الفاصل القاري
الخط الفاصل القاري Continental Divide تعبير يُستعمل ليحدد خط الأرض المرتفعة المستخدمة في فصل المناطق التي يتم تصريف أنهارها إلى جهات مضادة في القارة. ففي أمريكا الشمالية، حيث يُسمى هذا الخط أيضًا مقسم الماء العظيم، يقوم هذا الفاصل القاري بفصل مصارف المياه المتجهة شرقًا عن تلك المتجهة غربًا. انظر: مقسم الماء العظيم. وفي أمريكا الجنوبية، فإن الفاصل العظيم يتبع الجزء الغربي من جبال الأنديز. وفي أوروبا، فإن الخط الفاصل يفصل الأنهار التي تصب في المحيط الأطلسي والمحيط المتجمد الشمالي في الشمال، وتلك التي تصب في البحر الأبيض المتوسط والبحر الأسود في الجنوب. أما في آسيا، فإن الخط الفاصل يفصل الأنهار التي تصب في المحيط المتجمد الشمالي في الشمال والمحيط الهادئ في الشرق عن تلك التي تصرف المياه في المحيط الهندي في الجنوب. ويفصل الخط الفاصل في إفريقيا تصريف المياه في المحيط الأطلسي غربًا من التصريف الذي يحدث في المحيط الهندي شرقًا.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
أمثلة

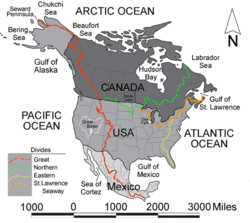
- أمريكا الشمالية can claim 3 or five continental divides, depending on how drainage basins are categorized:
- The Continental Divide of the Americas, also called the Great Divide, separates the watersheds of the المحيط الهادي from those of the Atlantic or المحيطات المتجمدة. It runs from the Seward Peninsula in ألاسكا, through western كندا along the crest of the Rocky Mountains to نيو مكسيكو. From there, it follows the crest of Mexico's Sierra Madre Occidental and extends to the tip of أمريكا الجنوبية. It is crossed by the قناة پنما.
- The Northern Divide, or Laurentian Divide, separates the watershed of the Atlantic Ocean from that of Hudson Bay. The western part of it from the Rocky Mountains to the Great Lakes watershed marked the northern boundary of the Louisiana Purchase and was the border between the United States and British North America until it was superseded by the 49th parallel in the treaty of 1818. In Canada, it historically marked the southern boundary of the fur trading monopoly area of the شركة خليج هدسن, and the easternmost portion still marks part of the boundary between كويبك ولبرادور. The divide traverses very flat terrain, especially in North Dakota, causing many travelers to believe the sign marking the divide is a joke. [1]
- The St. Lawrence River Divide separates the Great Lakes Basin from the rest of the Atlantic Ocean watershed. Two canals cross the divide: The Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal crosses the Chicago Portage and connects Lake Michigan to the Mississippi River watershed. The Erie Canal connects Lake Erie to the Hudson River watershed. Historically there were additional canals, e.g., the Ohio and Erie Canal, but most of these are no longer in operation.
- The Eastern Continental Divide separates the watershed of the Gulf of Mexico from the Atlantic Ocean. It runs from the Twin Tiers of نيويورك and پنسلڤانيا down the Appalachian Mountains to the tip of فلوريدا, dividing the Atlantic from the Gulf of Mexico. The city of Atlanta sits atop this divide.
- كندا can be considered to have another continental divide separating the Arctic Ocean watershed from the Hudson Bay watershed, since Hudson Bay is often considered a separate body of water from the Arctic Ocean. This divide, which is sometimes called the Arctic Divide, was a barrier to transportation until the Methye Portage was discovered in 1778, which opened up the Arctic rivers to the fur traders and became part of a transcontinental trade route from Atlantic to Pacific. It was of significance in Canadian history because it marked the northern boundary of Rupert's Land, the trading monopoly area of the Hudson's Bay Company.[2]
- In South America, the Continental Divide of the Americas lies along the Andes, but the divide does not always run along the highest peaks of the mountain system. In Patagonia many moraine-dammed streams used to drain to the Atlantic rather than the Pacific before the Pleistocene glaciations.
- In Australia the Great Dividing Range largely separates those rivers flowing to the eastern seaboard and the Pacific Ocean from those flowing westward to the Murray-Darling Basin and to the Southern Ocean. However, Australia has fewer distinct ocean boundaries and fewer prominent mountain ranges, which makes it hard to clearly and precisely define any one divide. Much of the interior of the continent drains into the endorheic Lake Eyre Basin.
- Eurasia has various divides, depending on the definition of "ocean" (for example, the Mediterranean Sea and its various lobes, the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the Baltic Sea, the Arctic Ocean and the Black Sea with Europe). Examples include:
- آسيا:
- Tibetan Plateau (Himalayas): Indian Ocean, Pacific Ocean
- Himachal Pradesh (Indus-Ganges): Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal
- Lake Baikal (Yenisei-Lena): Kara Sea, Laptev Sea
- Perm Krai/Urals (Volga-Pechora/Ob): Caspian Sea, Arctic Sea
- اوروبا-آسيا:
- Don-Volga: البحر الأسود, بحر قزوين
- اوروبا:
- Lunghin Pass, Alps (Rhine-Danube-Po): North Sea, Black Sea, Adriatic Sea
- آسيا:
- The most significant continental divide in Africa is that between the watersheds of the Nile and the Congo, passing through the area of the African Great Lakes. Between the Congo and the Sahara, a vast area drains into the endorheic Lake Chad, so puncturing the Atlantic-Mediterranean divide. The Mediterranean-Indian Ocean divide is punctured in East Africa by the endorheic lake systems of the Great Rift Valley; in the south of the continent the divide between the Atlantic and Indian Oceans snakes between the watersheds of the Congo, Zambezi, Limpopo and Orange Rivers, with the Okavango terminating in the Kalahari Desert.
- The interior of Antarctica receives very little precipitation, and that in the form of snow, and the continent is entirely surrounded by the Southern Ocean. Therefore, Antarctica is not generally considered to have a continental divide. The Transantarctic Mountains divide the ice streams draining West Antarctica into the Ronne Ice Shelf, toward the Pacific and into the Ross Ice Shelf, from those draining East Antarctica toward the Atlantic and Indian Oceans
الهامش
- ^
Gonzalez, Mark (2007). "Continental Divides in North Dakota and North America" (PDF). NDGS Newsletter. NDGS. Retrieved 2009-03-29.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^
Foster, John E. (1985). "Fur Trade". The Canadian Encyclopedia. The Historica Foundation of Canada. Retrieved 2007-12-30.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)