إقليم الهندوملايو
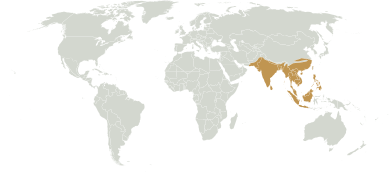
إقليم الهندوملايو Indomalayan realm هو واحد من ثمانية biogeographic realms.[1] It extends across most of South and Southeast Asia and into the southern parts of East Asia.
Also called the Oriental realm by biogeographers, Indomalaya spreads all over the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia to lowland southern China, and through Indonesia as far as Sumatra, Java, Bali, and Borneo, east of which lies the Wallace line, the realm boundary named after Alfred Russel Wallace which separates Indomalaya from Australasia. Indomalaya also includes the Philippines, lowland Taiwan، وجزر ريوكيو باليابان.
Most of Indomalaya was originally covered by forest, and includes tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, with tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests predominant in much of India and parts of Southeast Asia. The tropical forests of Indomalaya are highly variable and diverse, with economically important trees, especially in the families Dipterocarpaceae and Fabaceae.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
المناطق البيئية الرئيسية
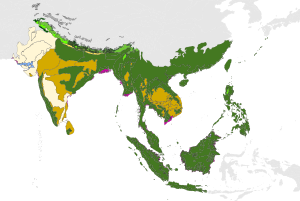
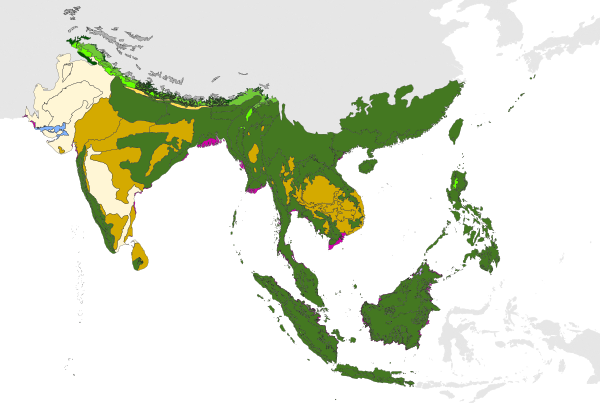
The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) divides Indomalayan realm into three bio-regions, which it defines as "geographic clusters of eco-regions that may span several habitat types, but have strong biogeographic affinities, particularly at taxonomic levels higher than the species level (genus, family)".
شبه القارة الهندية
The Indian subcontinent bioregion covers most of India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and Sri Lanka and eastern parts of Pakistan. The Hindu Kush, Karakoram, Himalaya, and Patkai ranges bound the bioregion on the northwest, north, and northeast; these ranges were formed by the collision of the northward-drifting Indian subcontinent with Asia beginning 45 million years ago. The Hindu Kush, Karakoram, and Himalaya are a major biogeographic boundary between the subtropical and tropical flora and fauna of the Indian subcontinent and the temperate-climate Palearctic realm.
الهند الصينية
The Indochina bioregion includes most of mainland Southeast Asia, including Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and Cambodia, as well as the subtropical forests of southern China.
رصيف سوندا والفلپين
Malesia is a botanical province which straddles the boundary between Indomalaya and Australasia. It includes the Malay Peninsula and the western Indonesian islands (known as Sundaland), the Philippines, the eastern Indonesian islands, and New Guinea. While the Malesia has much in common botanically, the portions east and west of the Wallace Line differ greatly in land animal species; Sundaland shares its fauna with mainland Asia, while terrestrial fauna on the islands east of the Wallace line are derived at least in part from species of Australian origin, such as marsupial mammals and ratite birds.
الحيومات
يضم الإقليم الحيومات التالية:[2]
- Tropical and subtropical forest: It constitutes the predominant vegetation throughout the region.
- غابات جافة
- Tropical coniferous forest
- Temperate deciduous forest
- Temperate coniferous forest
- Meadow
- Flooded meadow
- Mountain meadows and scrublands
- الصحراء
- Mangrove swamp
التاريخ
The flora of Indomalaya blends elements from the ancient supercontinents of Laurasia and Gondwana. Gondwanian elements were first introduced by India, which detached from Gondwana approximately 90 MYA, carrying its Gondwana-derived flora and fauna northward, which included cichlid fish and the plant families Crypteroniaceae and possibly Dipterocarpaceae. India collided with Asia 30-45 MYA, and exchanged species. Later, as Australia-New Guinea drifted north, the collision of the Australian and Asian plates pushed up the islands of Wallacea, which were separated from one another by narrow straits, allowing a botanic exchange between Indomalaya and Australasia. Asian rainforest flora, including the dipterocarps, island-hopped across Wallacea to New Guinea, and several Gondwanian plant families, including podocarps and araucarias, moved westward from Australia-New Guinea into western Malesia and Southeast Asia.
النبيت
The subfamily Dipterocarpoideae comprises characteristic tree species in Indomalaya's moist and seasonally dry forests, with the greatest species diversity in the moist forests of Borneo.[3] Teak (Tectona) is characteristic of the seasonally dry forests of the Indomalaya, from India through Indochina, Malaysia, and the Philippines. Tropical pitcher plants (Nepenthes) are also characteristic of Indomalaya, and the greatest diversity of species is in Sumatra, Borneo, and the Philippines.
The tropical forests of Indomalaya and Australasia share many lineages of plants, which have managed over millions of years to disperse across the straits and islands between Sundaland and New Guinea. The two floras evolved in long isolation, and the fossil record suggests that Asian species dispersed to Australasia starting 33 million years ago as Australasia moved northwards, and dispersal increased 12 million years ago as the two continents approached their present positions. The exchange was asymmetric, with more Indomalayan species spreading to Australasia than Australasian species to Indomalaya.[4]
الوحيش
Two orders of mammals, the colugos (Dermoptera) and treeshrews (Scandentia), are endemic to the realm, as are families Craseonycteridae (Kitti's hog-nosed bat), Diatomyidae, Platacanthomyidae, Tarsiidae (tarsiers) and Hylobatidae (gibbons). Large mammals characteristic of Indomalaya include the leopard, tigers, water buffalos, Asian elephant, Indian rhinoceros, Javan rhinoceros, Malayan tapir, orangutans, and gibbons.
Indomalaya has three endemic bird families, the Irenidae (fairy bluebirds), Megalaimidae and Rhabdornithidae (Philippine creepers). Also characteristic are pheasants, pittas, Old World babblers, and flowerpeckers.
Indomalaya has 1000 species of amphibians in 81 genera, about 17 of global species. 800 Indomalayan species, or 80%, are endemic. Indomalaya has three endemic families of amphibians, Nasikabatrachidae, Ichthyophiidae, and Uraeotyphlidae. 329, or 33%, of Indomalayan amphibians are considered threatened or extinct, with habitat loss as the principal cause.[5]
المزيد من المعلومات موجود في وحيش إقليم الهندوملايو.
المناطق البيئية
قالب:Indomalayan tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregions قالب:Indomalayan tropical and subtropical coniferous forest ecoregions قالب:Indomalayan temperate broadleaf and mixed forest ecoregions قالب:Indomalayan temperate coniferous forest ecoregions قالب:Indomalayan tropical and subtropical grassland, savanna, and shrubland ecoregions قالب:Indomalayan flooded grassland and savanna ecoregions قالب:Indomalayan montane grassland and shrubland ecoregions قالب:Indomalayan desert and xeric shrubland ecoregions قالب:Indomalayan mangrove ecoregions
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
انظر أيضاً
- Ecoregions of India
- Ecoregions of the Philippines
- Mainland Southeast Asia (the Indochinese Peninsula)
- Malesia
- Sundaland
ببليوجرافيا
- Wikramanayake, E., E. Dinerstein, C. J. Loucks, D. M. Olson, J. Morrison, J. L. Lamoreux, M. McKnight, and P. Hedao. 2002. Terrestrial ecoregions of the Indo-Pacific: a conservation assessment. Island Press, Washington, DC, USA, [2].
المراجع
- ^ Indomalayan realm Archived 2022-10-06 at the Wayback Machine biologyonline.com. Retrieved 29 August 2021
- ^ List of Ecoregions, TERRESTRIAL ECOREGIONS Archive copy at the Internet Archive WWF
- ^ Appanah, Simmathiri and Jennifer M. Turnbull, eds. (1998). A Review of Dipterocarps: Taxonomy, ecology and silviculture. Center for International Forestry Research, 1998.
- ^ Ebach, Malte C. (2017). Handbook of Australasian Biogeography. CRC Press, Jan 6, 2017.
- ^ Bain, R.H., Biju, S.D., Brown, R.M., Das, I., Diesmos, A.C., Dutta, S.K., Gower, D.J., Inger, R.F., Iskandar, D.T., Kaneko, Y., Neng, M.W., Lau, Meegaskumbura, M., Ohler, A., Papenfuss, T., Pethiyagoda, R., Stuart, B.L., & Wilkinson, M. (2008). Amphibians of the Indomalayan Realm. [1]
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Indomalayan realm
- Biogeographic realms
- Biogeography
- Ecoregions of Asia
- Environment of Asia
- Flora of tropical Asia
- Natural history of Asia
- Phytogeography