay | South America | [64] – Also known as the War of the Triple Alliance | |
| Austro-Prussian War | 40,000+ | 1866 | Austrian states vs. German states | Central Europe | ||
| Ten Years' War | 241,000+ | 1868–1878 | Spain vs. Cuba and Dominican volunteers[65] | Cuba | [29] – Also known as the Great War | |
| Franco-Prussian War | 433,571+ | 1870–1871 | France vs. German states | France and Prussia | ||
| Conquest of the Desert | 30,000–35,000 | 1870s–1884 | Argentina vs. Mapuche people | Patagonia | ||
| Aceh War | 97,000–107,000 | 1873–1914 | Kingdom of the Netherlands vs. Aceh Sultanate | Indonesia | [66] – Also known as the Infidel War | |
| First Sino–Japanese War | 48,311+ | 1894–1895 | Qing China vs. Japan | East Asia | ||
| Cuban War of Independence | 362,000+ | 1895–1898 | USA and Cuba vs. Spain | Cuba | [29] | |
| War of Canudos | 30,000+ | 1896-1897 | First Brazilian Republic vs. Canudos inhabitants | Brazil | ||
| Thousand Days' War | 120,000+ | 1899–1902 | Colombian Conservatives vs. Colombian Liberals | Colombia | [67] | |
| Boxer Rebellion | 100,000 | 1899–1901 | Boxers vs. Foreign powers | China | ||
| South African War (Second Boer War) | 73,000–90,000 | 1899-1902 | United Kingdom and allies vs. South African Republic and Orange Free State | South Africa | [68] | |
| Philippine–American War | 234,000+ | 1899–1912 | Philippines vs. USA | Philippines | [69] – Also known as the Philippine War | |
| Russo-Japanese War | 101,300–206,100 | 1904–1905 | Russia vs. Japan | Northeast Asia | ||
| Mexican Revolution | 1,000,000–3,500,000 | 1910–1920 | Pro-government vs. Anti-government | Mexico | [70] | |
| 1911 Revolution | 220,000 | 1911 | Qing China vs. Revolutionaries | China | ||
| Balkan Wars | 140,000+ | 1912–1913 | See Balkan wars | Balkan Peninsula | ||
| World War I | 17,000,000 (excluding the Spanish flu) | 1914–1918 | Allied Powers vs. Central Powers | Worldwide | [25] – Also known as the Great War | |
| Russian Civil War | 5,000,000–9,000,000 | 1917–1922 | Red army and allies vs. White army and allies | Russia | [71] | |
| Kurdish separatism in Iran | 15,000–58,000 | 1918–present | Qajar dynasty vs. Shekak (tribe) | Iran | [72] | |
| Iraqi–Kurdish conflict | 138,800–320,100 | 1918–2003 | Kurdistan/Iraqi Kurdistan and allies vs. Iraq and allies | Iraq | [73][74] | |
| Rif War | 90,000 | 1921–1926 | Spain vs. Republic of the Rif | Morocco | [75] | |
| Kurdish–Turkish conflict | 100,000+ | 1921–present | Turkey vs. Kurdish people | Middle East | ||
| Second Italo-Senussi War | 40,000+ | 1923–1932 | Italy vs. Senussi Order | Libya | ||
| Chinese Civil War | 8,000,000–11٬692٬000 | 1927–1949 | ROC vs. PRC | China | [76] | |
| Chaco War | 85,000–130,000 | 1932–1935 | Bolivia vs. Paraguay | Gran Chaco | ||
| Second Italo–Ethiopian War | 278,000+ | 1935–1936 | Ethiopian Empire vs. Italy | Ethiopia | According to Italian government statistics, the Italians suffered 1,148 KIA, 125 DOW, and 31 MIA.[77] According to the Ethiopian government, at least 275,000 Ethiopians died in the brief war.[77][78] – Also known as the Second Italo–Abyssinian War | |
| Spanish Civil War | 500,000–1,000,000 | 1936–1939 | Nationalists vs. Republicans | Spain | [29] | |
| Second Sino-Japanese War | 20,000,000–25,000,000 | 1937–1945 | Republic of China and allies vs. Japan | China | [79] – Part of World War II | |
| World War II | 80,000,000 | 1939–1945 | Allied powers vs. Axis Powers | Worldwide | [25] – Largest and deadliest war in history | |
| Winter War | 153,736–194,837 | 1939–1940 | Finland vs. Soviet Union | Finland | – Part of World War II | |
| Greco-Italian War | 27,000+ | 1940–1941 | Greece vs. Italy | Southeast Europe | – Part of World War II | |
| Continuation War | 387,300+ | 1941–1944 | Finland and Germany vs. Soviet Union | Northern Europe | – Part of World War II | |
| Soviet–Japanese War | 33,420–95,768 | 1945 | Soviet Union and Mongolia vs. Japan | Manchuria | – Part of World War II | |
| First Indochina War | 400,000+ | 1946–1954 | France vs. Việt Minh, Lao Assara, and Khmer Issarak | Southeast Asia | – Also known as the Indochina War | |
| Partition of India | 200,000–2,000,000 | 1946–1948 | India and Pakistan | South Asia | Partition of India | |
| Greek Civil War | 158,000+ | 1946–1949 | Greek Government army vs. DSE | Greece | [80][81][82][83] | |
| Kashmir conflict | 80,000–110,000 | 1947–present | India vs. Pakistan | North India / Pakistan | ||
| La Violencia | 192,700–194,700 | 1948–1958 | Colombian Conservative Party vs. Colombian Liberal Party | Colombia | ||
| Internal conflict in Myanmar | 130,000–250,000 | 1948–present | Myanmar vs. Burmese Insurgent Groups | Myanmar | [84] | |
| Arab–Israeli conflict | 116,074+ | 1948–present | Arab Countries vs. Israel | Middle East | [85] | |
| Annexation of Hyderabad | 29,000–242,000 | 1948 | Dominion of India vs. Hyderabad | India | – Also known as Operation Polo | |
| Korean War | 1,500,000–4,500,000 | 1950–1953 | South Korea and allies vs. North Korea and allies | Korea | [86] American casualties in the Korean War included 54,246 dead and 103,284 wounded. | |
| Algerian War | 400,000–1,500,000 | 1954–1962 | Algeria vs. France | Algeria | [87] – Also known as the Algerian War of Independence | |
| Ethnic conflict in Nagaland | 34,000+ | 1954–present | India and Myanmar vs. Naga People | Northeast India | [88] | |
| Vietnam War | 1,300,000–4,300,000 | 1955–1975 | South Vietnam and allies vs. North Vietnam and allies | Vietnam | [89][90][91] American casualties in the Vietnam War included 58,226 dead and 304,000 wounded. – Also known as the Second Indochina War - Includes deaths in Cambodia and Laos | |
| First Sudanese Civil War | 500,000+ | 1955–1972 | Sudan vs. South Sudanese Rebels | Sudan | ||
| Congo Crisis | 100,000+ | 1960–1965 | DRC, USA, and Belgium vs. Simba and Kwilu Rebels | Congo | [92] | |
| Angolan War of Independence | 83,000–103,000 | 1961–1974 | Angola vs. Portugal and South Africa | Angola | ||
| North Yemen Civil War | 100,000–200,000 | 1962–1970 | Kingdom of Yemen and Saudi Arabia vs. Yemen Arab Republic and United Arab Republic | Yemen | [93] | |
| Mozambican War of Independence | 63,500–88,500 | 1964–1974 | FRELIMO vs. Portugal | Mozambique | [94] | |
| Insurgency in Northeast India | 25,000+ | 1964–present | India and allies vs. Insurgent Groups | Northeast India | [84] | |
| Colombian conflict | 220,000+ | 1964–present | Colombia and allies vs. Far Left guerillas and Far Right paramilitares | Colombia | [95] | |
| Nigerian Civil War | 1,000,000–3,000,000 | 1967–1970 | Nigeria vs. Biafra | Nigeria | – Also known as the Biafran War | |
| Moro conflict | 120,000+ | 1969–2019 | Philippines vs. Jihadist Groups vs. Bangsamoro | Philippines | [96] | |
| Communist rebellion in the Philippines | 30,000–43,000 | 1969–present | Philippines vs. Communist Party of the Philippines | Philippines | [97] | |
| Bangladesh Liberation War | 400,000–3,600,000+ | 1971 | India and Bangladesh vs. Pakistan | Bangladesh | [98] – Also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence
Figure includes 30,000 military dead, 300,000 to 3,000,000 Bengali civilian and 64,000 to 600,000 Bihari civilian deaths [99][100] | |
| Ethiopian Civil War | 500,000–1,500,000 | 1974–1991 | Derg, PEDR, and Cuba vs. Anti-Communist rebel groups | Ethiopia | ||
| Angolan Civil War | 504,158+ | 1975–2002 | MPLA and Cuba vs. UNITA and South Africa | Angola | ||
| South African invasion of Angola | 50,000+ | 1975–1976 | Cuba and MPLA vs. South Africa, FNLA, UNITA and Zaire | Angola | 50,000 Angolans dead (mostly civilians)[29] – Part of the South African Border War and the Angolan Civil War | |
| Indonesian invasion of East Timor | 100,000-200,000 | 1975–1976 | Indonesia vs. East Timor | East Timor | ||
| Lebanese Civil War | 120,000–150,000 | 1975–1990 | Various groups | Lebanon | ||
| Insurgency in Laos | 100,000+ | 1975–2007 | Laos and Vietnam vs. "Secret army" and Hmong people | Laos | [101] | |
| Ogaden War | 60,000 | 1977–1978 | Ethiopia and Cuba vs. Somalia | Ethiopia | [102] | |
| Afghanistan conflict | 1,400,000–2,500,000 | 1978–present | see Afghanistan conflict | Afghanistan | [103] | |
| Kurdish–Turkish conflict | 45,000+ | 1978–present | Turkey vs. KCK | Middle East | [104] – Part of the Kurdish rebellions in Turkey | |
| Soviet–Afghan War | 600,000–2,000,000 | 1979–1989 | Soviet Union and Afghanistan vs. Insurgent groups | Afghanistan | [105][106][107] – Part of War in Afghanistan | |
| Salvadoran Civil War | 70,000–80,000 | 1979–1992 | El Salvador vs. FMLN | El Salvador | [108][109] | |
| Iran–Iraq War | 500,000-1,500,000 | 1980–1988 | Iran and allies vs. Iraq and allies | Middle East | [110] | |
| Internal conflict in Peru | 70,000+ | 1980–present | Peru vs. PCP-SL and MRTA | Peru | [111] | |
| Ugandan Bush War | 100,000–500,000 | 1981–1986 | ULNF and Tanzania vs. National Resistance Army | Uganda | [112][113] – Also known as the Luwero War | |
| Second Sudanese Civil War | 1,000,000–2,000,000 | 1983–2005 | Sudan vs. South Sudanese rebels | Sudan | ||
| Sri Lankan Civil War | 80,000–100,000 | 1983–2009 | Sri Lanka vs. Tamil Tigers | Sri Lanka | [114] | |
| Somali Civil War | 300,000–500,000 | 1986–present | Varying Somali governments vs. insurgent groups | Somalia | [115][116] | |
| Lord's Resistance Army insurgency | 100,000–500,000 | 1987–present | Lord's Resistance Army vs. Central African states | Central Africa | [117] | |
| Nagorno-Karabakh conflict | 50,000+ | 1988–present | Artsakh and Armenia vs. Azerbaijan and allies | Caucasus region | – Also known as the Artsakh Liberation War | |
| Gulf War | 25,500–40,500 | 1990–1991 | Iraq vs. Coalition Forces | Kuwait, Iraq and Saudi Arabia | ||
| Rwandan Civil War | 500,000–807,500 | 1990–1994 | Rwandan Patriotic Front rebel forces vs. Rwanda | Rwanda | – The majority of casualties were civilians killed by Hutu rebels in the Rwandan genocide. | |
| Algerian Civil War | 44,000–200,000 | 1991–2002 | Algeria vs. FIS loyalists vs. GIA | Algeria | [118] | |
| Bosnian War | 97,000–105,000 | 1991–1995 | Bosnia and Herzegovinian governments and allies vs. Republika Srpska and allies | Bosnia | ||
| 1991 Iraqi uprisings | 85,000–235,000 | 1991 | Iraq vs various rebels | Iraq | [119][120][121] – Also known as the Sha'aban Intifada | |
| Eritrean–Ethiopian War | 70,000–300,000 | 1998–2000 | see Eritrean–Ethiopian War | Eritrean–Ethiopian border | ||
| Sierra Leone Civil War | 50,000–300,000 | 1991–2002 | see Sierra Leone Civil War | Sierra Leone | ||
| Burundian Civil War | 300,000+ | 1993–2005 | Burundi vs. Hutu rebels vs. Tutsi rebels | Burundi | [122] | |
| First Congo War | 250,000–800,000 | 1996–1997 | Zaire and allies vs. AFDL and allies | Congo | ||
| Second Congo War | 2,500,000–5,400,000 | 1998–2003 | See Second Congo War | Central Africa | [123][124][125][126] – Also known as the Great War of Africa | |
| Ituri conflict | 60,000+ | 1999–2003 | Lendu Tribe vs. Hemu Tribe and allies | Congo | [127] – Part of the Second Congo War | |
| War on terror | 272,000–1,260,000 | 2001–2021 | Anti-Terrorist Forces vs. Terrorist groups | Worldwide | [128][129][130][131] – Also known as the Global War on Terrorism | |
| War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) | 212,191+ | 2001–2021 | See War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) | Afghanistan | [129] – Part of the War on Terror and Afghanistan conflict | |
| Insurgency in the Maghreb | 54,000+ | 2002–present | See Insurgency in the Maghreb (2002–present) | Algeria, Libya, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Chad, Mauritania and other Maghreb and Sahel countries | Part of the War on Terror. Includes Mali War, Libyan crisis (various factions of Libyan crisis vs Islamists) Jihadist insurgency in Burkina Faso and Jihadist insurgency in Niger. | |
| Iraq War | 405,000–654,965 | 2003–2011 | See Iraq War | Iraq | [130][131][129]
– Part of the War on Terror See: Casualties of the Iraq War | |
| War in Darfur | 300,000+ | 2003–present | SRF and allies vs. Sudan and allies vs. UNAMID | Sudan | [132] | |
| Kivu Conflict | 100,000+ | 2004–present | see Kivu Conflict | Congo | – Part of the Second Congo War | |
| Insurgency in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | 45,900–79,000 | 2004–2017 | Pakistan, USA, and UK vs. Terrorist groups | Pakistan | [129] – Also known as the War in Waziristan
– Part of the War on Terror and War in Afghanistan (2001–present) | |
| Mexican drug war | 200,000–400,000+ | 2006–present | Mexico vs. Drug cartels, including inter-cartel conflicts | Mexico | [133][134] – Also known as the Mexican War on Drugs | |
| Boko Haram insurgency | 350,000+ | 2009–present | Multinational Joint Task Force vs. Boko Haram | Nigeria | 2,400,000 internally displaced | |
| Libyan crisis | 30,000–43,000[135][136][137][138] | 2011–present | First stage: Libyan Arab Jamahiriya vs Anti-Gaddafi forces; Second stage: Libyan National Army vs various militias (including jihadists); Third stage: House of Representatives vs Government of National Accord vs Islamic State and other jihadist militias | Libya | Includes the First Libyan Civil War, Factional violence in Libya and the Second Libyan Civil War | |
| Syrian civil war | 503,000–613,000+ | 2011–present | Syrian Arab Republic vs. Republic of Syria vs. ISIL vs. Syrian Democratic Forces | Syria | See: Casualties of the Syrian civil war | |
| Rojava–Islamist conflict | 50,000+ | 2013–present | Syrian Democratic Forces vs. Islamic States of Iraq and Levant vs. al-Nusra Front | Syria | 100,000[139] Syrian Kurds fleeing to Turkey | |
| South Sudanese Civil War | 383,000+[140] | 2013–2020 | South Sudan vs. SPLM-IO | South Sudan | About 190,000 died of violence and 383,000 died if healthcare services disruption and war-caused food scarcity factored in as of 2018 | |
| War in Iraq (2013–2017) | 195,000–200,000+ | 2013–2017 | Iraq and allies vs. ISIL | Iraq | ||
| Yemeni Civil War | 377,000+ | 2014–present | Yemen's Supreme Political Council vs. Hadi Government, Saudi-led Coalition and the UAE-backed Southern Movement vs Al-Qaeda | Yemen | UNDP estimate for the end of 2021. 60% attributable to hunger and disease. Also part of the Arab Winter. | |
| Tigray War | 162,000–378,000+ (Including famine victims, per Ghent University)[141] | 2020–2022 | UFEFCF vs. Ethiopian and Eritrean Government | Ethiopia (Tigray, Afar and Amhara Regions) | Part of the Ethiopian civil conflict. | |
| Myanmar Civil War | 40,302 | 2021–present | National Unity Government vs. State Administration Council | Myanmar | Part of the Internal conflict in Myanmar. | |
| Russian invasion of Ukraine | 300,000+ | 2022–present | Russia vs. Ukraine | Ukraine | Estimates of deaths vary widely.[142][143] The Ukrainian government stopped publishing country's demographic statistics starting from Jan'22. |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الحروب الحديثة بأقل من 25.000 قتيل
- 22.211 – حرب الاستقلال الكرواتية (1991–1995)[144]
- 22,000+ – Dominican Restoration War (1863–1865)[أ]
- 21.000+ – حرب 1967[145]
- 20.068 – Reform War (1857–1860)
- 20.000+ – Yaqui Wars (1533–1929)[25]
- 20.000+ – War of the Quadruple Alliance (1718–1720)[29]
- 20.000+ – Ragamuffin War (1835–1845)[146]
- 20.000+ – الحرب الإيطالية التركية (1911–1912)[25]
- 20.000 – Anglo-Spanish War (1727–1729)[25]
- 19.619+ – Rhodesian Bush War (1964–1979)
- 19.000+ – الحرب الأمريكية المكسيكية (1846–1848)[25]
- 18.069–20.069 – حرب الأفيون الأولى (1839–1842)[147]
- 17,200+ – First Anglo-Afghan War (1839–1842)[148]
- 16.765–17.065 – النزاع البلوشستاني (1948–الحاضر)[149][150][151]
- 16.000+ – حرب المحيط الهادي (1879–1883)
- 16.000+ – الحرب الأهلية النيپالية (1996–2006)
- 16.000+ – الحرب الأمريكية الإسپانية (1898)[25]
- 15.200–15.300 – Peasants' War (1798) – Part of the French Revolutionary Wars
- 15.000+ – Nigerian Sharia conflict (2009–present)[152][153][154]
- 15,000 – Anglo-Spanish War (1654–1660)
- 14,460–14,922 – South African Border War (1966–1990)
- 14,077–22,077 – Mau Mau rebellion (1952–1960)
- 13,929+ – Republic of the Congo Civil War (1997–1999)[116]
- 13,812+ – Naxalite–Maoist insurgency (1967–present)[155][156]
- 13,100–34,000 – Kurdish separatism in Iran (1918–present)[145]
- 13,073–26,373 – 1948 Arab–Israeli War (1948–1949)[157]
- 12,000+ – Israel–Hamas war (2023–present)
- 11,500–12,843 – Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 – Part of the Bangladesh Liberation War
- 11,342–89,000 – Malagasy Uprising (1947–1948)[158][159]
- 10,700–14,300 – Yom Kippur War (1973)[75]
- 10,000+ – Assam separatist movements (1979–present)
- 10,000+ – Malayan Emergency (1948–1960)[160]
- 10,000+ – War in Donbas[161] – Part of the Russian military intervention in Ukraine (2014–present)
- 10,000+ – First Italo-Ethiopian War (1894–1896)[25]
- 10,000+ – Second Melillan campaign (1909)[25]
- 10,000+ – Hispano-Moroccan War (1859–1860)[25]
- 10,000+ – Spanish conquest of Tripoli (1510)[162]
- 9.400+ – الحرب الأهلية الليبية (2011) (2011)[163]
- 8,136+ – Iraqi insurgency (2011–2013)[164]
- 7,500–21,741 – حرب 1812 (1812–1815)[25][165]
- 7,400–16,200 – الحرب الأهلية اليمنية (2014–الحاضر) (2014–الحاضر)
- 7,050+ - Portuguese conquest of Goa (1510)[166]
- 7,104+ – Indo-Pakistani War of 1947–1948 (1947–1949)[167]
- 7,000+ – الحرب الأهلية التشادية (2005–2010) (2005–2010)[168]
- 6,800–13,459 – Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 (1965)
- 6,859+ – 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh conflict (2020–الحاضر)
- 5,641–6,991 - Opposition–Islamic State conflict during the Syrian civil war ( 2014–present )
- 6,543+ – South Thailand insurgency (2004–present)[169]
- 6,295+ – Central African Republic conflict (2012–present)
- 6,000+ – Permesta Rebellion (1958–1961)
- 5,641+ – Sudanese nomadic conflicts (2009–present)[170][171]
- 5,100+ – Gaza–Israel conflict (2006–present) – Part of the Arab–Israeli conflict
- 5,000+ – Casamance conflict (1982–2014)[172]
- 5,000+ – Chilean Civil War of 1891 (1891)[173]
- 5,000+ – Cuban Revolution (1953–1959)[174]
- 5,000 – War of the Reunions (1683–1684)
- 4,715+ – Libyan Civil War (2014–present) (2014–present)
- 4,275 – Dominican Civil War (1965)[175]
- 4,200+ – Shifta War (1963–1967)[176]
- 4,000–10,000 – Conflict in the Niger Delta (2004–present)[177]
- 4,000 – War of Devolution (1667–1668)
- 3,699+ – Al-Qaeda insurgency in Yemen (1992–present)[116]
- 3,552+ – First Schleswig War (1848–1852)
- 3,529+ – The Northern Ireland Troubles (1966–1998)[178]
- 3,366+ – Insurgency in the North Caucasus (2009–2017)[179]
- 3,270+ – Second Schleswig War (1864)
- 3,222–3,722 – Hungarian Revolution of 1956 (1956)
- 3,144+ – Allied Democratic Forces insurgency (1996–present)
- 3,114+ – 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine (1947–1948) – Part of the 1948 Palestine war
- 3,007+ – War of the Golden Stool (1900)[بحاجة لمصدر]
- 3,000–6,000 – Negro Rebellion (1912)[180][181]
- 3,000–5,000 – Croatian–Slovene Peasant Revolt (1573) [182]
- 3,000 – 1958 Lebanon crisis (1958)
- 3,000+ – Second Ivorian Civil War (2010–2011)[183]
- 3,000+ – Banana Wars (1914–1933)[57]
- 3,000+ – Dominican War of Independence (1844)
- 2,800+ – Northern Mali conflict (2012–present)
- 2,781+ – Iranian Revolution (1978–1979)[184]
- 2,751+ – Third Anglo-Afghan War (1919)[185]
- 2,557+ – Sudan internal conflict (2011–present) (2011–present)[186][187][188]
- 2,394+ – Sinai insurgency (2011–present)[189]
- 2,300+ – Conflict in the Niger Delta (2003–present)[190][191]
- 2,270–2,971 – Second Opium War (1856–1860)
- 2,221–2,406 – 2014 Israel–Gaza conflict (2014) – Part of the Gaza–Israel conflict
- 2,150+ – Persian expedition of 1796 (1796)
- 2,096+ – Aden Emergency (1963–1967)
- 2,054+ – South Yemen insurgency (2009–2015)
- 2,014 – Irish War of Independence (1919–1921)
- 2,000–3,800 - Albanian Civil War (1997)
- 2,000+ – Costa Rican civil war (1948)
- 2,000+ – Six-Day War (2000) (2000)[192]
- 2,000+ – 2010 South Kyrgyzstan ethnic clashes (2010)[193][194][195]
- 2,000 – Iran crisis of 1946 (1946)[196]
- 1,817+ – Mexican Border War (1910–1919)
- 1,810+ – Anglo-Iraqi War (1941) – Part of World War II
- 1,774+ – Lapland War (1944–1945) – Part of World War II
- 1,648 – Sinaloa Cartel–Gulf Cartel conflict ( 2004–present )
- 1,643–2,237 – Transnistria War (1992)[197][198][199][200]
- 1,600+ – Texas Revolution (1835–1836)[ب]
- 1,561 – Islamic State-related terrorist attacks in Turkey (2013–present)
- 1,500+ – Irish Civil War (1922–1923)
- 1,480 – Ifni War (1957–1958)[75]
- 1,444 – Taliban-ISIL conflict in Afghanistan ( 2015–present )
- 1,300+ – Allied Democratic Forces insurgency (1996–present)[201]
- 1,295+ – Siachen conflict (1984–2011)
- 1,229+ – Basque conflict (1959–2011)[202]
- 1,227–5,600 – Kargil War (1999)[203][204][205][206]
- 1,000–1,500 – Cabinda conflict (1994–present)[207]
- 1,000+ – Djiboutian Civil War (1991–1994)
- 1,000+ – 1991–1992 South Ossetia War (1991–1992)[208]
- 1,000+ – Xinjiang conflict (1930–present)
- 1,000+ – Chincha Islands War (1864–1866)[25]
- 1,000+ – Houthi–Saudi Arabian conflict (2015–present) – Part of the Yemeni Civil War (2014–present)
- 1,000 – Second Mafia War (1980-1983)
- 968+ – Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961)
- 907 – Falklands War (1982)[209]
- 898 – Barbary Wars (1801–1815)
- 864 – Jamaican political conflict (1943–present)
- 850 – Syrian civil war spillover in Lebanon (2011–2017) – Part of the Syrian Civil War
- 846 – 2011 Egyptian revolution (2011)
- 818 – Korean DMZ Conflict (1966–1969)
- 808 – Sino-Russian border conflicts (1652–1689)
- 789–1,874 – 2001–2002 India–Pakistan standoff (2001–2002)
- 771 – Insurgency in Egypt (2013–present) (2013–present)
- 740 – Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation (1963–1966)[210][211]
- 722 – Kamwina Nsapu rebellion (2016–2019)
- 700–800 – Anglo-Aro War (1901–1902)
- 638–838 – Operation Just Cause (1989–1990)
- 670+ Infighting in the Gulf Cartel (2010–present)
- 659–2,496 – Russo–Georgian War (2008)
- 650+ – Infighting in Los Zetas (2010–present)
- 643–1,500 – Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile (2011–present)[188][187]
- 621 – Second 'Ndrangheta war (1985-1991)
- 316 – Chiapas conflict (1994–1996)
- 302 – Operation Uphold Democracy (1994–1995)
- 300+ – Islamic Army–Al-Qaeda conflict (2006-2007)
- 547 – Cyprus Emergency (1955–1959)
- 542 – East Prigorodny Conflict (1992)
- 500 – Anglo-Zanzibar War (1896)
- 483-494 2007 Lebanon conflict
- 422 – Franco-Thai War (1940–1941)
- 327 – RENAMO insurgency (2013–2021)
- 275–569 – Second Afar insurgency (1995–2018) Part of the Eritrean–Ethiopian border conflict
- 247 – Cortina Troubles (1859–1861)
- 246–353 – Korean Expedition (1871)
- 236 – Batwa–Luba clashes (2013–2018)
- 233 – First 'Ndrangheta war (1974–1976)
- 233 – Anglophone Crisis (2017–present)[ت]
- 217 – Cuban invasion of the Dominican Republic (1959)
- 213–523+ – Jebel Akhdar War (1954–1959)[217]
- 206–345 – Arab separatism in Khuzestan (1922–2022)
- 200+ – 1967 Opium War (1967)
- 200 – 1935 Yazidi revolt (1935)[بحاجة لمصدر]
- 174–194 – United States occupation of Veracruz (1914)[218]
- 160+ – Quebec Biker War (1994-2002)
- 159 – Islamic State insurgency in Tunisia (2015–present)[بحاجة لمصدر]
- 141 – 2006 São Paulo violence outbreak (2006)
- 126 – Kasese clashes (2016)[219][220]
- 115 – Pool War (2016–present)
- 112 – Operation Urgent Fury (1983)
- 108 – Islamist insurgency in Mozambique (2017–present)[ث]
- 102–227 – 2016–2018 India–Pakistan border skirmishes (2016–2018)
- 99–500 – Sand War (1963–1964)
- 95 – 2013 Guinea clashes (2013)[232]
- 84–134 – 2013 Lahad Datu standoff (2013)[233][234]
- 82 – Quasi-War (1798–1800)[بحاجة لمصدر]
- 82 – North-West Rebellion (1885)[235]
- 80+ – Las Cuevas War (1875)
- 71 – Paraguayan People's Army insurgency (2005–present)[بحاجة لمصدر]
- 70+ – DHKP/C insurgency in Turkey (1990–present)
- 63–77 – Operation El Dorado Canyon (1986)
- 63 – Ten-Day War (1991)
- 56+ – Dissident Irish Republican campaign (1998–present)
- 50 – Second Samoan Civil War (1898–1899)
- 46 – Annexation of Dadra and Nagar Haveli (1954)
- 45+ – 2020–2021 China–India skirmishes (2020–2021)
- 41 – 2010 Rio de Janeiro security crisis (2010)
- 39–111 – 2014–2015 India–Pakistan border skirmishes (2014–2015)
- 37 – 2013 India–Pakistan border skirmishes (2013)
- 36 – 2016 Niger Delta conflict (2016–Present)[236] – Part of the Conflict in the Niger Delta
- 12–61 – 2017 Afghanistan–Pakistan border skirmish (2017) – Part of the Afghanistan–Pakistan border skirmishes
- 11–30 – 2008 Kufra conflict (2008)
- 8 – 2011 India–Pakistan border skirmish (2011)
Charts and graphs
See also
- Casualty recording
- Timeline of wars
- List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll
- List of battles by casualties
- List of number of conflicts per year
- Lists of wars
- List of ongoing armed conflicts
- List of genocides by death toll
- List of countries by refugee population
Notes
- ^ One estimate placed total Spanish deaths from all causes at 18,000. The fatal losses among the Dominican insurgents were estimated at 4,000.[29]
- ^ One author estimates Mexican casualties at 1,000 dead, 700 prisoners, and 400 wounded. Desertion and noncombat deaths would significantly increase these numbers. The Texans lost about 600 killed and 350 wounded.
- ^ See[212][213][214][215][216]
- ^ See[221][222][223][224][225][226][227][228][229][230][231]
References
- ^ Peers, Chris, (1998). Warlords of China, 700 BC to AD 1662, (London: Arms and Armour), p 59.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Atrocity statistics from the Roman Era". Necrometrics.
- ^ Estimated at "several millions." Alföldy, Géza, (1975). The Social History of Rome, (London & Sydney: Johns Hopkins University Press), p 91.
- ^ "Atrocity statistics from the Roman Era". users.erols.com.
- ^ أ ب "The Jewish Roman Wars". www.jewishwikipedia.info. Retrieved 2020-07-28.
- ^ Robert B. Marks (2011). China: Its Environment and History (World Social Change). Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. ISBN 978-1442212756.
- ^ Graziella Caselli (2005). Demography – Analysis and Synthesis: A Treatise in Population. Academic Press. ISBN 012765660X.
- ^ Aletheia (1897). The Rationalist's Manual.
- ^ Book of Sui. 636.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Selected Death Tolls for Wars, Massacres and Atrocities Before the 20th Century". Necrometrics. Retrieved 2011-01-24.
- ^ "귀주대첩 [네이버 지식백과] 귀주대첩 [龜州大捷] (두산백과)". Naver. Retrieved 4 July 2013.
- ^ Chapuis, Oscar (1995). A History of Vietnam: from Hong Bang to Tu Duc. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 77. ISBN 0-313-29622-7.
- ^ Xu Zizhi Tongjian Changbian《長編》卷三百上載出師兵員“死者二十萬”,“上曰:「朝廷以交址犯順,故興師討罪,郭逵不能剪滅,垂成而還。今廣源瘴癘之地,我得之未為利,彼失之未為害,一夫不獲,朕尚閔之,况十死五六邪?」又安南之師,死者二十萬,朝廷當任其咎。《續資治通鑑長編·卷三百》”。 《越史略》載廣西被殺者“無慮十萬”。 《玉海》卷一九三上稱“兵夫三十萬人冒暑涉瘴地,死者過半”。
- ^ Robertson, John M., "A Short History of Christianity" (1902) p.278. Cited by White
- ^ White, Matthew. "Crusades (1095-1291)". Necrometrics.
- ^ "Massacre of the Pure". Time. April 28, 1961. Archived from the original on January 20, 2008.
- ^ McEvedy, Colin; Jones, Richard M. (1978). Atlas of World Population History. New York, NY: Puffin. p. 172. ISBN 9780140510768.
- ^ Ping-ti Ho, "An Estimate of the Total Population of Sung-Chin China", in Études Song, Series 1, No 1, (1970) pp. 33–53.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Mongol Conquests". Necrometrics. Retrieved 2011-01-24.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Twentieth Century Atlas – Historical Body Count". Necrometrics.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Timur Lenk (1369–1405)". Necrometrics. Retrieved 2011-01-24.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Miscellaneous Oriental Atrocities". Necrometrics. Retrieved 2011-01-24.
- ^ "War Statistics – Death Tolls, Length, and More". Archived from the original on 10 March 2017.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ ر "De re Militari: muertos en Guerras, Dictaduras y Genocidios". remilitari.com.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ ر ز س ش ص ض ط ظ ع غ Nash (1976). Darkest Hours. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 9781590775264.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Peasants' War, Germany (1524-25)". Necrometrics.
- ^ Knecht, Robert J. (2002). The French Religious Wars 1562–1598. Osprey Publishing. pp. 91. ISBN 9781841763958.
- ^ Carlton, Charles (2011-11-22). This Seat of Mars: War and the British Isles, 1485-1746. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0300180886.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ ر ز س ش ص Clodfelter, M (2017). Warfare and Armed Conflicts: A Statistical Encyclopedia of Casualty and Other Figures, 1492-2015, 4th ed. McFarland.
- ^ Jones, Geo H. (1899). "The Japanese Invasion of Korea — 1592" (PDF). The China Review. 23 (5): 234. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2019-07-10. Retrieved 2018-05-13.
Thus ended for a time one of the bloodiest wars in history. During the two years and more the loss of life was frightful; nothing remains upon which to base a reliable estimate, but the War Monument at Kiuto, and the accounts of such battles as Kyong-chu, Choung-chu, Haing chu, the Im Chiu River, Pyongyang, Yenan, the massacre at Söul, Ulsan and Chiu-chu, and fifty other engagements would make a million lives a conservative estimate.
- ^ McFarlane, Alan: The Savage Wars of Peace: England, Japan and the Malthusian Trap, Blackwell 2003, ISBN 0-631-18117-2, ISBN 978-0-631-18117-0 – cited by White
- ^ White, Matthew. "The Thirty Years War (1618-48)". Necrometrics.
- ^ Carlton 2002, p. 211.
- ^ Carlton 2002, p. 212.
- ^ Carlton 2002, p. 213.
- ^ Grabieże szwedzkie w Polsce (1). Przyczyny, charakterystyka i skutki
- ^ Matthew White (2011). Atrocitology: Humanity's 100 Deadliest Achievements. Canongate Books. p. 113. ISBN 9780857861252.
- ^ Matthew White (2011), Aurangzeb - in Atrocities: The 100 Deadliest Episodes in Human History, W.W. Norton & Co., ISBN 978-0393081923
- ^ Levy, Jack S (1983). War in the Modern Great Power System: 1495 to 1975. University Press of Kentucky. Page 90.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Northern War (1700-21)". Necrometrics.
- ^ Walpole, Horace (2015). Delphi Complete Works of Horace Walpole (Illustrated).
We have already lost seven millions of money and thirty thousand men in the Spanish war and all the fruit of all this blood and treasure is the glory of having Admiral Vernon's head on alehouse signs!
- ^ P. J. Marshall (2006). Bengal: The British Bridgehead: Eastern India 1740-1828. Cambridge University Press. p. 73. ISBN 9780521028226.
- ^ Kirti N. Chaudhuri (2006). The Trading World of Asia and the English East India Company: 1660-1760. Cambridge University Press. p. 253. ISBN 9780521031592.
- ^ Peckham, Howard H., ed. (1974). The Toll of Independence: Engagements and Battle Casualties of the American Revolution. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- ^ Dawson, Warrington. "The 2112 Frenchmen who died in the United States from 1777 to 1783 while fighting for the American Independence". Washington-Rochambeau Revolutionary Route. Journal de la societe des Americanistes. Archived from the original on 5 June 2017. Retrieved 4 June 2017.
- ^ "Spanish casualties in The American Revolutionary war". Necrometrics.
- ^ Annual Register, 1783 (1785), pp. 199–200.
- ^ أ ب "De re Militari: muertos en Guerras, Dictaduras y Genocidios". remilitari.com.
- ^ "Shaka: Zulu Chieftain". HistoryNet.com. June 12, 2006.
- ^ Hanson, Victor (18 December 2007). Carnage and Culture: Landmark Battles in the Rise to Western Power. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-307-42518-8.
- ^ Walter, Eugene Victor (1969). Terror and resistance: a study of political violence, with case studies of some primitive African communities. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Wright, John; Cobbing, Julian (1988-09-12). "The Mfecane: Beginning the inquest". Wits Institutional Repository African Studies Institute - Seminar Papers.
- ^ Jalata, Asafa (2016). Phases of Terrorism in the Age of Globalization: From Christopher Columbus to Osama bin Laden. Palgrave Macmillan US. pp. 92–3. ISBN 978-1-137-55234-1.
Within the first three decades, the French military massacred between half a million to one million from approximately three million Algerian people.
- ^ Kiernan, Ben (2007). Blood and Soil: A World History of Genocide and Extermination from Sparta to Darfur. Yale University Press. pp. 364–ff. ISBN 978-0-300-10098-3.
In Algeria, colonization and genocidal massacres proceeded in tandem. From 1830 to 1847, its European settler population quadrupled to 104,000. Of the native Algerian population of approximately 3 million in 1830, about 500,000 to 1 million perished in the first three decades of French conquest.
- ^ Bennoune, Mahfoud (2002-08-22). The Making of Contemporary Algeria, 1830-1987. Cambridge University Press. p. 42. ISBN 9780521524322.
- ^ "Nineteenth Century Death Tolls". necrometrics.com.
- ^ أ ب Gruhl, Werner (2007). Imperial Japan's World War Two: 1931 - 1945. Transaction Publishers. p. 181. ISBN 9780765803528.
- ^ Cao, Shuji (2001). Zhongguo Renkou Shi [A History of China's Population] (in الصينية). Shanghai: Fudan Daxue Chubanshe. pp. 455, 509.
- ^ Hans Bielenstein. Chinese historical demography A.D. 2-1982. Östasiatiska museet. p 17
- ^ Ramesh, Randeep (24 August 2007). "India's secret history: 'A holocaust, one where millions disappeared...'". The Guardian.
- ^ Recounting the dead, Associate Professor J. David Hacker, "estimates, based on Census data, indicate that the death toll was at least 750,000, and may have been as high as 850,000" (study refers only to military casualties)
- ^ James M. McPherson, "Battle Cry of Freedom", Oxford University Press, Oct 24, 2003, page 619. "Suffering and death were widespread, nevertheless, and a fair estimate of war-related civilian deaths might total 50,000".
- ^ Professor James Downs. "Color blindness in the demographic death toll of the Civil War". Oxford University Press, April 13th 2012. "An 2 April 2012 New York Times article, "New Estimate Raises Civil War Death Toll," reports that a new study ratchets up the death toll from an estimated 650,000 to a staggering 850,000 people. As horrific as this new number is, it fails to reflect the mortality of former slaves during the war. If former slaves were included in this figure, the Civil War death toll would likely be over a million casualties... the rough 19th century estimate was that 60,000 former slaves died from [war-related diseases and starvation], but doctors treating black patients often claimed that they were unable to keep accurate records due to demands on their time and the lack of manpower and resources... tens of thousands of other slaves who died had no contact with army doctors, leaving no records of their deaths".
- ^ Doratioto, Francisco (2003). Maldita guerra: nova história da Guerra do Paraguai. Companhia das Letras. pp. 445–446. ISBN 978-85-359-0224-2. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ^ Foner, Philip S. (1989). Antonio Maceo: The "Bronze Titan" of Cuba's Struggle for Independence. NYU Press. p. 21.
With reinforcements and guidance from the Dominicans, the rebels defeated Spanish detachments, cut railway lines, and gained dominance over vast sections of the eastern portion of the island.
- ^ Vickers, Adrian (2005). A History of Modern Indonesia. New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 13. ISBN 0-521-54262-6.
- ^ BBC (14 August 2012). "Colombia Timeline". Retrieved 11 May 2016.
- ^ "South African War". Encyclopedia Britannica. December 11, 2017.
- ^ Gates, John M. (August 1984). "War-Related Deaths in the Philippines, 1898-1902". Pacific Historical Review. 53 (3): 367–378. doi:10.2307/3639234. JSTOR 3639234. PMID 11635503.
- ^ McCaa, Robert (2001). "Missing Millions: The human cost of the Mexican Revolution, 1910–1921".
- ^ "Russian Civil War". Spartacus-Educational.com. Archived from the original on 2010-12-05. Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ "Iran/Kurds (1943-present)". Archived from the original on 25 يناير 2016. Retrieved 23 يناير 2016.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Twentieth Century Atlas – Death Tolls". Necrometrics.
- ^ Lortz, Michael G. (2005). Willing to Face Death: A History of Kurdish Military Forces — the Peshmerga — from the Ottoman Empire to Present-Day Iraq (MA). Florida State University. OCLC 64130374. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ^ أ ب ت "De re Militari: muertos en Guerras, Dictaduras y Genocidios". remilitari.com.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Twentieth Century Atlas – Death Tolls". Necrometrics. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ^ أ ب Shinn, David H.; Ofcansky, Thomas P. (2013). Historical Dictionary of Ethiopia. Lanham: Scarecrow Press. p. 234. ISBN 9780810874572.
- ^ "Secondary Wars and Atrocities of the Twentieth Century". Necrometrics.
- ^ Anderson, Duncan (2011-02-17). "World Wars: Nuclear Power: The End of the War Against Japan". BBC.
- ^ Jones, Howard (1989). A New Kind of War. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195045819.
- ^ Edgar O'Ballance, The Greek Civil War : 1944–1949 (1966)
- ^ T. Lomperis, From People's War to People's Rule (1996)
- ^ "B&J": Jacob Bercovitch and Richard Jackson, International Conflict : A Chronological Encyclopedia of Conflicts and Their Management 1945–1995 (1997)
- ^ أ ب "Modern Conflicts Database: Alternative Estimates for Death Tolls" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-10-11.
- ^ "Vital Statistics: Total Casualties, Arab-Israeli Conflict (1860–Present)". Jewish Virtual Library.
- ^ Lacina, Bethany (September 2009). "The PRIO Battle Deaths Dataset, 1946-2008, Version 3.0" (PDF). Peace Research Institute Oslo. pp. 359–362. Retrieved 2019-08-30.
- ^ France remembers the Algerian War, 50 years on France 24
- ^ "Chronological Index of Wars and Conflicts from 1950 to 1959". www.onwar.com.
- ^ Hirschman, Charles; Preston, Samuel; Vu Manh Loi (December 1995). "Vietnamese Casualties During the American War: A New Estimate" (PDF). Population and Development Review. 21 (4): 783. doi:10.2307/2137774. JSTOR 2137774.
- ^ Shenon, Philip (23 April 1995). "20 Years After Victory, Vietnamese Communists Ponder How to Celebrate". The New York Times. Retrieved 24 February 2011.
- ^ Obermeyer, Ziad; Murray, Christopher J L; Gakidou, Emmanuela (26 June 2008). "Fifty years of violent war deaths from Vietnam to Bosnia: analysis of data from the world health survey programme". BMJ. 336 (7659): 1482–6. doi:10.1136/bmj.a137. PMC 2440905. PMID 18566045.
From 1955 to 2002, data from the surveys indicated an estimated 5.4 million violent war deaths ... 3.8 million in Vietnam.
- ^ Mwakikagile, Godfrey (2014). Statecraft and Nation Building in Africa: A Post-colonial Study. Dar es Salaam: New Africa Press. p. 72. ISBN 978-9987-16-039-6.
- ^ "Yemen's First Civil War Offers Lessons for Ending the Country's Current Conflict". 21 April 2015. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Mozambique, Anti-colonial war (1961-1975)". Necrometrics. Retrieved 11 July 2013.
- ^ Dear, John (October 2, 2010). "Georgetown Welcomes Colombia's Ex-Pres. Uribe". Archived from the original on 2010-11-13. Retrieved 2010-10-02.
- ^ Schiavo-Campo, Salvatore; Judd, Mary (2005-02-01). The Mindanao conflict in the Philippines: roots, costs, and potential peace dividend. World Bank. Archived from the original. You must specify the date the archive was made using the
|archivedate=parameter. http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTCPR/214578-1111996036679/20482477/WP24_Web.pdf. - ^ Holden, William Norman (2013). "The Never Ending War in the Wounded Land: The New People's Army on Samar" (PDF). Journal of Geography and Geology. 5 (4). doi:10.5539/jgg.v5n4p29. ISSN 1916-9787.
- ^ Matthew White's Death Tolls for the Major Wars and Atrocities of the Twentieth Century
- ^ Gerlach, Christian (2010). Extremely Violent Societies: Mass Violence in the Twentieth-Century World. Cambridge University Press. p. 148. ISBN 978-1-139-49351-2.
- ^ Willem van Schendel (2009). A History of Bangladesh. Cambridge University Press. p. 173. ISBN 978-1-316-26497-3. Archived from the original on 26 May 2019. Retrieved 28 June 2018.
- ^ Rummel, Rudolph Joseph (1998). "Table 15.1: Lesser Murdering States, Quasi-States, and Groups". Statistics of Democide: Genocide and Mass Murder Since 1900. Münster: LIT Verlag. p. 314. ISBN 9783825840105.
- ^ "La Fuerza Aérea de Cuba en la Guerra de Etiopía (Ogadén) • Rubén Urribarres". Aviación Cubana • Rubén Urribarres.
- ^ Dowling, Timothy C. (2014). Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond ... ABC-CLIO. p. 7. ISBN 9781598849486. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "Erdogan Rules Out Amnesty for Kurdish Rebels". Naharnet.
- ^ Isby, David (1986). Russia's war in Afghanistan. London: Osprey. ISBN 9780850456912.
- ^ Giustozzi, Antonio (2000). War, Politics and Society in Afghanistan, 1978–1992. Hurst. ISBN 9781850653967.
- ^ Khalidi, Noor Ahmad (1991). "Afghanistan: Demographic consequences of war, 1978–1987" (PDF). Central Asian Survey. 10 (3): 101–126. doi:10.1080/02634939108400750. PMID 12317412.
- ^ Report of the UN Truth Commission on El Salvador. United Nations. April 1, 1993. Archived from the original. You must specify the date the archive was made using the
|archivedate=parameter. http://www.derechos.org/nizkor/salvador/informes/truth.html. - ^ Andrews Bounds (2001), South America, Central America and The Caribbean 2002, El Salvador: History (10a ed.), London: Routledge, pp. 384, ISBN 978-1-85743-121-6
- ^ "Iran-Iraq War | Causes, Summary, Casualties, & Facts". Encyclopedia Britannica (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2021-09-02.
Estimates of total casualties range from 1,000,000 to twice that number. The number killed on both sides was perhaps 500,000, with Iran suffering the greatest losses.
- ^ "Peru Shining Path Arrests: 24 Seized". BBC News. 10 April 2014. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ^ Eckhardt, William, in World Military and Social Expenditures 1987–88 (12th ed., 1987) by Ruth Leger Sivard.
- ^ Wasswa, Henry (October 10, 2005). "Uganda's first prime minister, and two-time president, dead at 80". Associated Press.
- ^ "Up to 100,000 killed in Sri Lanka's civil war: UN". ABC News. 20 May 2009.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Twentieth Century Atlas – Death Tolls and Casualty Statistics for Wars, Dictatorships and Genocides". Necrometrics. Retrieved April 20, 2011.
- ^ أ ب ت Allansson, Marie; Melander, Erik; Themnér, Lotta (2017). "Organized violence, 1989–2016". Journal of Peace Research. 54 (4): 574–587. doi:10.1177/0022343317718773. ISSN 0022-3433.
- ^ "Uganda (1987– 2010)". Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- ^ Sage, Adam (December 12, 2007). "Attacks raise spectre of civil war". The Australian.
- ^ Moore, Solomon (5 June 2006). "2 Mass Graves in Iraq Unearthed". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Black, Ian (21 August 2007). "'Chemical Ali' on trial for brutal crushing of Shia uprising". The Guardian. London.
- ^ Endless Torment: The 1991 Uprising in Iraq And Its Aftermath. US: Human Rights Watch. June 1992. ISBN 1-56432-069-3.
- ^ "Heavy shelling in Burundi capital". BBC News. 18 April 2008.
- ^ Brennan, Richard (2006-07-16). "Inside Congo, An Unspeakable Toll". Theirc.org. Retrieved 2011-01-24.
- ^ James Astill in Bukavu & Isabelle Chevallot (2003-04-08). "Conflict in Congo has killed 4.7m, charity says". Guardian. London. Retrieved 2011-01-24.
- ^ "Come Back, Colonialism, All Is Forgiven". Time. 14 February 2008. Archived from the original on February 15, 2008.
- ^ Lacina, Bethany; Gleditsch, Nils Petter (2005). "Monitoring Trends in Global Combat: A New Dataset of Battle Deaths" (PDF). European Journal of Population. 21 (2–3): 145–166. doi:10.1007/s10680-005-6851-6. S2CID 14344770.
- ^ Allen, Karen (30 November 2006). "Eastern DR Congo rebels to disarm". BBC News. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ^ Casualty Figures after 10 Years of the "War on Terror": Iraq, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. International Physicians for the Prevention of Nuclear War. March 2015. ISBN 978-3-9817315-0-7. Archived from the original. You must specify the date the archive was made using the
|archivedate=parameter. http://www.ippnw.de/commonFiles/pdfs/Frieden/Body_Count_first_international_edition_2015_final.pdf. - ^ أ ب ت ث "Human costs of war: Direct war death in Afghanistan, Iraq and Pakistan October 2001 – February 2013" (PDF). Costs of War. February 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 April 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- ^ أ ب "Update on Iraqi Casualty Data" Archived 2008-02-01 at the Wayback Machine by Opinion Research Business. January 2008.
- ^ أ ب "Revised Casualty Analysis. New Analysis 'Confirms' 1 Million+ Iraq Casualties" Archived 2009-02-19 at the Wayback Machine. January 28, 2008. Opinion Research Business. Word Viewer for.doc files.
- ^ Degomme, Olivier; Guha-Sapir, Debarati (23 January 2010). "Patterns of mortality rates in Darfur conflict". The Lancet. 375 (9711): 294–300. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61967-X. PMID 20109956. S2CID 24643946.
- ^ Booth, William (20 November 2012). "Mexico's crime wave has left about 25,000 missing, government documents show". The Washington Post. Retrieved 26 July 2013.
- ^ "Shooting at Mexico bar leaves many dead". Al Jazeera. 30 March 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2013.
- ^ "ACLED Version 6 (1997–2015)". Armed Conflict Location & Event Data Project. Archived from the original on 18 يناير 2016. Retrieved 13 يناير 2015.
- ^ "Libyan revolution casualties lower than expected, says new government". The Guardian. 8 January 2013. "4,700 rebel supporters died and 2,100 are missing, with unconfirmed similar casualty figures on the opposing side"
- ^ Kuperman, Alan (March–April 2015). "Obama's Libya Debacle". Foreign Affairs (March/April 2015). "the conflict killed at least 500 people a year in 2012 and 2013"
- ^ "Violent Deaths in 2014 & 2015". Libya Body Count. Retrieved 10 October 2015.
- ^ "Syria refugee flood to Turkey hits 100,000". The Daily Star Newspaper - Lebanon. Archived from the original on 5 November 2014. Retrieved 5 November 2014.
- ^ "Study estimates 190,000 people killed in South Sudan's civil war". Reuters. 26 September 2018.
- ^ Plaut, Martin (24 May 2023). "Updated assessment of civilian starvation deaths during the Tigray war".
- ^ Crawford, Neta C. "Reliable death tolls from the Ukraine war are hard to come by – the result of undercounts and manipulation". The Conversation.
- ^ Varghese, Sanjana (May 4, 2022). "Counting the Dead in Ukraine".
- ^ Zebić, Enis (15 January 2018). "Ljudski gubici u ratu u Hrvatskoj: 22.211 osoba" [Human Casualties in the Croatian War: 22,211 Persons]. Radio Free Europe (in الكرواتية). Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ^ أ ب Hicks, Neil (April 2000). "The Human Rights of Kurds in the Islamic Republic of Iran" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 August 2011.
- ^ Treece, Dave (2000). Exiles, allies, rebels : Brazil's indianist movement, indigenist politics, and the imperial nation-state. Westport, Conn: Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0-313-31125-3.
- ^ Martin, Robert Montgomery (1847). China: Political, Commercial, and Social; In an Official Report to Her Majesty's Government. Volume 2. James Madden. pp. 81–82.
- ^ Blood, Peter R., ed. (2001). "The First Anglo-Afghan War". Afghanistan: A Country Study. Washington: GPO.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Twentieth Century Atlas – Death Tolls". Necrometrics.
- ^ "Balochistan Assessment - 2017". www.satp.org.
- ^ "Balochistan: Pakistan's internal war - Europe Solidaire Sans Frontières". www.europe-solidaire.org.
- ^ Isaacs, Dan (5 May 2004). "Analysis: Behind Nigeria's violence". BBC News.
- ^ "Curfew relaxed in Nigeria's violence-wracked city: army". AFP. 25 January 2018. Archived from the original on 28 January 2010.
- ^ "'Hundreds dead' in Nigeria attack". BBC News. 8 March 2010.
- ^ Al Jazeera Correspondent. "India's Silent War". Archived from the original on 2019-05-25. Retrieved 2013-04-14.
- ^ Annual Report 2003–2004: Departments of Internal Security, Jammu & Kashmir Affairs, Border Management, States and Home. Government of India Ministry of Home Affairs. Archived from the original. You must specify the date the archive was made using the
|archivedate=parameter. http://www.mha.nic.in/pdfs/ar0304-Eng.pdf. - ^ Adam M. Garfinkle (2000). Politics and Society in Modern Israel: Myths and Realities. M.E. Sharpe. p. 61. ISBN 978-0-7656-0514-6.
- ^ "Madagascar se souvient de l'insurrection de 1947 et des massacres du corps expéditionnaire français". Le Monde (in الفرنسية). 28 February 1989. Archived from the original on 15 December 2013. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ Jean Fremigacci, "La vérité sur la grande révolte de Madagascar," L'Histoire, n°318, March 2007.
- ^ "Royal Malaysian Police (Malaysia)". Crwflags.com. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- ^ "Situation in eastern Ukraine worsening, says UN report". OHCHR. 15 September 2016. Retrieved 16 September 2016.
- ^ Setton, Kenneth (1976). The Papacy and the Levant : 1204–1571. Vol. 3. Philadelphia, PA: American Philosophical Society. p. 85. ISBN 978-0-87169-161-3.
- ^ Black, Ian (8 January 2013). "Libyan revolution casualties lower than expected, says new government". London: Guardian. Retrieved 2013-10-02.
- ^ "Iraq Body Count". www.iraqbodycount.org.
- ^ "War of 1812 Statistics". historyguy.com. Retrieved September 4, 2016.
- ^ Gaspar Correia (1558–1563) Lendas da Índia, 1864 edition, Academia Real das Sciencias de Lisboa, book II p.94.
- ^ Malik, V. P. (2010). Kargil from Surprise to Victory (paperback ed.). HarperCollins Publishers India. p. 343. ISBN 9789350293133.
- ^ Vicenç Fisas. Anuario 2009 de procesos de paz Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine. Barcelona: Icaria Editorial, pp. 75. ISBN 978-84-9888-076-2.
- ^ "Insurgency claimed 6,543 lives in last 12 years". Bangkok Post. January 4, 2016. Retrieved February 29, 2016.
- ^ "TIMELINE-Violence spirals in south Sudan". Reuters. 7 January 2010. Archived from the original on 26 July 2012.
- ^ Gettleman, Jeffrey (5 January 2012). "In South Sudan, Massacre of 3,000 Is Reported". The New York Times.
- ^ Bacary Domingo Mané (13 January 2011). "Casamance: no peace after thirty years of war". Guin Guin Bali. Archived from the original on 3 January 2013.
- ^ White, Matthew. "Nineteenth Century Death Tolls". Necrometrics. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ^ Jacob Bercovitch and Richard Jackson (1997). International Conflict: A Chronological Encyclopedia of Conflicts and Their Management, 1945–1995. Congressional Quarterly.
- ^ "Congressional Bills 117th Congress". GovInfo.
- ^ Bercovitch, Jacob (2019-07-15), From Conflict Management to Conflict Resolution: The Problem-Solving Approach, Routledge, pp. 19–35, doi:, ISBN 978-0-429-30625-9, http://dx.doi.org/10.4324/9780429306259-2, retrieved on 2021-07-02
- ^ "Armed Conflicts Report – Nigeria". Archived from the original on 10 October 2006.
- ^ "CAIN: Sutton Index of Deaths". cain.ulster.ac.uk.
- ^ "Infographics. Total number of victims in Northern Caucasus in 2010–2014 under the data of the Caucasian Knot". Caucasian Knot. 19 February 2015. Archived from the original on 12 January 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- ^ Garcia, Pedro Antonio (2 July 2007). "Over three thousand black and mulatto Cubans killed in this act of force of the great national bourgeoisie". Afro Cuba Web. Retrieved 4 June 2013.
- ^ Escamilla, Luis (28 May 2013). "Partido de independiente de color (Cuba, 1908–1912)". Black Past. Retrieved 4 June 2013.
- ^ Čečuk 1960, p. 500.
- ^ "First-ever video proof documenting murder of suspected Gbagbo militants". The France 24 Observers. Archived from the original on 2015-06-05. Retrieved 2013-04-18.
- ^ Kadivar, Cyrus (8 August 2003). "A Question of Numbers". Rouzegar-Now.
- ^ "Armed Conflict Year Index". Archived from the original on 2012-04-06. Retrieved 2013-05-04.
- ^ "Home – Radio Dabanga". Archived from the original on 15 October 2014. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ^ أ ب "UN report: 1,500 killed and 73,000 displaced in S. Sudan conflicts – Sudan Tribune: Plural news and views on Sudan". Archived from the original on 29 November 2011. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ^ أ ب "DailyTimes – Your Right To Know". Archived from the original on 2012-10-24. Retrieved 2017-05-24.
- ^ "Egypt's Sinai rocked by wave of deadly attacks". BBC News. July 2015. Retrieved 4 July 2015.
- ^ "Nigeria (1990 – first combat deaths)". Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- ^ "ACLED Version 6 (1997–2015)". Archived from the original on 18 يناير 2016. Retrieved 21 يناير 2016.
- ^ Otim, Dennis (6 September 2010). "Revealed: 2,000 UPDF troops died in Kisangani". Uganda Corresponden. Retrieved 22 April 2018.
- ^ ""Комсомольская правда": в Оше тысячи погибших, беспорядки начинаются в Джалал-Абаде". polit.ru.
- ^ "Президент Узбекского национально-культурного центра Кыргызской Республики обратился с открытым письмо к Исламу Каримову". Фергана - международное агентство новостей.
- ^ "Отунбаева, зачем врать? Число погибших на юге Киргизии превысило две тысячи человек – ЦентрАзия". Archived from the original on 2019-07-09. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- ^ "CSP - Major Episodes of Political Violence, 1946-2012". Archived from the original on January 21, 2014. Retrieved 2013-11-14.
- ^ "Страница не найдена".
- ^ "Страница не найдена". Archived from the original on 2014-02-22. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- ^ "ВОЗРОЖДЕННОМУ В ПРИДНЕСТРОВЬЕ". Archived from the original on 2007-05-03.
- ^ "MONUMENTE.MD: Памятники из натурального гранита". monumente.md.
- ^ "Congo refugees pour into Uganda after attack". Al Jazeera. 13 July 2013. Retrieved 21 July 2013.
- ^ "Datos significativos del conflicto Vasco, 1968–2003" (in الإسبانية). Eusko Ikaskuntza. 18 January 2016.
- ^ "Kargil war brings into sharp focus India's commitment to peace". Press Information Bureau, Government of India. Archived from the original on 28 فبراير 2017. Retrieved 23 مايو 2014.
- ^ "Indian Army-Martyrs Home Page". Archived from the original on 22 December 2007.
- ^ "Musharraf claims Kargil was a big success militarily for Pak". Greater Kashmir. Press Trust of India. 1 February 2013. Archived from the original on 29 May 2013.
- ^ "Over 4,000 soldiers killed in Kargil: Sharif". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 17 August 2003. Archived from the original on 3 October 2003.
- ^ "Angola-Cabinda (1994 – first combat deaths) Update: January 2007 – The Institute For Global Church Studies (IGCS) Forum". Archived from the original on 2 مارس 2017. Retrieved 31 أكتوبر 2016.
- ^ Georgia: Avoiding war in South Ossetia. International Crisis Group. 26 November 2004. Archived from the original. You must specify the date the archive was made using the
|archivedate=parameter. http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/UNTC/UNPAN019224.pdf. Retrieved on 29 April 2013. - ^ "Argentine Falklands War troops 'tortured by their own side'". BBC News. 14 September 2015.
- ^ Carver, Michael (1986). "Conventional Warfare in the Nuclear Age". In Paret, Peter (ed.). The Makers of Modern Strategy: From Machiavelli to the Nuclear Age. Princeton: Princeton University Press. p. 806. ISBN 978-0-691-02764-7.
- ^ Pimlott, John, ed. (1984). British Military Operations 1945–1985. London: Bison. p. 99. ISBN 978-0-86124-147-7.
- ^ "Cameroon's Civil War Intensifies, Casualties Mount". Voice of America News. 23 May 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ "Dozens of Cameroon Youth Killed in South". Voice of America News. 27 May 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ "Video: Cameroon's Anglophone secessionists try abducted cop, send him to their Ambazonia prison". Today's News Africa. 7 June 2018. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ "Cameroon soldier killed in restive English-speaking region". News24. 11 June 2018. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ "Police Officer killed in Fundong". Journal du Cameroun. 18 June 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ Air Vice-Marshal Peter Dye. The Jebel Akhdar War: The Royal Air Force in Oman Archived 3 مارس 2016 at the Wayback Machine. (PDF). Air Power Review. Centre for Air Power Studies. ISSN 1463-6298 Volume 11, Number 3, Winter 2008
- ^ Cantu, Gaston Garcia (1996). The U.S. invasions in Mexico. Fondo de Cultura Económica. ISBN 9789681650834. Retrieved 1 July 2013.
- ^ "Kasese clashes death toll increases to 126, twenty-five new bodies discovered – The Ugandan". The Ugandan. 29 November 2016. Retrieved 30 May 2017.
- ^ "Uganda clashes; death toll from Kasese fighting rises to 126" (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 30 May 2017.
- ^ "ISS Today: Mozambique's first Islamist attacks shock the region". Daily Maverick. 11 October 2017. Archived from the original on 19 December 2017. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "Mais um ataque em Mocimboa da Praia". Voz da América Portugues (in البرتغالية). 4 December 2017. Archived from the original on 26 December 2017. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "50 Killed As Police Attack Islamic Terrorists In Mocimboa De Praia Mozam". Mozambique. Archived from the original on 2 January 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "Novo ataque de grupo armado faz cinco mortos no nordeste de Moçambique" (in البرتغالية). 15 January 2018. Archived from the original on 16 January 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "Mozambique: Three Islamist Attacks Reported Over Weekend". Agencia de Informacao de Mocambique (Maputo). 25 April 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "Mozambique 'jihadists behead' villagers". BBC News. 29 May 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "Al Shabaab moçambicano mata mais 12 civis em Cabo Delgado; Presidente Nyusi mudo". Verdade Online (in البرتغالية). 6 June 2018. Archived from the original on 10 June 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "At least 7 killed in machete attack in Mozambique, police say". Africa News. 5 June 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "Al menos 6 muertos en un nuevo ataque yihadista en el norte de Mozambique". La Vanguardia (in البرتغالية). 7 June 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "Mozambique: Four dead in new terrorist attack in Changa, Nangade district – AIM report". Club of Mozambique. 12 June 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "Breaking: Insurgents wreak death and destruction in Nathuko, Macomia – Mozambique". Club of Mozambique. 12 June 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- ^ "95 killed in Guinea clashes". The Times of India. 24 July 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2013.
- ^ "Lahad Datu: 52 gunmen killed in gunfights so far, says IGP". The Star. 7 March 2013. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- ^ Golingai, Philip (9 March 2013). "Lahad Datu: Security forces shoot dead one gunman at Tanjung Batu village". The Star. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- ^ Beal, Bob. "North-West Rebellion". The Canadian Encyclopedia (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2017-02-05.
- ^ "Nigeria soldiers kill 15 Niger Delta militants". TODAY.ng. Archived from the original on 2016-05-30. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
Works cited
- Carlton, Charles (2002). Going to the Wars: The Experience of the British Civil Wars 1638-1651. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-203-42558-9.
- Čečuk, Božidar (March 1960). "Tragom poginulih seljaka u Seljačkoj buni 1573. godine" (PDF). Papers and Proceedings of the Department of Historical Research of the Institute of Historical and Social Research of Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts (in الكرواتية). Zagreb, Croatia: Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts. 3: 499–503. Retrieved 5 September 2017.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Further reading
- Steven Pinker (2011). The Better Angels of Our Nature: Why Violence Has Declined. Penguin Books. ISBN 1101544643. pp. 832. (see also: 2016 update)
- Levy, Jack S. (1983). War in the Modern Great Power System: 1495-1975. University Press of Kentucky, USA. ISBN 081316365X.
External links
- An Interactive map of all the battles fought around the world in the last 4,000 years
- Information on 1,500 conflicts since 1800
- Max Roser: 'War and Peace'. (2016). Published online at OurWorldInData.org.
- CS1 الصينية-language sources (zh)
- CS1 الكرواتية-language sources (hr)
- CS1 الفرنسية-language sources (fr)
- CS1 الإسبانية-language sources (es)
- CS1 البرتغالية-language sources (pt)
- Articles with unsourced statements from January 2019
- مقالات ذات عبارات بحاجة لمصادر
- كل المقالات بدون مراجع موثوقة
- كل المقالات بدون مراجع موثوقة from May 2018
- Articles with unsourced statements from December 2016
- War and politics
- Politics-related lists
- History-related lists
- Lists of wars
- Lists of military conflicts
- Lists by death toll