نايمان
 موقع خانية النايمان في بداية الامبراطورية المنغولية | |
| المناطق ذات التجمعات المعتبرة | |
|---|---|
| [كمية][بحاجة لمصدر] | |
| [كمية][بحاجة لمصدر] | |
| 940.000[3] | |
| اللغات | |
| اللهجة الفرعية للنايمان من اللغات المنغولية والتوركية[5][6][7] القزخية، الروسية | |
| الدين | |
| البوذية التبتية (منغوليا) الإسلام (قزخستان) الشامانية | |
نايمان (Naiman ؛ بالمنغولية: Найман/Naiman، "ثمانية"؛ بالقزخية: Найман; بالأوزبكية: Nayman) هي قبيلة تنحدر من منغوليا (الخاقانية التوركية الشرقية)، أحد القبائل في جوز الوسطى في الأمة القزخية.
التاريخ
في التاريخ السري للمنغول، فخذ قبيلة نايمان المدعو "گچگد Güchügüd" مذكور. وحسب رأي عالم التوركيات الروسي نيقولاي أريستوڤ، فإن الحد الغربي لخانية النايمان بلغ نهر إرتش وحدها الشرقي بلغ نهر تامير المنغولي. جبال ألطاي وجنوب جمهورية ألطاي كانوا جزءاً من خانية نايمان.[8] They had diplomatic relations with the Kara-Khitans, and were subservient to them until 1175.[9] Some scholars classified them as a Turkic people من Sekiz Oghuz (تعني "الغز الثمانية" في بالتوركية).[10][11][12][13] However, the term "Naiman" has Mongolian origin meaning "eight", but their titles are Turkic, and they are thought by some to be possibly Mongolized Turks.[14] They have been described as Turkic-speaking,[14] as well as Mongolian-speaking.[15] Like the Khitans and the Uyghurs, many of them were Nestorian Christians or Buddhists.
The Naimans were located to the west of the Mongols, and there were more Naimans than Mongols in the late 12th century. In 1199, Temüjin (Genghis Khan) together with an ally Ong khan launched a campaign against the Naimans.[16] They defeat Buyirugh, a Naiman khan who ruled the mountain lineage. In 1203, the last Tayang khan, the ruler of Naimans of the steppe, was killed after a battle with Genghis Khan. His son Kuchlug with his remaining Naiman troops then fled to the Kara-Khitan Khanate. Kuchlug was well received there and the Khitan Khan gave him his daughter in marriage. Kuchlug soon began plotting against his new father-in-law, and after he usurped the throne, he began to persecute Muslims in the Hami Oases. But his action was opposed by local people and he was later defeated by the Mongols under Jebe.
Although the Naiman Khanlig was crushed by the Mongols, they were seen in every part of the Mongol Empire. Ogedei's great khatun ("queen") Töregene might have been from this tribe. Hulegu had a Naiman general, Ketbuqa, who died in the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260.
بين المنغول
The modern Naiman tribe is a Mongol[17] ethnic group in Naiman Banner, Inner Mongolia of China. The clan Naiman changed the clan name and mixed with other tribes in منغوليا.
الهزارة النايمان
There is a small population of Naimans in Afghanistan. They belong to the Hazara tribes and reside in the Shekh Ali District.
بين الشعوب التوركية
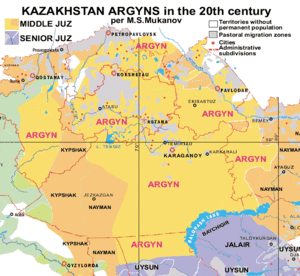
Modern Kazakh historians claim that more than 2 million of the Kazakh population are Naimans (see Modern Kazakh tribes or Middle Juz). They originate from eastern Kazakhstan. Some Naimans dissimilated with the Kyrgyz and Uzbek ethnicities and are still found among them. Now, the Naimans are one of the big tribes of modern Kazakh peoples, they belong to Middle Juz of Kazakhs, live mainly in the eastern, central and southern parts of Kazakhstan, with a population of approximately 2 million among Kazakhs in Kazakhstan.

They also exist with considerable population among the Kazakhs in China, Uzbekistan and Russia, the Naiman tribe populations in the Kazakhs in China is one million or more, mostly living in the western part of Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region of China, in the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture. Naimans are also one of the major tribe among Kazakhs in the Uzbekistan, they also exist among Kazakhs in Kyrgyzstan and Russia.See Naimans introduction in Kazakh language, "Kazakh shezhire". The most recently Y-DNA tests which investigated by KZ DNA Project in Kazakhstan shows that the Y-DNA haplogroup of Naiman tribe of Kazakhs mostly carries O-M122 and some C, G, N haplogroups see KZ DNA Project.
الدين
They remained so after the Mongol conquest and were among the second wave of Christians to enter China with Kublai Khan.[19] The Naimans who settled in the western khanates of the Mongol Empire all eventually converted to Islam. There was a tradition that the Naimans and their Christian relatives, the Keraites, descended from the Biblical Magi.[20] The commander of the Mongol army that invaded Syria in 1259, Kitbuqa, was a Naiman: he is recorded to have "loved and honoured the Christians, because he was of the lineage of the Three Kings of Orient who came to Bethlehem to adore the nativity of Our Lord".[21] However, Kitbuqa was slain and his army decisively defeated at the Battle of Ain Jalut, ensuring continued Muslim hegemony over the Levant. Southern Mongolian Naimans converted to Buddhism in the sixteenth century.
انظر أيضاً
المراجع
- ^ Үндэсний Статистикийн Хороо. Найман.
- ^ أ ب Очир А. Монгольские этнонимы: вопросы происхождения и этнического состава монгольских народов / д.и.н. Э. П. Бакаева, д.и.н. К. В. Орлова. — Элиста: КИГИ РАН, 2016. — 286 с. — С. 116—119. — ISBN 978-5-903833-93-1.
- ^ Казахов посчитали по родам: самые многочисленные — аргыны и дулаты https://365info.kz/2016/08/kazahov-poschitali-po-rodam-samye-mnogochislennye-argyny-i-dulaty
- ^ D. Kassymova, Z. Kundakbayeva, U. Markus. Historical Dictionary of Kazakhstan. — Scarecrow Press, 2012. — 362 p. — P. 191. — ISBN 9780810879836.
- ^ Man, John (2013). Genghis Khan: Life, Death, and Resurrection. St. Martin's Publishing Group. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-1-4668-6156-5.
- ^ Rossabi, Morris (2012). The Mongols: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-19-993935-0.
- ^ Mote, Frederick W. (2003). Imperial China 900-1800. Harvard University Press. p. 407. ISBN 978-0-674-01212-7.
- ^ History of Mongolia, Volume II, 2003
- ^ Michael Biran. The Empire of the Kara Khitai in Eurasian History,2005, page 57.
- ^ Ratchnevsky, Paul. "Genghis Khan: His Life and Legacy". 2000, pp.1–4.
- ^ Roemer, Hans Robert; Scharlipp, Wolfgang-Ekkehard (2000). History of the Turkic Peoples in the Pre-Islamic Period. Klaus Schwarz Verlag. ISBN 3879972834.
- ^ Czaplicka, Marie Antoinette (2001). The Turks of Central Asia in History and at the Present Day. Adamant Media Corporation. ISBN 978-1402163326.
- ^ Runciman, Steven (1987). A History of the Crusades. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-34770-9.
- ^ أ ب Hidden Treasures and Intercultural Encounters. 2. Auflage: Studies on East Syriac Christianity in China and Central Asia. Lit Verlag. 29 May 2009. ISBN 978-3643500458.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ Barbara A. West (ed.). Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Asia and Oceania. Chelsea House Publishers. p. 577. ISBN 9781438119137.
- ^ The Cambridge History of China: Volume 6, Alien Regimes and Border States, 907–1368: Alien Regimes and Border States, 710 -1368 v. 6. Cambridge University Press. 26 January 1995. pp. 338–339. ISBN 978-0521243315.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ The Empire of the Steppes: A History of Central Asia, by René Grousset, p190
- ^ Муканов М. С., Этническая территория казахов в 18 – нач. 20 вв ("Ethnic territory of Kazakhs from the 18th to the beginning of the 20th century"), Almaty, 1991.
- ^ Cary-Elwes, Columba. China and the Cross. (New York: P. J. Kennedy and Sons, 1956) p. 37
- ^ In regno Tarsae sunt tres prouinciae, quarum dominatores se reges faciunt appellari. Homines illius patriae nominant Iogour. Semper idola coluerunt, et adhuc colunt omnes, praeter decem cognationes illorum regum, qui per demonstrationem stellae uenerunt adorare natiuitatem in Bethlehem Judae. Et adhuc multi magni et nobiles inueniunt inter Tartaros de cognatione illa, qui tenent firmiter fidem Christi. (In the kingdom of Tarsis there are three provinces, whose rulers have called themselves kings. the men of that country are called Uighours. They always worshipped idols, and they all still worship them, except ten families of those Kings who through the appearance of the Star came to adore the Nativity in Bethlehem of Judah. And there are still many of the great and noble of that family found among the Tartars who hold firmly to the faith of Christ.) De Tartaris Liber,, 1307 AD, also called La flor des estoires de la terre d'Orient, by Hayton of Corycus in Novus orbis regionum ac insularum veteribus incognitarum, edited by Simon Grynaeus and Johannes Huttichius, Basel, 1532, caput ii, De Regno Tarsae, p.420. English translation.
- ^ Hayton of Corycus, La flor des estoires de la terre d'Orient (1307), quoted in Ugo Monneret de Villard, Le Leggende orientali sui Magi evangelici, Citta del Vaticano, Biblioteca apostolica vaticana, 1952, p.162. Also found in De Tartaris Liber, caput XXX, De Cobila Can quinto Imperatore Tartarorum , on page 445: "Nam ipse [Guiboga] fuerat de progenie trium regum, qui uenerunt natiuitatem domini adorare" ("For he was a descendant of the Three Kings who came to the Nativity to adore the Lord").
وصلات خارجية
- CS1 errors: unsupported parameter
- كل المقالات ذات العبارات غير المسندة
- مقالات ذات عبارات غير مسندة from May 2019
- Articles with unsourced statements from May 2019
- Articles using infobox ethnic group with image parameters
- شعوب منغولية
- تاريخ منغوليا
- تاريخ منغوليا الداخلية
- Mongolian tribes and clans
- Hazara tribes
- Nestorianism
- Kazakh tribes
- شعوب توركية