نتريد الليثيوم
 | |
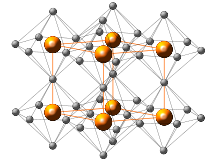 Crystal structure of lithium nitride.
| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك المفضل
Lithium nitride | |
| أسماء أخرى
Trilithium nitride
| |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.043.144 |
| رقم EC |
|
| مرجع Gmelin | 1156 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | Li3N |
| كتلة مولية | 34.83 g/mol |
| المظهر | red, purple solid |
| الكثافة | 1.270 g/cm3 |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | reacts |
| log P | 3.24 |
| البنية | |
| البنية البلورية | see text |
| المخاطر | |
| خطر رئيسي | reacts with water to release ammonia |
| ن.م.ع. مخطط تصويري |  
|
| ن.م.ع. كلمة الاشارة | Danger |
| H260, H314 | |
| P223, P231+P232, P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P335+P334, P363, P370+P378, P402+P404, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |
أنيونات أخرى
|
Lithium oxide |
كاتيونات أخرى
|
Sodium nitride Potassium nitride |
مركـّبات ذات علاقة
|
Lithium amide Lithium imide |
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
Lithium nitride is a compound with the formula Li3N. It is the only stable alkali metal nitride. The solid has a reddish-pink color and high melting point.[1]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Preparation and handling
Lithium nitride is prepared by direct combination of elemental lithium with nitrogen gas:[2]
- 6 Li + N2 → 2 Li3N
Instead of burning lithium metal in an atmosphere of nitrogen, a solution of lithium in liquid sodium metal can be treated with N2. Lithium nitride reacts violently with water to produce ammonia:
- Li3N + 3 H2O → 3 LiOH + NH3
Structure and properties
alpha-Li3N (stable at room temperature and pressure) has an unusual crystal structure that consists of two types of layers, one sheet has the composition Li2N− contains 6-coordinate N centers and the other sheet consists only of lithium cations.[3] Two other forms are known: beta-Lithium nitride, formed from the alpha phase at 4,200 bars (4,100 atm) has the sodium arsenide (Na3As) structure; gamma-Lithium nitride (same structure as Li3Bi) forms from the beta form at 35 to 45 gigapascals (350,000 to 440,000 atm).[4]
Lithium nitride shows ionic conductivity for Li+, with a value of c. 2×10−4Ω−1cm−1, and an (intracrystal) activation energy of c. 0.26eV (c. 24 kJ/mol). Hydrogen doping increases conductivity, whilst doping with metal ions (Al, Cu, Mg) reduces it.[5][6] The activation energy for lithium transfer across lithium nitride crystals (intercrystalline) has been determined to be higher at c. 68.5 kJ/mol.[7] The alpha form is a semiconductor with band gap of c. 2.1 eV.[4]
Reaction with hydrogen at under 300 °C (0.5 MPa pressure) produces lithium hydride and lithium amide.[8]
Lithium nitride has been investigated as a storage medium for hydrogen gas, as the reaction is reversible at 270 °C. Up to 11.5% by weight absorption of hydrogen has been achieved.[9]
Reacting lithium nitride with carbon dioxide results in amorphous carbon nitride (C3N4), a semiconductor, and lithium cyanamide (Li2CN2), a precursor to fertilizers, in an exothermic reaction.[10] [11]
References
- ^ Greenwood, N. N. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edition ed.). Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ E. Döneges "Lithium Nitride" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, New York. Vol. 1. p. 984.
- ^ Barker M. G.; Blake A. J.; Edwards P. P.; Gregory D. H.; Hamor T. A.; Siddons D. J.; Smith S. E. (1999). "Novel layered lithium nitridonickelates; effect of Li vacancy concentration on N co-ordination geometry and Ni oxidation state". Chemical Communications (13): 1187–1188. doi:10.1039/a902962a.
- ^ أ ب Walker, G, ed. (2008). Solid-State Hydrogen Storage: Materials and Chemistry. §16.2.1 Lithium nitride and hydrogen:a historical perspective.
- ^ Lapp, Torben; Skaarup, Steen; Hooper, Alan (October 1983). "Ionic conductivity of pure and doped Li3N". Solid State Ionics. 11 (2): 97–103. doi:10.1016/0167-2738(83)90045-0.
- ^ Boukamp, B. A.; Huggins, R. A. (6 September 1976). "Lithium ion conductivity in lithium nitride". Physics Letters A. 58 (4): 231–233. Bibcode:1976PhLA...58..231B. doi:10.1016/0375-9601(76)90082-7.
- ^ Boukamp, B. A.; Huggins, R. A. (January 1978). "Fast ionic conductivity in lithium nitride". Materials Research Bulletin. 13 (1): 23–32. doi:10.1016/0025-5408(78)90023-5.
- ^ Goshome, Kiyotaka; Miyaoka, Hiroki; Yamamoto, Hikaru; Ichikawa, Tomoyuki; Ichikawa, Takayuki; Kojima, Yoshitsugu (2015). "Ammonia Synthesis via Non-Equilibrium Reaction of Lithium Nitride in Hydrogen Flow Condition". Materials Transactions. 56 (3): 410–414. doi:10.2320/matertrans.M2014382.
- ^ Ping Chen; Zhitao Xiong; Jizhong Luo; Jianyi Lin; Kuang Lee Tan (2002). "Interaction of hydrogen with metal nitrides and amides". Nature. 420 (6913): 302–304. Bibcode:2002Natur.420..302C. doi:10.1038/nature01210. PMID 12447436. S2CID 95588150.
- ^ Yun Hang Hu, Yan Huo (12 September 2011). "Fast and Exothermic Reaction of CO2 and Li3N into C–N-Containing Solid Materials". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 115 (42), 11678-11681. 115 (42): 11678–11681. Bibcode:2011JPCA..11511678H. doi:10.1021/jp205499e. PMID 21910502.
- ^ Darren Quick (21 May 2012). "Chemical reaction eats up CO2 to produce energy...and other useful stuff". NewAtlas.com. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
See also
| الأملاح والمشتقات المكافئة لأيون النيتريد | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3 | He(N2)11 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Li3N | Be3N2 | BN | β-C3N4 g-C3N4 |
N2 | NxOy | NF3 | Ne | ||||||||||||
| Na3N | Mg3N2 | AlN | SiN | PN P3N5 |
SxNy SN S4N4 |
NCl3 | Ar | ||||||||||||
| K3N | Ca3N2 | ScN | TiN | VN | CrN Cr2N |
MnxNy | FexNy | CoN | Ni3N | CuN | Zn3N2 | GaN | Ge3N4 | As | Se | NBr3 | Kr | ||
| Rb3N | Sr3N2 | YN | ZrN | NbN | β-Mo2N | Tc | Ru | Rh | PdN | Ag3N | CdN | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||
| Cs3N | Ba3N2 | Hf3N4 | TaN | WN | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg3N2 | TlN | Pb | BiN | Po | At | Rn | |||
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |||
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| La | CeN | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | GdN | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UN | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||||
