جزيرة نورفوك
جزيرة نورفوك | |
|---|---|
| إقليم جزيرة نورفوك Teratri a' Norf'k Ailen (Norfuk)[1] | |
| Motto: "Inasmuch"[2] | |
| Anthem: "ليحفظ الرب الملك"[بحاجة لمصدر] | |
| النشيد الإقليمي: "Come Ye Blessed" | |
 موقع جزيرة نورفوك | |
| الدولة السيادية | أستراليا |
| الانفصال عن مستعمرة تسمانيا | 1 نوفمبر 1856 |
| الانتقال إلى أستراليا | 1 يوليو 1914 |
| المجانس | Mary Howard, Duchess of Norfolk |
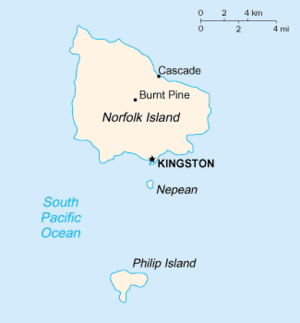
| العاصمة | كنگستون 29°03′22″S 167°57′40″E / 29.056°S 167.961°E |
| أكبر مدينة | برنت پاين |
| اللغات الرسمية | |
| الجماعات العرقية (2016) | |
| صفة المواطن | سكان جزيرة نورفوك[5] |
| الحكومة | إقليم تابع مدار مباشرة |
• العاهل | تشارلز الثالث |
| ديڤد هرلي | |
• الإداري | إريك هتشنسون |
| البرلمان | |
| يمثلها سناتورات ACT (منذ 2016) | |
| مضمن في قسم بين (منذ 2018) | |
| المساحة | |
• Total | 34.6 km2 (13.4 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | negligible |
| أعلى منسوب | 319 m (1٬047 ft) |
| التعداد | |
• 2021 census | 2.188[6] (غير مرتبة) |
• Density | 61.9/km2 (160.3/sq mi) (غير مرتبة) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2016 estimate |
• Total | 60,209,320 دولار أمريكي[7] |
| العملة | الدولار الأسترالي (AU$) (AUD) |
| Time zone | UTC+11:00 (NFT) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+12:00 (NFDT) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +672 |
| Postcode | NSW 2899 |
| ISO 3166 code | NF |
| Internet TLD | .nf |
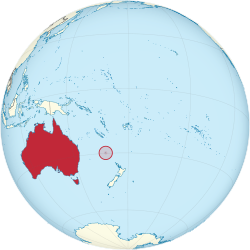
جزيرة نورفوك (إنگليزية: Norfolk Island، /ˈnɔːrfək/، local /ˈnɔːrfoʊk/;[8] Norfuk: Norf'k Ailen[9])، هو إقليم خارجي تابع لأستراليا يقع في المحيط الهادي بين نيوزيلندا وكاليدونيا الجديدة، على بعد 1412 كم من ساحل إيڤان جدز، و900 كم تقريباً من جزيرة لورد هوي. تشكل نورفوك وجزيرتي فيليپ ونپيان المجاورتين، ما يُعرف بإقليم جزيرة نورفوك.[10] في تعداد 2021، كان عزز سكان جزيرة نورفوك 2.188 نسمة يعيشون على مساحة 35 كم².[6] عاصمتها كنگستون.
أول المستوطنين المعروفين في نورفوك كانوا من شرق پولينيزيا but they had already departed when Great Britain settled it as part of its 1788 settlement of Australia. The island served as a convict penal settlement from 6 March 1788 until 5 May 1855, except for an 11-year hiatus between 15 February 1814 and 6 June 1825,[11][12] when it lay abandoned. On 8 June 1856, permanent civilian residence on the island began when descendants of the Bounty mutineers were relocated from Pitcairn Island. In 1914 the UK handed Norfolk Island over to Australia to administer as an external territory.[13]
Native to the island, the evergreen Norfolk Island pine is a symbol of the island and is pictured on its flag. The pine is a key export for Norfolk Island, being a popular ornamental tree in Australia (where two related species grow), and also worldwide.
التاريخ
الاستيطان المبكر
Norfolk Island was uninhabited when first settled by Europeans, but evidence of earlier habitation was obvious. Archaeological investigation suggests that in the 13th or 14th century the island was settled by East Polynesian seafarers, either from the Kermadec Islands north of New Zealand, or from the North Island of New Zealand. However, both Polynesian and Melanesian artefacts have been found, so it is possible that people from New Caledonia, relatively close to the north, also reached Norfolk Island. Human occupation must have ceased at least a few hundred years before Europeans arrived in the late 18th century. Ultimately, the relative isolation of the island, and its poor horticultural environment, were not favourable to long-term settlement.[14]
التسوية الجزائية الأولى (1788–1814)

التسوية الجزائية الثانية (1824 – 1856)

The first European known to have sighted and landed on the island was Captain James Cook, on 10 October 1774,[11][12] on his second voyage to the South Pacific on إتشإمإس Resolution. He named it after Mary Howard, Duchess of Norfolk.[15] Sir John Call argued the advantages of Norfolk Island in that it was uninhabited and that New Zealand flax grew there.
استيطانها من قبل سكان جزر پيتكيرن (1856 – الحاضر)
القرن 20
القرن 21
تراجع الحكم الذاتي 2016
الجغرافيا
المناخ
| أظهرClimate data for مطار جزيرة نورفوك (درجات الحرارة القصوى والدنيا 1991-2010)، ارتفاع 12 متر |
|---|
البيئة
الحياة النباتية

الحياة الحيوانية
الديموغرافيا
الديانات
اللغات
التعليم
الثقافة
الحكومة والسياسة
الوضع الدستوري
الهجرة والجنسية
الرعاية الصحية
الدفاع وإنفاذ القانون
المحاكم
التعداد
الخدمة البريدية
الاقتصا
الضرائب
الاتصالات
النقل
الرياضة
انظر أيضاً
الهوامش
المصادر
- ^ Buffett, Alice, An Encyclopædia of the Norfolk Island Language, 1999
- ^ "The Legislative Assembly of Norfolk Island". Archived from the original on 18 December 2014. Retrieved 18 October 2014.
- ^ "Norfolk Island Language (Norf'k) Act 2004". Archived from the original on 25 July 2008.
- ^ 2016 Census QuickStats Archived 2 أكتوبر 2017 at the Wayback Machine – Norfolk Island – Ancestry, top responses
- ^ "Norfolk Island". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 16 October 2012. Retrieved 27 October 2012.
- ^ أ ب قالب:Census 2021 AUS
- ^ KPMG (2019). Monitoring the Norfolk Island Economy (PDF). Norfolk Islands: Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Cities and Regional Development. p. 4.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2008). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.). Longman. ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0.
- ^ "NI Arrival Card" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 November 2011.
- ^ "Norfolk Island Act 1979". Federal Register of Legislation. Archived from the original on 16 July 2019. Retrieved 17 July 2019. Schedule 1.
- ^ أ ب "History and Culture on Norfolk Island". Archived from the original on 12 July 2012.
- ^ أ ب "Norfolk Island: A Short History". Archived from the original on 7 March 2016.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةRoberts-Wray - ^ Anderson, Atholl; White, Peter (2001). "Prehistoric Settlement on Norfolk Island and its Oceanic Context" (PDF). Records of the Australian Museum. 27 (Supplement 27): 135–141. doi:10.3853/j.0812-7387.27.2001.1348. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016.
- ^ Channers On Norfolk Island Info Archived 3 نوفمبر 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Channersonnorfolk.com (15 March 2013). Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- ^ "Climate Statistics: Norfolk Island Aero (1991–2020 normals)". Australian Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 26 April 2022.
- ^ "Weather-Atlas (Sunshine)". Weather-Atlas. Retrieved 26 April 2022.
المراجع
- Anderson, Atholl; White, Peter (2001). "The Prehistoric Archaeology of Norfolk Island, Southwest Pacific" (PDF). Records of the Australian Museum. Australian Museum. 27 (Supplement 27): 1–142. doi:10.3853/j.0812-7387.27.2001.1334. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- Andrew Kippis, The Life and Voyages of Captain James Cook, Westminster 1788, Reprint London and New York 1904, pp. 246 ff
- Nobbs, Raymond, Norfolk Island and its Third Settlement: The First Hundred Years 1856–1956 Sydney, Library of Australian History, 2006.
- تاريخ التسويات الجزائية
- Causer, Tim '"The Worst Types of Sub-Human Beings": the Myth and Reality of the Convicts of the Norfolk Island Penal Settlement, 1825–1855', Islands of History, Sydney, 2011, pp. 8–31. (ISBN 978-0-9803354-5-3).
- Causer, Tim 'Norfolk Island's "Suicide Lotteries": Myth and Reality', Islands of History, Sydney, 2011, pp. 61–68. (ISBN 978-0-9803354-5-3).
- Clark, Manning, A History of Australia, Vols. I–III, Melbourne, Melbourne University Press, 1962, 1968, 1973.
- Clarke, Marcus, For the Term of his Natural Life (novel).
- Hazzard, Margaret, Punishment Short of Death: a history of the penal settlement at Norfolk Island, Melbourne, Hyland, 1984. (ISBN 0-908090-64-1).
- Murray-Brown, David, Norfolk Island Cancellations and Postal Markings. London: Pacific Islands Study Circle, 3rd edition, 2012, 978-1-899833-20-7, 130pp; http://www.pisc.org.uk
- Hughes, Robert, The Fatal Shore, London, Pan, 1988. (ISBN 0-330-29892-5).
- Wright, R., The Forgotten Generation of Norfolk Island and Van Diemen's Land, Sydney, Library of Australian History, 1986.
قراءات إضافية
- Barry, John Vincent – Alexander Maconochie of Norfolk Island.
- Clune, Frank – Norfolk Island Story.
- Hazzard, Margaret – Punishment Short of Death: A history of the Penal Settlement at Norfolk Island.
- Hoare, Merval – Norfolk Island: An Outline of Its History 1774–1987.
- Specht, Jim – The Prehistoric Archaeology of Norfolk Island.
وصلات خارجية
| Find more about جزيرة نورفوك at Wikipedia's sister projects | |
| Definitions from Wiktionary | |
| Media from Commons | |
| Quotations from Wikiquote | |
| Source texts from Wikisource | |
| Textbooks from Wikibooks | |
| Travel guide from Wikivoyage | |
| Learning resources from Wikiversity | |
الحكومة
معلومات عامة
- Norfolk Island. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- جزيرة نورفوك at Curlie
 Wikimedia Atlas of Norfolk Island
Wikimedia Atlas of Norfolk Island
الآثار والمستوطنة الپولينيزية في عصور ما قبل التاريخ
- Anderson, Atholl; White, Peter (2001). "The Prehistoric Archaeology of Norfolk Island, Southwest Pacific" (PDF). Records of the Australian Museum. Australian Museum. 27 (Supplement 27): 1–142. doi:10.3853/j.0812-7387.27.2001.1334. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- Anderson, Atholl; White, Peter (2001). "Approaching the Prehistory of Norfolk Island" (PDF). Records of the Australian Museum. Australian Museum. 27 (Supplement 27): 1–9. doi:10.3853/j.0812-7387.27.2001.1335. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- Anderson, Atholl; Smith, Ian; White, Peter (2001). "Archaeological Fieldwork on Norfolk Island" (PDF). Records of the Australian Museum. Australian Museum. 27 (Supplement 27): 11–32. doi:10.3853/j.0812-7387.27.2001.1336. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
أخرى
- Quis custodiet ipsos custodes? Inquiry into Governance on Norfolk Island Commonwealth Parliament, Joint Standing Committee on the National Capital and External Territories, 2003
- Norfolk Island and Its Inhabitants 1879 account by Joseph Campbell
- قالب:WWF ecoregion
- Anglican history on Norfolk Island Primary texts and photographs
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Missing redirects
- Articles with unsourced statements from May 2020
- Articles containing إنگليزية-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Articles with Curlie links
- دول اوقيانوسية
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- جزيرة نورفوك
- جزر جزيرة نورفوك
- بلدان جزر
- 1856 establishments in the United Kingdom
- 1914 establishments in Australia
- Australian penal colonies
- Defunct prisons in Australia
- Extinct volcanoes
- Former penal colonies
- Geography of Polynesia
- Important Bird Areas of Australian External Territories
- جزر المحيط الهادي
- Pliocene Oceania
- Pliocene volcanoes
- Polygenetic volcanoes
- Prison museums in Australia
- States and territories established in 1856
- States and territories of Australia
- Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests
- Volcanoes of Australia
- Volcanoes of the Pacific Ocean
- Volcanoes of Zealandia
- Whaling stations in Australia
- Important Bird Areas of Oceania
- IBRA subregions
- صفحات مع الخرائط