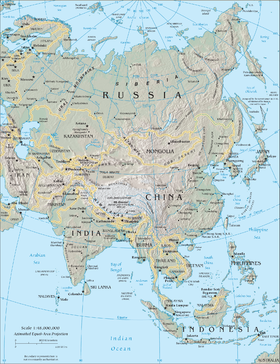
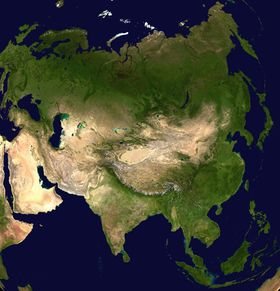
جغرافيا آسيا
Asia is the central and eastern part of أوراسيا, comprising approximately fifty countries. It has an area, including islands, of roughly 49,694,700 km². Asia is joined to Africa by the Isthmus of السويس and to Europe by a long border generally following the جبال الأورال.
Medieval Europeans considered Asia as a قارة, a distinct landmass. The European concept of the three continents in the العالم القديم goes back to classical antiquity with the علم تاريخ الألفاظ of the word rooted in the ancient Near and الشرق الأوسط. The demarcation between Asia and أفريقيا is the isthmus of السويس and the البحر الأحمر. The boundary between Asia and Europe is commonly believed to run through the الدردنيل, the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, the Black Sea, the Caucasus Mountains, the Caspian Sea, the Ural River to its source, and the Ural Mountains to the Kara Sea near Kara, روسيا. However, modern discovery of the extent of Africa and Asia made this definition rather anachronistic, especially in the case of Asia, which would have several regions that would be considered distinct landmasses if these criteria were used (for example, South Asia and East Asia).
Geologists and physical geographers no longer consider Europe and Asia to be separate continents. It is either defined in terms of geological landmasses (physical geography) or tectonic plates (geology). In the former case, Europe is a western peninsula of أوراسيا or the Africa-Eurasia landmass. In the latter, Europe and Asia are parts of the Eurasian plate, which excludes the Arabian and Indian tectonic plates.
In human geography, there are two schools of thought. One school follows historical convention and treats Europe and Asia as different continents, categorizing Europe, East Asia (the Orient), South Asia (British India), and the Middle East (Arabia and Persia) as specific regions for more detailed analysis. The other schools equate the word "continent" in terms of geographical region when referring to Europe, and use the term "region" to describe Asia in terms of physical geography. It is becoming increasingly common to substitute the term "region" for "continent" because in linguistic terms, "continent" implies a distinct landmass.
There is much confusion in European languages with the term "Asian", which almost always refers to a subcategory of people from Asia rather than referring to "Asian" defined in term of "Asia", because a category implies homogeneity. In American English, Asian refers to East Asians, while in British English, Asian refers to South Asians. Some definitions of Asia exclude Turkey, the Middle East, or Russia. The term is sometimes used more strictly in reference to Asia Pacific, which does not include the Middle East or Russia, but does include islands in the Pacific Ocean — many of which are considered part of Australasia or Oceania. Asia contains the Indian subcontinent, Arabian peninsula, as well as a piece of the North American plate in Siberia.
السمات الجغرافية الرئيسية
Southwest Asia is often called the الشرق الأوسط by Europeans and Americans. الشرق الأوسط (to some interpretations) is often used to also refer to some countries in شمال أفريقيا. Southwest Asia can be further divided into:
- Anatolia (i.e. Asia Minor), constituting the Asian part of Turkey
- The island nation of Cyprus in the Mediterranean Sea
- The الشام or الشرق الأدنى, which includes سوريا, الاردن, لبنان, العراق and the Asian portion of مصر
- The Arabian Peninsula, including المملكة العربية السعودية, الإمارات, البحرين, قطر, عمان, اليمن and الكويت
- The Caucasus region (which straddles both Asia and Europe), namely Transcaucasia, including a small portion of Russia and, arguably, most if not all of Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan
- The الهضبة الإيرانية, including إيران, Afghanistan, and پاكستان
جدول المقاطعات والأقاليم
| Name of territory, with flag |
Area (km²) |
Population (1 July 2002 est.) |
Population density (per km²) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| شرق آسيا: | ||||
| 9,584,492 | 1,284,303,705 | 134.0 | بكين | |
| 1,092 | 7,303,334 | 6,688.0 | — | |
| 377,835 | 126,974,628 | 336.1 | طوكيو | |
| 25 | 461,833 | 18,473.3 | — | |
| 1,565,000 | 2,694,432 | 1.7 | Ulan Bator | |
| 120,540 | 22,224,195 | 184.4 | پيونگ يانگ | |
| 98,480 | 48,324,000 | 490.7 | سيول | |
| 35,980 | 22,548,009 | 626.7 | Taipei | |
| [[[جنوب شرق آسيا]]: | ||||
| 5,770 | 350,898 | 60.8 | Bandar Seri Begawan | |
| 181,040 | 12,775,324 | 70.6 | پنوم پن | |
| 1,919,440 | 231,328,092 | 120.5 | جاكرتا | |
| 236,800 | 5,777,180 | 24.4 | ڤيتنام | |
| 329,750 | 27,721,769 | 84.1 | كوالا لمپور | |
| 678,500 | 42,238,224 | 62.3 | Naypyidaw | |
| 300,000 | 84,525,639 | 281.8 | Manila | |
| 693 | 4,452,732 | 6,425.3 | سنغافورة | |
| 514,000 | 62,354,402 | 121.3 | بانكوك | |
| 15,007 | 952,618 | 63.5 | Dili | |
| 329,560 | 81,098,416 | 246.1 | Hanoi | |
| جنوب آسيا: | ||||
| 647,500 | 27,755,775 | 42.9 | كابول | |
| 144,000 | 133,376,684 | 926.2 | دكا | |
| 3,064,898 | 1,045,845,226 | 341.2 | نيودلهي | |
| قالب:Country data مالديڤ جزر المالديڤ | 300 | 320,165 | 1,067.2 | Malé |
| قالب:بيانات بلد نيپال نيپال | 140,800 | 25,873,917 | 183.8 | كاثماندو |
| 803,940 | 147,663,429 | 183.7 | إسلام أباد | |
| 65,610 | 19,576,783 | 298.4 | Sri Jayawardenapura Kotte | |
مراجع
- ^ Monk, K.A. (1996). The Ecology of Nusa Tenggara and Maluku. Hong Kong: Periplus Editions Ltd. p. 7. ISBN 962-593-076-0.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ The current state is formally known as the People's Republic of China (PRC), which is subsumed by the titular entity and civilisation
- ^ أ ب Hong Kong and Macau are Special Administrative Regions (SAR) of the People’s جمهورية الصين
- ^ Taiwan is a contested territory of the Republic of China (ROC) and claimed by the PRC (Taiwan, Province of China): the two are not co-terminous and the ROC is not recognised by the UN as a sovereign state
- ^ أ ب Indonesia and تيمور الشرقية are often considered transcontinental countries in Southeast Asia and أوقيانوسيا
روابط خارجية
- Soil Maps of Asia European Digital Archive on the Soil Maps of the world
- http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/asia.html
- Asia GeoQuest game [1]