الپرانس العليا (إقليم فرنسي)
Hautes-Pyrénées
| |
|---|---|
 Prefecture building in Tarbes | |
 Location of Hautes-Pyrénées in France | |
| الإحداثيات: 43°12′N 0°8′E / 43.200°N 0.133°E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Occitania |
| Prefecture | Tarbes |
| Subprefectures | Argelès-Gazost Bagnères-de-Bigorre |
| الحكومة | |
| • President of the Departmental Council | Michel Pélieu[1] (PRG) |
| المساحة | |
| • الإجمالي | 4٬464 كم² (1٬724 ميل²) |
| التعداد (يناير 2019) | |
| • الإجمالي | 229٬567 |
| • الترتيب | 86th |
| • الكثافة | 51/km2 (130/sq mi) |
| منطقة التوقيت | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • الصيف (التوقيت الصيفي) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Department number | 65 |
| Arrondissements | 3 |
| Cantons | 17 |
| Communes | 469 |
| ^1 French Land Register data, which exclude estuaries and lakes, ponds and glaciers larger than 1 km2 | |
الپرانس العليا ( Hautes-Pyrénées ؛ النطق الفرنسي: [ot piʁene] (![]() استمع); Gascon/Occitan: Nauts Pirenèus / Hauts Pirenèus ['awts piɾeˈnɛʊs]; إسپانية: Altos Pirineos; قطلان: Alts Pirineus ['alts piɾiˈneʊs]; ) هو إقليم في جنوب غرب فرنسا. وهي جزء من المنطقة ميدي بيرينيه. In 2019, its population was 229,567;[2] its prefecture is Tarbes. It is named after the Pyrenees mountain range.
استمع); Gascon/Occitan: Nauts Pirenèus / Hauts Pirenèus ['awts piɾeˈnɛʊs]; إسپانية: Altos Pirineos; قطلان: Alts Pirineus ['alts piɾiˈneʊs]; ) هو إقليم في جنوب غرب فرنسا. وهي جزء من المنطقة ميدي بيرينيه. In 2019, its population was 229,567;[2] its prefecture is Tarbes. It is named after the Pyrenees mountain range.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التاريخ
Historically the area broadly covered by the département known as Bigorre, a territory at times independent but later part of Gascony province. Large parts of the area were held by the English after the Treaty of Brétigny, 1360. In the 16th century, it was part of the Huguenot domain of the monarchs of Navarre, brought to France by Henri IV. For its early history, see Bigorre and Gascony.
The département of Hautes-Pyrénées was created at the time of the French Revolution, on 4 March 1790, through the influence of French politician Bertrand Barère, a member of the Convention.
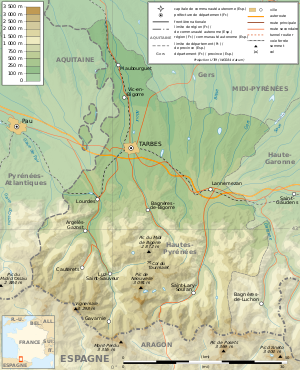
الجغرافيا
Hautes-Pyrénées consists of several distinct geographical areas. The southern portion, along the border with Spain, consists of mountains such as the Vignemale, the Pic du Midi de Bigorre, and the Neouvielle and Arbizon ranges. A second area consists of low-altitude rolling hills. The Northern part of the département consists of largely flat agricultural land. Hautes-Pyrénées has two small territorial exclaves—a remnant from the Middle Ages—located within the neighboring département of Pyrénées-Atlantiques.
Principal towns
The greater Tarbes area is the economic and administrative focus of the département, while Lourdes, the second-biggest city in Hautes-Pyrénées, is dedicated almost exclusively to the religious pilgrimage industry. As of 2019, there are 7 communes with more than 5,000 inhabitants:[2]
| Commune | Population (2019) |
|---|---|
| Tarbes | 42,758 |
| Lourdes | 13,132 |
| Aureilhan | 7,864 |
| Bagnères-de-Bigorre | 7,085 |
| Lannemezan | 5,816 |
| Bordères-sur-l'Échez | 5,357 |
| Séméac | 5,085 |
السكان
Population development since 1801:
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sources:[3][4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
السياحة
The Western Pyrenees National Park covers a significant area, and includes well-known attractions such as the Cirque de Gavarnie and the Pont d'Espagne. The entire area is a favorite destination of hikers and mountain enthusiasts.
The area has been known perhaps since Antiquity for its hot springs, and several towns were built around these, most notably Cauterets, Luz-Saint-Sauveur and Bagnères-de-Bigorre.
A notable lake in the area is Lac Bleu d'Ilhéou, southwest of Cauterets.
There are a number of popular ski resorts in Hautes-Pyrénées such as Barèges-La Mongie, Gavarnie, Luz-Ardiden, Cauterets, Hautacam, Piau-Engaly and Saint-Lary-Soulan.
The area is a nearly-permanent fixture on the Tour de France's itinerary, with significantly difficult passes such as the Tourmalet, the Aubisque and the Soulor.
The region's premier avant-garde jazz festival is held each year in Luz-Saint-Sauveur: Jazz a Luz. Tarbes hosts an annual horse festival, Equestria, and a Tango festival, Tarbes en Tango.
Lourdes sanctuary
انظر أيضاً
- Cantons of the Hautes-Pyrénées department
- Communes of the Hautes-Pyrénées department
- Arrondissements of the Hautes-Pyrénées department
المصادر
وصلات خارجية
- Tourism & culture in Hautes-Pyrenees
- (بالفرنسية) General Council of Hautes-Pyrénées website
- (بالفرنسية) Prefecture website
- Western Pyrenees National Park
- Jazz a Luz
- Equestria
- ^ "Répertoire national des élus: les conseillers départementaux". data.gouv.fr, Plateforme ouverte des données publiques françaises (in الفرنسية). 4 May 2022.
- ^ أ ب Populations légales 2019: 65 Hautes-Pyrénées, INSEE
- ^ "Historique des Hautes-Pyrénées". Le SPLAF.
- ^ "Évolution et structure de la population en 2016". INSEE.
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- صفحات بها مخططات
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles containing أوكسيتان (بعد 1500)-language text
- Articles containing إسپانية-language text
- Articles containing قطلان-language text
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- أقاليم فرنسا
- الپرانس العليا
- CS1 الفرنسية-language sources (fr)