أوكسالات الصوديوم
| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك المفضل
Disodium oxalate | |
| أسماء أخرى
Oxalic acid, disodium salt
Sodium ethanedioate | |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.501 |
| رقم EC |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| رقم RTECS |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| الخصائص | |
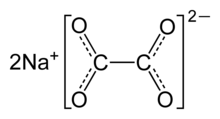
| الصيغة الجزيئية | Na2C2O4 |
| كتلة مولية | 133.999 g mol−1 |
| الكثافة | 2.34 g cm−3 |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | 2.69 g/100 mL (0 °C) 3.7 g/100 mL (20 °C) 6.25 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
| قابلية الذوبان | soluble in formic acid insoluble in alcohol, ether |
| البنية | |
| البنية البلورية | monoclinic |
| الكيمياء الحرارية | |
| الإنتالپية المعيارية للتشكل ΔfH |
-1318 kJ/mol |
| المخاطر | |
| صفحة بيانات السلامة | Oxford MSDS[مصدر غير موثوق به؟] |
| ن.م.ع. مخطط تصويري | 
|
| ن.م.ع. كلمة الاشارة | warning |
| H302, H312 | |
| P280, P301+P312, P302+P352 | |
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |
| الجرعة أو التركيز القاتل (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (الجرعة الوسطى)
|
11160 mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] |
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
أوكسالات ثنائية الصوديوم أو اختصاراً أكسالات الصوديوم مركب كيميائي له الصيغة Na2C2O4، وهو ملح الصوديوم لحمض الأكساليك.
يمكن لأوكسالات الصوديوم أن تعمل كمختزل، وقد تـُستخدم كمعيار أولي لمعايرة محاليل پرمنگنات الپوتاسيوم (KMnO4).
الشكل المعدني لأوكسالات الصوديوم هو ناتروكسالات. من النادر جداً العثور عليه ويقتصر على أحوال صودية فائقة من الپگماتيتات فائقة القلوية.[3]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الخواص
- لمركب أكسالات الصوديوم انحلالية ضعيفة في الماء، وهو غير منحل في الكحول وفي الإيثر الإيثيلي.
التحضير
أوكسالات الصوديوم يمكن تحضيرها عبر تحييد حمض الأوكساليك باستخدام هيدروكسيد الصوديوم (NaOH) في نسبة مولية قاعدية 1:2 . البخر يُنتج الأوكسالات اللامائية[4] التي يمكن تجفيفها تماماً بالتسخين إلى ما بين 200 و 250 °س.[5]
ويمكن تحقيق نصف التحييد باستخدام NaOH في نسبة 1:1 التي تنتج NaHC2O4، أوكسالات الصوديوم أحادية القاعدة أو هيدروجين أوكسالات الصوديوم.
وبدلاً من ذلك، يمكن انتاج أوكسالات الصوديوم بتحلل فورمات الصوديوم بتسخينها لدرجة حرارة تفوق 360 °س.[بحاجة لمصدر]
كما ينتج بكميات كبيرة كناتج ثانوي في طريقة باير لإنتاج أكسيد الألومنيوم من معدن البوكسيت.
التفاعلات
تبدأ أوكسالات الصوديوم في التحلل فوق درجة حرارة 290 °س إلى كربونات الصوديوم و أول أكسيد الكربون:[5]
- Na 2C 2O 4 → Na 2CO 3 + CO
وحين يُسخّن لدرجة حرارة بين 200 و 525°س مع أكسيد الڤناديوم الخماسي بنسبة مولية 1:2، فإن التفاعل المذكور أعلاه يـُخمَد، منتجاً بدلاً من ذلك صوديوم ڤناديوم أكسيبرونز مع إطلاق ثاني أكسيد الكربون[6]
- x Na 2C 2O 4 + 2 V 2O 5 → 2 Na xV 2O 5 + 2x CO 2
مع زيادة x حتى 1 مع ارتفاع درجة الحرارة.
Sodium oxalate is used to standardize potassium permanganate solutions. It is desirable that the temperature of the titration mixture be greater than 60 °C to ensure that all the permanganate added reacts quickly. The kinetics of the reaction are complex, and the manganese(II) ions formed catalyze the further reaction between permanganate and oxalic acid (formed in situ by the addition of excess sulfuric acid). The final equation is as follows:[7]
- 5 Na2C2O4 + 2 KMnO4 + 8 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 5 Na2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 10 CO2 + 8 H2O
النشاط الحيوي
Like several other oxalates, sodium oxalate is toxic to humans. It can cause burning pain in the mouth, throat and stomach, bloody vomiting, headache, muscle cramps, cramps and convulsions, drop in blood pressure, heart failure, shock, coma, and possible death. Mean lethal dose by ingestion of oxalates is 10-15 grams/kilogram of body weight (per MSDS).
Sodium oxalate, like citrates, can also be used to remove calcium ions (Ca2+) from blood plasma. It also prevents blood from clotting. Note that by removing calcium ions from the blood, sodium oxalate can impair brain function, and deposit calcium oxalate in the kidneys.
الاستخدامات
- يستخدم مركب أكسالات الصوديوم بشكل أساسي في تقييس محاليل فوق منگنات البوتاسيوم.
- يستخدم من أجل تحديد أيونات الكالسيوم في بلازما الدم، كما أنه من موانع التخثر.
- يدخل في خلطات الألعاب النارية حيث يعطي اللون الأصفر البرتقالي.
- له تطبيقات أخرى في صناعة النسيج وكمكون في بعض أنواع الاسمنت الخاصة.
المصادر
- موسوعة رومب الكيميائية Römpp Lexikon Chemie, Georg Thieme Verlag
- [1]
- ^ أ ب "ChemIDplus - 62-76-0 - ZNCPFRVNHGOPAG-UHFFFAOYSA-L - Disodium oxalate - Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information". chem.nlm.nih.gov (in الإنجليزية). NIH. Retrieved 7 January 2019.
- ^ GHS: GESTIS 570199
- ^ "Natroxolate" (PDF). RRUFF. Mineral Data Publishing. Retrieved 7 January 2019.
- ^ H. W. Foote and John E. Vance (1933), "The system; sodium iodate, sodium oxalate, water". American Journal of Science, series 5, volume 26, issue 151, pages 16-18. DOI:10.2475/ajs.s5-26.151.16
- ^ أ ب Yoshimori T1, Asano Y, Toriumi Y, Shiota T. (1978) "Investigation on the drying and decomposition of sodium oxalate". Talanta, volume 25, issue 10, pages 603-605. DOI:10.1016/0039-9140(78)80158-1
- ^ D. Ballivet-Tkatchenko, J. Galy, -M. Savariault (1994): "Thermal decomposition of sodium oxalate in the presence of V2O5: Mechanistic approach of sodium oxibronzes formation". Thermochimica Acta, volume 232, issue 2, pages 215-223. DOI:10.1016/0040-6031(94)80061-8
- ^ Mcbride, R. S. (1912). "The standardization of potassium permanganate solution by sodium oxalate". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 34 (4): 393–416. doi:10.1021/ja02205a009.
- Articles with changed EBI identifier
- Articles with changed ChemSpider identifier
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles with changed InChI identifier
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Chembox
- All articles lacking reliable references
- Articles lacking reliable references from May 2020
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles with unsourced statements from April 2017
- أوكسالات
- مركبات الصوديوم
