سيريس (كوكب قزم)
 Ceres as seen by Hubble Space Telescope (ACS). The contrast has been enhanced to reveal surface details. | |||||||||
| الاكتشاف | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| اكتشفه | جيوسپه پياتسي | ||||||||
| تاريخ الاكتشاف | 1 يناير, 1801 | ||||||||
| التسميات | |||||||||
| تعيين الكوكب الأصغر | سيريس 1 | ||||||||
| A899 OF; 1943 XB | |||||||||
| كوكب قزم main belt | |||||||||
| الصفات | Cererian, Cerian | ||||||||
| السمات المدارية | |||||||||
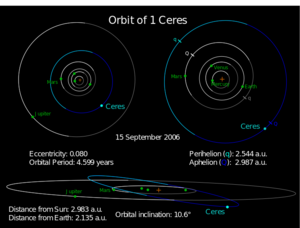
| حقبة November 26, 2005 (JD 2453700.5)[1] | |||||||||
| Aphelion | 447,838,164 km 2.987 AU | ||||||||
| Perihelion | 381,419,582 km 2.545 AU | ||||||||
| 414,703,838 km 2.765 956 424 AU[2] | |||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.07976017[2] | ||||||||
| 1679.819 days 4.599 years | |||||||||
Average orbital speed | 17.882 km/s | ||||||||
| 108.509° | |||||||||
| Inclination | 10.586712°[2] | ||||||||
| 80.40696°[2] | |||||||||
| 73.15073°[2] | |||||||||
| السمات الطبيعية | |||||||||
Equatorial radius | 487.3 ± 1.8 km[3] | ||||||||
Polar radius | 454.7 ± 1.6 km[3] | ||||||||
| Mass | 9.43 ± 0.07×1020 kg[4] | ||||||||
Mean density | 2.077 ± 0.036 g/cm³[3] | ||||||||
| 0.27 m/s² 0.028 g[5] | |||||||||
| 0.51 km/s[5] | |||||||||
Sidereal rotation period | 0.3781 d 9.074170 h[6][7] | ||||||||
| about 3°[3] | |||||||||
North pole right ascension | 19 h 24 min 291°[3] | ||||||||
North pole declination | 59°[3] | ||||||||
| Albedo | 0.090 ± 0.0033 (V-band geometric)[8] | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Spectral type | C[9] | ||||||||
| 6.7[10] to 9.32[11] | |||||||||
| 3.36 ± 0.02[8] | |||||||||
| 0.84"[12] to 0.33"[5] | |||||||||
سيريس أو قيرس هو أوّل ما اكتشف من الكويكبات سنة 1801 على يد الفلكي الإيطالي جوزپى پياتسي. يعدّ أكبر الكويكبات بقطر يقارب 1000 كلم. تمّ يوم 24 أغسطس تعداده من ضمن السّيّارات القميئة عن طريق الاتّحاد الدّوليّ لعلوم الفلك.
الإكتشاف
التسمية
الحالة
الخصائص الفيزيائية

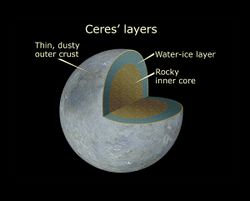
السطج
يحتمل تكوين سطح سيريس خليطا من الماء والثليج وبعض مركبات الهيدرات المعدنية مثا الكربونات والطفل. ويعتقد أن له قلب صخري وثليج.
ويتراوح قدر لمعانه بين 7و6 و 3و9 قدر ظاهري وعلى ذلك فهو لا يرى بالعين المجردة حتى وقت لمعانه الأشد.وقد أطلقت ناسا في 27 سبتمبر 2007 مسباراً فضائياً يسمى دون Dawn للقيام باكتشاف ڤستا 4 Vesta عام 2011 - 2012 وسيريس عام 2015.
الغلاف الجوي
المدار
المنشأ والتطور
معلومات
التنقيب
في 22 يناير 2014، كشف علماء وكالة الفضاء الأوروپية، عن اكتشاف بخار الماء لأول مرة، على الكوكب القزم سيريس، أكبر جرم في حزام الكويكبات.[14] تم التحقق باستخدام بقدرات تحت الحمراء بكثير في مرصد هرشل الفضائي.[15] الاكتشاف كان غير متوقع لأن المذنبات ليست كويكبات، والتي كانت تعتبر "نفثات وزغب وليد اللحظة sprout jets and plumes". حسب أحد العلماء، "الفواصل بين المذنبات والكويكبات أصبحت أكثر ضبابية."[15]
انظر أيضاً
المصادر
- ^ Bowell, Ted; Koehn, Bruce (January 2, 2003). "Asteroid Observing Services". Lowell Observatory. Retrieved 2007-01-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ أ ب ت ث ج Yeomans, Donald K. (July 5, 2007). "1 Ceres". JPL Small-Body Database Browser. Retrieved 2007-07-05.—The listed values were rounded at the magnitude of uncertainty (1-sigma).
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةThomas2005 - ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةCarry2008 - ^ أ ب ت Calculated based on the known parameters
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةNSSDC - ^ Chamberlain, Matthew A. (2007). "Ceres lightcurve analysis – Period determination". Icarus. 188: 451–456. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2006.11.025.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ أ ب خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةLi2006 - ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةRivkin2006 - ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةPasachoff1983 - ^ APmag and AngSize generated with Horizons (Ephemeris: Observer Table: Quantities = 9,13,20,29)
- ^ Ceres Angular Size @ Feb 2009 Opposition: 974 km diam. / (1.58319 AU * 149 597 870 km) * 206265 = 0.84"
- ^ أ ب Saint-Pé, O. (1993). "Ceres surface properties by high-resolution imaging from Earth". Icarus. 105: 271–281. doi:10.1006/icar.1993.1125.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Küppers, Michael; O'Rourke, Laurence; Bockelée-Morvan, Dominique; Zakharov, Vladimir; Lee, Seungwon; von Allmen, Paul; Carry, Benoît; Teyssier, David; Marston, Anthony; Müller, Thomas; Crovisier, Jacques; Barucci, M. Antonietta; Moreno, Raphael (2014). "Localized sources of water vapour on the dwarf planet (1) Ceres". Nature. 505 (7484): 525–527. doi:10.1038/nature12918. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 24451541.
- ^ أ ب Harrington, J.D. (22 January 2014). "Herschel Telescope Detects Water on Dwarf Planet – Release 14-021". NASA. Retrieved 22 January 2014.
الرزنامة
- Hilton, James L., U.S. Naval Observatory Ephemerides of the Largest Asteroids The Astronomical Journal, Vol. 117, p. 1077 (1999).
- Yeomans, Donald K. "Horizons system". NASA JPL. Retrieved 2007-03-20. — Horizons can be used to obtain a current ephemeris
وصلات خارجية
- Movie of one Ceres rotation (processed Hubble images)
- How Gauss determined the orbit of Ceres from keplersdiscovery.com
- An up-to-date summary of knowledge about Ceres, plus an Earth-Ceres size comparison (the Planetary Society)
- A simulation of the orbit of Ceres
- A website dedicated entirely to 1 Ceres