الغزو الياباني لمنشوريا
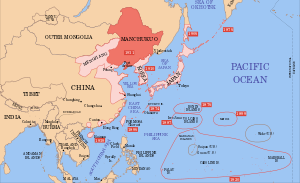
الغزو الياباني لمنشوريا بدأ في 18 سبتمبر 1931، حين غزا جيش كوانتونگ التابع لإمبراطورية اليابان منشوريا مباشرة في أعقاب حادثة موكدن. في نهاية الحرب في فبراير 1932، أسس اليابانيون دولة دمية اسمها مانچوكوو، واستمر احتلالهم حتى نجاح الاتحاد السوڤيتي ومنغوليا في عملية الهجوم الاستراتيجي على منشوريا في منتصف أغسطس 1945.
The South Manchuria Railway Zone and the Korean Peninsula had been under the control of the Japanese Empire since the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905. Japan's ongoing industrialization and militarization ensured their growing dependence on oil and metal imports from the US.[2] The US sanctions which prevented trade with the United States (which had occupied the Philippines around the same time) resulted in Japan furthering its expansion in the territory of China and Southeast Asia.[3] The invasion, or the Marco Polo Bridge Incident of 7 July 1937, is sometimes cited as an alternative starting date for World War II, in contrast with the more commonly accepted one of September 1939.[4]
With the invasion having attracted great international attention, the League of Nations produced the Lytton Commission (headed by British politician Victor Bulwer-Lytton) to evaluate the situation, with the organization delivering its findings in October 1932. Its findings and recommendations that the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo not be recognized and the return of Manchuria to Chinese sovereignty prompted the Japanese government to withdraw from the League entirely.
خلفية
Believing that a conflict in Manchuria would be in the best interests of Japan, and acting in the spirit of the Japanese concept of gekokujō, Kwantung Army Colonel Seishirō Itagaki and Lieutenant Colonel Kanji Ishiwara independently devised a plan to provoke Japan into invading Manchuria by setting up a false flag incident for the pretext of invasion.
The plan was originally executed on 28 September, but the plan has changed to 18 September. When 1st Lieutenant Suemori Komoto of the Independent Garrison Unit (独立守備隊) of the 29th Infantry Regiment, which guarded the South Manchuria Railway, placed explosives near the tracks, but far enough away to do no real damage. At around 10:20 pm (22:20), 18 September, the explosives were detonated. However, the explosion was minor and only a 1.5-meter section on one side of the rail was damaged. In fact, a train from Changchun passed by the site on this damaged track without difficulty and arrived at Shenyang at 10:30 pm (22:30).[5]
On the morning of 19 September, two artillery pieces installed at the Mukden officers' club opened fire on the Chinese garrison nearby, in response to the alleged Chinese attack on the railway. القوة الجوية الصغيرة لـژانگ شوىليانگ تم تدميرها، و فر جنوده من ثكنات بـِيْداينگ المدمرة، مع هجوم قوة من خمسمائة ياباني على الحامية الصينية مكونة من سبة آلاف جندي. The Chinese troops were no match for the experienced Japanese troops. By the evening, the fighting was over, and the Japanese had occupied Mukden at the cost of five hundred Chinese lives and only two Japanese lives, thus starting the greater invasion of Manchuria.
الضم الأوّلي
The Chinese–Japanese dispute in July 1931 known as the Wanpaoshan Incident was followed by the Mukden Incident. On 18 September 1931 the Japanese Imperial General Headquarters, which had decided upon a policy of localizing the incident, communicated its decision to the Kwantung Army command. However, Kwantung Army commander-in-chief General Shigeru Honjō instead ordered his forces to proceed to expand operations all along the South Manchuria Railway. Under orders from Lieutenant General Jirō Tamon, troops of the 2nd Division moved up the rail line and captured virtually every city along its 1,170-kilometre (730-mile) length in a matter of days.
Likewise on 19 September, in response to General Honjō's request, the Joseon army in Korea under General Senjūrō Hayashi ordered the 20th Infantry Division to split its force, forming the 39th Mixed Brigade, which departed on that day for Manchuria without authorization from the Emperor. On 19 September, the Japanese occupied Yingkou, Liaoyang, Shenyang, Fushun, Dandong, Siping (Jilin Province), and Changchun. On 21 September, the Japanese captured Jilin City. On 23 September, the Japanese took Jiaohe (Jilin) Province) and Dunhua. On 1 October, Zhang Haipeng surrendered the Taonan area. Sometime in October, Ji Xing (吉興) surrendered the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture area[6] and on 17 October, Yu Zhishan surrendered Eastern Liaoning to the Japanese.
Tokyo was shocked by the news of the Army acting without orders from the central government. The Japanese civilian government was thrown into disarray by this act of "gekokujō" insubordination, but as reports of one quick victory after another began to arrive, it felt powerless to oppose the Army, and its decision was to immediately send three more infantry divisions from Japan, beginning with the 14th Mixed Brigade of the IJA 7th Division.[when?] During this era, the elected government could be held hostage by the Army and Navy, since Army and Navy members were constitutionally necessary for the formation of cabinets. Without their support, the government would collapse.
الحركات الانفصالية
After the Liaoning Provincial government fled Mukden, it was replaced by a "Peoples Preservation Committee" which declared the secession of Liaoning province from the Republic of China. Other secessionist movements were organized in Japanese-occupied Kirin by General Xi Qia head of the "New Kirin" Army, and at Harbin, by General Chang Ching-hui. In early October, at Taonan in northwest Liaoning province, General Zhang Haipeng declared his district independent of China, in return for a shipment of a large number of military supplies by the Japanese Army.
On 13 October, General Chang Hai-peng ordered three regiments of the Hsingan Reclamation Army under General Xu Jinglong north to take the capital of Heilongjiang province at Qiqihar. Some elements in the city offered to peacefully surrender the old walled town, and Chang advanced cautiously to accept. However his advance guard was attacked by General Dou Lianfang's troops, and in a savage fight with an engineering company defending the north bank, were sent fleeing with heavy losses. During this fight, the Nenjiang railroad bridge was dynamited by troops loyal to General Ma Zhanshan to prevent its use.
مقاومة الغزو الياباني
Using the repair of the Nen River Bridge as the pretext, the Japanese sent a repair party in early November under the protection of Japanese troops. Fighting erupted between the Japanese forces and troops loyal to the acting governor of Heilongjiang province Muslim General Ma Zhanshan, who chose to disobey the Kuomintang government's ban on further resistance to the Japanese invasion.
Despite his failure to hold the bridge, General Ma Zhanshan became a national hero in China for his resistance at Nenjiang Bridge, which was widely reported in the Chinese and international press. The publicity inspired more volunteers to enlist in the Anti-Japanese Volunteer Armies.
The repaired bridge made possible the further advance of Japanese forces and their armored trains. Additional troops from Japan, notably the 4th Mixed Brigade from the 8th Division, were sent in November.
On 15 November 1931, despite having lost more than 400 men and 300 left wounded since 5 November, General Ma declined a Japanese ultimatum to surrender Qiqihar. On 17 November, in subzero weather, 3,500 Japanese troops, under the command of General Jirō Tamon, mounted an attack, forcing General Ma from Qiqihar by 19 November.
العمليات في شمال شرق الصين الجنوبي
In late November 1931, General Honjō dispatched 10,000 soldiers in 13 armored trains, escorted by a squadron of bombers, in an advance on Chinchow from Mukden. This force had advanced to within 30 kilometres (19 mi) of Chinchow when it received an order to withdraw. The operation was cancelled by Japanese War Minister General Jirō Minami, due to the acceptance of modified form of a League of Nations proposal for a "neutral zone" to be established as a buffer zone between China proper and Manchuria pending a future Chinese-Japanese peace conference by the civilian government of Prime Minister Baron Wakatsuki in Tokyo.
However, the two sides failed to reach a lasting agreement. The Wakatsuki government soon fell and was replaced by a new cabinet led by Prime Minister Inukai Tsuyoshi. Further negotiations with the Kuomintang government failed, the Japanese government authorized the reinforcement of troops in Manchuria. In December, the rest of 20th Infantry Division, along with the 38th Mixed Brigade from the 19th Infantry Division were sent into Manchuria from Korea while the 8th Mixed Brigade from the 10th Infantry Division was sent from Japan. The total strength of the Kwantung Army was thus increased to around 60,450 men.[بحاجة لمصدر]
With this stronger force, the Japanese Army announced on 21 December the beginning of large-scale anti-bandit operations in Manchuria to quell a growing resistance movement by the local Chinese population in Liaoning and Kirin provinces.
On 28 December, a new government was formed in China after all members of the old Nanjing government resigned. This threw the military command into turmoil, and the Chinese army retreated to the south of the Great Wall into Hebei province, a humiliating move which lowered China's international image.[7] Japanese forces occupied Chinchow on 3 January 1932, after the Chinese defenders retreated without giving combat.
احتلال شمال شرق الصين
With southern Manchuria secure, the Japanese turned north to complete the occupation of Manchuria. As negotiations with Generals Ma Zhanshan and Ting Chao to defect to the pro-Japanese side had failed, in early January Colonel Kenji Doihara requested collaborationist General Qia Xi to advance his forces and take Harbin.
The last major Chinese regular force in northern Manchuria was led by General Ting Chao who organized the defense of Harbin successfully against General Xi until the arrival of the IJA 2nd Division under General Jirō Tamon. Japanese forces took Harbin on 4 February 1932.
By the end of February Ma had sought terms and joined the newly formed Manchukuo government as governor of Heilongjiang province and Minister of War.
On 27 February 1932, Ting offered to cease hostilities, ending official Chinese resistance in Manchuria, although combat by guerrilla and irregular forces continued as Japan spent many years in their campaign to pacify Manchukuo.
الأثر على الجبهة الداخلية اليابانية
The conquest of Manchuria, a land rich in natural resources, was widely seen as an economic "lifeline" to save Japan from the effects of the Great Depression, generating much public support.[8] The American historian Louise Young described Japan from September 1931 to the spring of 1933 as gripped by "war fever" as the conquest of Manchuria proved to be an extremely popular war.[9] The metaphor of a "lifeline" suggested that Manchuria was crucial to the functioning of the Japanese economy, which explains why the conquest of Manchuria was so popular and why afterwards Japanese public opinion was so hostile towards any suggestion of letting Manchuria go.[10]
At the time, censorship in Japan was nowhere near as stringent as it later became, and Young noted: "Had they wished, it would have been possible in 1931 and 1932 for journalists and editors to express anti-war sentiments".[11] The liberal journal Kaizō criticized the war with the journalist Gotō Shinobu in the November 1931 edition accusing the Kwangtung Army of a "two-fold coup d'état" against both the government in Tokyo and against the government of China.[11] Voices like Kaizō were a minority as mainstream newspapers like the Asahi soon discovered that an anti-war editorial position hurt sales, and so switched over to an aggressively militaristic editorial position as the best way to increase sales.[11] Japan's most famous pacifist, the poet Akiko Yosano had caused a sensation in 1904 with her anti-war poem "Brother Do Not Give Your Life", addressed to her younger brother serving in the Imperial Army that called the war with Russia stupid and senseless.[12] Such was the extent of "war fever" in Japan in 1931 that even Akiko succumbed, writing a poem in 1932 praising bushidō, urging the Kwantung Army to "smash the sissified dreams of compromise" and declared that to die for the Emperor in battle was the "purest" act a Japanese man could perform.[12]
الأثر الخارجي
The Western media reported on the events with accounts of atrocities such as bombing civilians or firing upon shell-shocked survivors.[13] It aroused considerable antipathy to Japan, which lasted until the end of World War II.[13]
When the Lytton Commission issued a report on the invasion, despite its statements that China had to a certain extent provoked Japan, and China's sovereignty over Manchuria was not absolute, Japan took it as an unacceptable rebuke and withdrew from the already declining League of Nations, which also helped create international isolation.[14]
The Manchurian Crisis had a significant negative effect on the moral strength and influence of the League of Nations. As critics had predicted, the League was powerless if a strong nation decided to pursue an aggressive policy against other countries, allowing a country such as Japan to commit blatant aggression without serious consequences. Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini were also aware of this, and ultimately both followed Japan's example in aggression against their neighbors: in the case of Italy, against Abyssinia; and Germany, against Czechoslovakia and Poland.[15]
انظر أيضاً
- الحرب الصينية اليابانية الثانية
- تشيانگ كاي-شك
- كومنتانگ
- عسكرية جمهورية الصين
- الجيش الثوري الوطني
- ژانگ شوىليانگ
- أزمة الحبشة
المراجع
الهامش
- ^ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/598171/Tojo-Hideki
- ^ Walker, Michael (2017). The 1929 Sino-Soviet War: The War Nobody Knew. Modern War Studies. ISBN 978-0700623754.
- ^ Meyer, Michael (9 February 2016). In Manchuria: A Village Called Wasteland and the Transformation of Rural China. ISBN 978-1620402887.
- ^ Simkin, John (February 5, 2007). "Sterling and Peggy Seagrave: Gold Warriors". The Education Forum. Archived from the original on June 13, 2008. Retrieved June 13, 2008.
Americans think of WW2 in Asia as having begun with Pearl Harbor, the British with the fall of Singapore, and so forth. The Chinese would correct this by identifying the Marco Polo Bridge incident as the start, or the Japanese seizure of Manchuria earlier.
- ^ CHRONOLOGY OF MAJOR INTERNATIONAL EVENTS FROM 1931 THROUGH 1943, WITH OSTENSIBLE REASONS ADVANCED FOR THE OCCURRENCE THEREOF 78th Congress, 2d Session. "An explosion undoubtedly occurred on or near the railroad between 10 and 10:30 p.m. on September 18th, but the damage, if any, to the railroad did not in fact prevent the punctual arrival of the south-bound train from Changchun, and was not in itself sufficient to justify military action. The military operations of the Japanese troops during this night, ... cannot be regarded as measures of legitimate self-defence..." [Opinion of Commission of Enquiry], ibid., p. 71
- ^ "延边地区抗日根据地研究.pdf". max.book118.com. Retrieved 2020-11-25.
- ^ Thorne, Christopher (1973). The Limits of Foreign Policy. New York: Capricorn. p. 329. ISBN 978-0399111242.
- ^ Young, Luise (1998). Japan's Total Empire: Manchuria and the Culture of Wartime Imperialism. Los Angeles: University of California Press. pp. 83–93. ISBN 9780520219342.
- ^ Young, Luise (1998). Japan's Total Empire: Manchuria and the Culture of Wartime Imperialism. Los Angeles: University of California Press. p. 90. ISBN 9780520219342.
- ^ Young, Luise (1998). Japan's Total Empire: Manchuria and the Culture of Wartime Imperialism. Los Angeles: University of California Press. p. 95. ISBN 9780520219342.
- ^ أ ب ت Young, Luise (1998). Japan's Total Empire: Manchuria and the Culture of Wartime Imperialism. Los Angeles: University of California Press. p. 85. ISBN 9780520219342.
- ^ أ ب Young, Luise (1998). Japan's Total Empire: Manchuria and the Culture of Wartime Imperialism. Los Angeles: University of California Press. p. 84. ISBN 9780520219342.
- ^ أ ب Meirion and Susie Harries, Soldiers of the Sun: The Rise and Fall of the Imperial Japanese Army p 161 ISBN 0-394-56935-0
- ^ Meirion and Susie Harries, Soldiers of the Sun: The Rise and Fall of the Imperial Japanese Army p 163 ISBN 0-394-56935-0
- ^ Ben Walsh, GCSE Modern World History - second edition 2001, p 247 ISBN 978-0719577130
المصادر
- Coogan, Anthony (1994). Northeast China and the Origins of the Anti-Japanese United Front. Modern China, Vol. 20, No. 3 (Jul., 1994), pp. 282-314: Sage Publications.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)CS1 maint: location (link) - Matsusaka, Yoshihisa Tak (2003). The Making of Japanese Manchuria, 1904-1932. Harvard University Asia Center. ISBN 0-674-01206-2.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - 中国抗日战争正面战场作战记 China's Anti-Japanese War Combat Operations
- Author : Guo Rugui, editor-in-chief Huang Yuzhang
- Press : Jiangsu People's Publishing House
- Date published : 2005-7-1
- ISBN 7-214-03034-9
- 中国抗日战争正面战场作战记 (China's Anti-Japanese War Combat Operations) Online in Chinese
- 第二部分:从“九一八”事变到西安事变“九一八”事变和东北沦陷 "9/18" Emergency and Northeast falls to the enemy
- 第二部分:从“九一八”事变到西安事变事变爆发和辽宁 吉林的沦陷[dead link] The emergency erupts with Liaoning, Jilin falling to the enemy
- 第二部分:从“九一八”事变到西安事变江桥抗战和黑龙江省的失陷[dead link] River bridge defense and Heilongjiang Province falls to the enemy
- 第二部分:从“九一八”事变到西安事变锦州作战及其失陷[dead link] The Jinzhou battle and its fall to the enemy
- 第二部分:从“九一八”事变到西安事变哈尔滨保卫战 The defense of Harbin
وصلات خارجية
- "On The Eastern Front", April 1932, Popular Science photo collection of Invasion of Manchuria and Shanghi International Settlement During the Shanghai Incident
- "MANCHURIA - What This Is All About", February 1932, Popular Mechanics
- Solving the "Manchurian Problem": Uchida Yasuya and Japanese Foreign Affairs before the Second World War
- Japan's "Sole Road for Survival": The Range of Views Within the Guandong Army over the Seizure of Manchuria and Mongolia"
- International Military Tribunal for the Far East Japanese Aggression Against China
- Monograph 144, Manchurian Incident
- Mukden Incident & Manchukuo, WW2 database
- Manchuria 1931-1932 Photos from the Manchurian campaign
- AMS Topographic maps of Manchuria
- Vague or ambiguous time from November 2013
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles with unsourced statements from June 2021
- CS1 maint: location
- Articles with dead external links from May 2016
- الحرب الصينية اليابانية الثانية
- نزاعات 1931
- نزاعات 1932
- معارك الحرب الصينية اليابانية الثانية
- 1931 في الصين
- 1932 في الصين
- تاريخ منشوريا
- 1931 في اليابان
- 1932 في اليابان
- فترة ما بين الحربين العالميتين
- المشاعر المعادية لليابانيين في الصين
- غزو الصين
- غزوات اليابان
- التاريخ العسكري لمنشوريا



