فوبوس (قمر)
(تم التحويل من Phobos (moon))
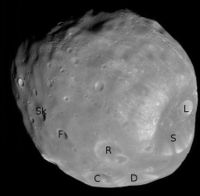
 Enhanced-color view of Phobos obtained by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on March 23, 2008. | |
| الاكتشاف | |
|---|---|
| اكتشفه | أساف هول |
| تاريخ الاكتشاف | 18 أغسطس، 1877 |
| التسميات | |
| المريخ 1 | |
| الصفات | Phobian |
| السمات المدارية | |
| حقبة J2000 | |
| Periapsis | 9,235.6 km (5,738.7 mi) |
| Apoapsis | 9,518.8 km (5,914.7 mi) |
| 9,377.2 km (5,826.7 mi)[1] | |
| Eccentricity | 0.0151 |
| 0.31891023 d (7 h 39.2 min) | |
Average orbital speed | 2.138 km/s (1.328 mi/s) |
| Inclination | 1.093° (to Mars's equator) 0.046° (to local Laplace plane) 26.04° (to the ecliptic) |
| Satellite of | Mars |
| السمات الطبيعية | |
| الأبعاد | 26.8 × 22.4 × 18.4 km (11.4 mi)[2] |
نصف القطر المتوسط | 11.1 km (6.9 mi)[3] (0.0021 Earths) |
Mean radius | 11.1 km (6.9 mi)[3] (0.0021 Earths) |
| ~6,100 km2 (2,400 sq mi) (11.9 µEarths) | |
| Volume | 5,680 km3 (1,360 cu mi)[4] (5.0 nEarths) |
| Mass | 1.072×1016 kg[5] (1.8 nEarths) |
Mean density | 1.876 g/cm³[6] |
| 0.0084–0.0019 m/s² (8.4-1.9 mm/s²) (860-190 µg) | |
| 11.3 m/s (40 km/h)[5] | |
| synchronous | |
Equatorial rotation velocity | 11.0 km/h (6.8 mph) (at longest axis' tips) |
| 0° | |
| Albedo | 0.071[3] |
| Temperature | ~233 K |
| 11.3[7] | |
فوبوس Phobos (تـُنطـَق /ˈfoʊbəs/ FOE-bəs، باليونانية Φόβος) (systematic designation: Mars I)أكبر وأقرب أقمار المريخ, والقمر الثاني هو ديموس. وقد تم اكتشافهما عام 1877. ويبلغ متوسط نصف قطر فوبوس 11.1 km (6.9 mi)، وتصل كتلته إلى 7.24 ضعف كتلة ديموس. وسمي على اسم الإله اليوناني فوبوس (ويعني "الخوف"), ابن أريس (المريخ).
الاكتشاف
الخصائص الفيزيائية
"Hollow Phobos" suggestions
خصائص جيولوجية مسماة
Color view of Stickney Crater by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Some of the named craters of Phobos. C = Clustril; D = Drunlo; F = Flimnap; L = Limtoc; R = Reldresal; S = Stickney; Sk = Skyresh. Grildrig is on the horizon below Skyresh and Flimnap.
الخصائص المدارية
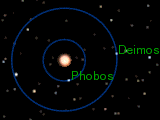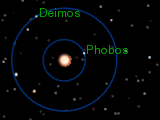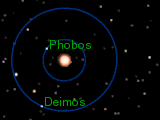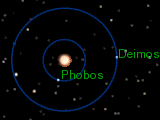
Orbits of Phobos and Deimos (to scale), seen from above Mars' north pole. Phobos is orbiting Mars 3.96 times faster than Deimos.
=العبور الشمسي
الفناء المستقبلي
المنشأ
الاستكشاف

The Phobos monolith (right of center) as taken by the Mars Global Surveyor (MOC Image 55103) in 1998.
مهمات مستقبلية
انظر أيضا
مشاع المعرفة فيه ميديا متعلقة بموضوع Phobos.
المصادر
- ^ NASA Celestia
- ^ "Mars: Moons: Phobos". NASA Solar System Exploration. September 30, 2003. Retrieved August 18, 2008.
- ^ أ ب "Planetary Satellite Physical Parameters". JPL (Solar System Dynamics). July 13, 2006. Retrieved January 29, 2008.
- ^ "Mars Express closes in on the origin of Mars' larger moon". DLR. October 16, 2008. Retrieved October 16, 2008.
- ^ أ ب use a spherical radius of 11.1 km (6.9 mi); volume of a sphere * density of 1.877 g/cm³ yields a mass (m=d*v) of 1.07×1016 kg and an escape velocity (sqrt((2*g*m)/r)) of 11.3 m/s (40 km/h)
- ^ "Precise mass determination and the nature of Phobos". Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 37. Retrieved May 31, 2010.
- ^ "Classic Satellites of the Solar System". Observatorio ARVAL. Retrieved September 28, 2007.