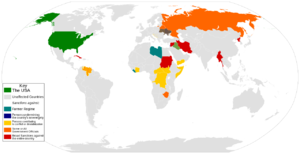
العقوبات الأمريكية
اعتباراً من 2014، بدأت حكومة الولايات المتحدة في فرض عقوبات اقتصادية وحظر على مختلف البلدان والأنشطة، ومن أشهرها تلك العقوبات المفروضة ضد البلدان التي أعلنت "كدول راعية للإرهاب" من قبل الحكومة الأمريكية.
وتتضمن العقوبات التي فرضتها الحكومة الأمريكية:
- السلع الغير متعلقة بالأسلحة[1]
- السيطرة على صادرات التكنولوجيا مزدوجة الاستخدام
- القيود على المساعدات الاقتصادية
- القيود المالية:
- مطالبة الولايات المتحدة بمعارضة قروض البنك الدولي والمؤسسات المالية الدولية الأخرى
- التلويح بالحصانة الدبلوماسية للسماح لعائلات ضحايا الإرهاب بالتقدم بدعاوى ضرر اجتماعي في المحاكم الأمريكية
- الائتمانات الضريبية للشركات والأفراد الممنوعة من التكسب من البلدان المدرجة في القائمة.
- إعفاء البضائع المعفاة من الرسوم مع وقف التنفيذ للواردات من تلك البلدان
- سلطة منع المواطن الأمريكي من الدخول في معاملات مالية مع الحكومات المدرجة في القائمة دون ترخيص من الحكومة الأمريكية
- منع وزارة الدفاع الأمريكية من إبرام مع الشركات المسيطر عليها من قبل البلدان المدرجة في القائمة بأكثر من 100.000 دولار أمريكي.[2]
الوكالات الفارضة للعقوبات
- مكتب الصناعة والأمن
- ادارة مراقبة تجارة الدفاع
- مكتب مراقبة الأصول الأجنبية
- حماية المستهلكين والحدود الأمريكية
- وزارة التجارة الأمريكية (تنظيم ادارة الصادرات)
- وزارة الدفاع الأمريكية
- وزارة الطاقة الأمريكية (التكنولوجيا النووية)
- وزارة أمن الوطن الأمريكية (المعابر الحدودية)
- وزارة العدل الأمريكية
- وزارة الخارجية الأمريكية
- وزارة الخزانة الأمريكية
القوانين المخولة لفرض العقوبات
القوانين التالية تخول الرئيس فرض عقوبات أو حظر:
- قانون التجارة مع العدو 1917
- قانون المساعدة الخارجية 1961
- قانون السلطات الاقتصادية للطوارئ الدولية 1977
- قانون ادارة الصادرات 1979
وتمنع القوانين التالية التجارة مع بعض البلدان:
- تنظيمات مراقبة الأصول الكوبية 1963
- قانون الديمقراطية الكوبية 1992
- قانون هلمس-برتون 1996 (كوبا)
- قانون العقوبات الإيرانية والليبية 1996
- قانون إصلاح العقوبات التجارية وتعزيز الصادرات 2000 (كوبا)
- قانون حرية ودعم إيران 2006
- قانون العقوبات والمساءلة وإبراء الذمة الشامل لإيران 2010
الأطراف المستهدفة
اعتباراً من أغسطس 2019، طرحت الولايات المتحدة عقوبات ضد:[3]
البلدان
| البلد | السنة | المقال | ملخص |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1979[أ] | United States sanctions against Iran | Near total economic embargo on all economic activities, including a ban on all Iranian imports, sanctions on Iranian financial institutions as well as restriction on the sale of aircraft and repair parts as well as arms embargoes. This policy began in 1979 as a response to the Iranian Revolution, but has been rapidly expanded over recent years due to the Iranian Nuclear Program and Iran's poor human rights record. Iran and the US have no diplomatic relations. Listed as state sponsor of terrorism.
On May 30, 2013, OFAC issued Iranian General License D, authorizing the exportation or reexportation, directly or indirectly, from the United States or by U.S. persons, wherever located, to persons in Iran of "certain services, software, and hardware incident to personal communications". General License D enumerates certain categories allowed to be exported to Iran. For scope and further details, see General License D and the Annex to General License D.[4] Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| 1950 | North Korea–United States relations | Severe sanctions justified by extreme human rights abuses by North Korea and the North Korean nuclear program. North Korea and the US currently have no diplomatic relations.
Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| 1986 | Syria–United States relations | Reasons cited for sanctions include Syria's poor human rights record, the present Civil War, and being listed as a state sponsor of terrorism. Syria and the US currently have no diplomatic relations as of 2012.
Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| 1993 | Sudan-United States relations | Reasons cited for sanctions include Sudan's poor human rights record, the present War in Darfur, and being listed as a state sponsor of terrorism. Most US sanctions on Sudan were lifted in October 2017 by Executive Order of the President of the United States, Donald Trump.[6] | |
| 1958 | United States embargo against Cuba | Reasons cited for the embargo include Cuba's poor human rights record. Since 1992, the UN General Assembly has regularly passed annual resolutions criticizing the ongoing impact of the embargo imposed by the United States. | |
| 2019[ب] | International sanctions during the Venezuelan crisis[7] | Reasons cited for sanctions includes Venezuela's poor human rights record, links with illegal drug trade, high levels of state corruption and electoral rigging.
Since 2019, Venezuela and the United States have no diplomatic relations but maintain relations through interim president Juan Guaidó.[8] Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] |
الأشخاص
| البلد | وصف |
|---|---|
| Certain persons the US government believes to be undermining democratic processes or institutions in Belarus (including President Alexander Lukashenko and other officials)
Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report. However Belarus is subject to some certain exemptions.[5] | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report. However Belize is subject to some certain exemptions, including International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS).[5] | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Persons who the US government claims threaten peace, security, or stability in Burundi
Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Persons the US government believes contribute to the conflict in the Central African Republic | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Certain persons the US government believes are contributing to the conflict in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report. However Eritrea is subject to some certain exemptions.[5] | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Specific individuals and entities associated with the former Ba'athist regime of Saddam Hussein, as well as parties the US government believes have committed, or pose a significant risk of committing acts of violence that threaten the peace or stability of Iraq or the Government of Iraq or undermine efforts to promote economic reconstruction and political reform in Iraq or make it more difficult for humanitarian workers to operate in Iraq. | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Persons the US government believes undermine the sovereignty of Lebanon or its democratic processes and institutions | |
| Persons associated with Muammar Gaddafi's regime | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Officials associated with the Rohingya crisis[9]
Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Persons associated with contributing to the 2018 Nicaraguan protests[10] | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report. However Papua New Guinea is subject to some certain exemptions.[5] | |
| Persons believed to be responsible for the detention, abuse, and death of Sergei Magnitsky and other reported violations of human rights in Russia (see Magnitsky Act of 2012). Since 2014, International sanctions during the Ukrainian crisis, since 2017 Countering America's Adversaries Through Sanctions Act.
Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Certain persons the US government believes are contributing to the conflict in Somalia | |
| Persons the US government alleges have contributed to the conflict in South Sudan or committed human rights abuses.
Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report which imposes ban on participating in International Military Education and Training (IMET), Foreign Military Financing (FMF), and Foreign Military Sales (FMS)[5] | |
| Country listed as Tier 3 on Trafficking in Persons Report. However Turkmenistan is subject to some certain exemptions.[5] | |
( |
Persons the US government believes undermine the peace, security, stability, territorial integrity and the democratic processes and institutions of Ukraine. Also persons administering areas of Ukraine without central government consent, also a number of Russian senior officials who are close to Vladimir Putin. |
| Persons who the US government believes are contributing to the ongoing crisis in Venezuela | |
| Persons who the US government claims threaten peace, security, or stability in Yemen | |
| Persons the US government believes undermine democratic processes or institutions in Zimbabwe, including a number of Government Officials |
There are also list-based sanctions related to countering terrorism, rough diamond trade controls (see Kimberley Process), counter narcotics, nuclear proliferation and transnational criminal organizations.[3]
Some countries listed are members of the World Trade Organization, but WTO rules allow trade restrictions for non-economic purposes.
Combined, the Treasury Department, the Commerce Department and the State Department list embargoes against 30 countries or territories: Afghanistan, Belarus, Burundi, Central African Republic, China (PR), Côte d'Ivoire, Crimea Region, Cuba, Cyprus, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eritrea, Fiji, Haiti, Iran, Iraq, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Lebanon, Liberia, Libya, Myanmar, North Korea, Palestinian Territories, Russia, Rwanda, Somalia, South Sudan, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Syria, Venezuela, Vietnam, Yemen, Zimbabwe.[11][3][12]
هيئات
في 2 أكتوبر 2019 بدأت الولايات المتحدة فرض عقوبات جمركية على منتجات قيمتها 7.5 مليار دولار من الاتحاد الأوروپي لدعمه إيرباص المنافسة لشركة صناعة الطائرات بوينگ الأمريكية المتعثرة.[13]
انظر أيضاً
- دولة راعية للإرهاب
- دولة مارقة
- عقوبات اقتصادية
- تعريفة الصلب الأمريكية 2002
- العلاقات التجارية الطبيعية الدائمة
- قانون مراقبة صادرات الأسلحة
الهوامش
- ^ Temporarily lifted in 1981 during Iran–Iraq War, re-introduced in 1987
- ^ In August 2019, President Donald Trump announced further sanctions on Venezuela, ordering a freeze on all Venezuelan government assets in the United States and barred transactions with US citizens or companies.
المصادر
- ^ Haidar, Jamal Ibrahim (2016-08-16). "Sanctions and Exports Deflection: Evidence from Iran" (PDF). Paris School of Economics. Retrieved 2017-03-11.
- ^ "Chapter 3: State Sponsors of Terrorism". Country Reports on Terrorism 2009. United States Department of State. 2010-08-05. Retrieved 2017-03-11.
- ^ أ ب ت "Sanctions Programs and Country Information". United States Department of the Treasury. 2017-03-09. Retrieved 2017-03-11.
- ^ "Iran Sanctions: Statement Relating to the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action "Implementation Day" of January 16, 2016". United States Department of the Treasury. 2017-03-09. Retrieved 2017-03-11.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ ر ز س ش ص ض ط ظ ع غ ف ق ك https://www.breakingbelizenews.com/2018/11/30/us-cuts-aid-to-belize-over-human-trafficking-tier-3-ranking/
- ^ "United States Eases Sudan Sanctions - White & Case LLP International Law Firm, Global Law Practice". www.whitecase.com. Retrieved 5 October 2018.
- ^ "Venezuela: Overview of U.S. sanctions" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Federation of American Scientists. 8 March 2019. Retrieved 3 April 2019.
- ^ Meredith, Sam (21 May 2018). "US likely to slap tough oil sanctions on Venezuela — and that's a 'game changer' for Maduro". Retrieved 5 October 2018.
- ^ News, A. B. C. (17 August 2018). "US sanctions Myanmar military over Rohingya ethnic cleansing". ABC News. Retrieved 5 October 2018.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ CNN, Laura Koran,. "US slaps new sanctions on Nicaragua over violence, corruption". Retrieved 5 October 2018.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Country Policies and Embargoes". United States Department of State. 2017-01-24. Retrieved 2017-03-11.
- ^ "Export Controlled or Embargoed Countries, Entities and Persons". Stanford University. 2016-12-15. Retrieved 2017-03-11.
- ^ "US to impose tariffs on $7.5 billion in EU goods over illegal Airbus subsidies". فرانس 24. 2019-10-03. Retrieved 2019-10-03.
وصلات خارجية
- Sanctions Programs and Country Information (United States Department of the Treasury)
- Commerce Control List (Bureau of Industry and Security)
- Countries Sanctioned By The U.S. - And Why (Investopedia, 2010-04-08)
- United States to Lift Sudan Sanctions (NY Times, 2017-01-13)