745
► | قرن 7 | << قرن 8 >> | قرن 9 | ◄
► | عقد 710 | عقد 720 | عقد 730 | << عقد 740 >> | عقد 750 | عقد 760 | عقد 770 | ◄
► | ► | 740 | 741 | 742 | 743 | 744 | << 745 >> | 746 | 747 | 748 | 749 | 750 | ◄ | ◄
تحويل 1-1-745م الى هجري (وصلة خارجية) | تحويل 31-12-745م الى هجري (وصلة خارجية) | ابحث في الموسوعة عن مواضيع متعلقة بسنة 745
| الألفية: | الألفية 1 |
|---|---|
| القرون: | القرن 7 - القرن 8 - القرن 9 |
| العقود: | عقد 710 عقد 720 عقد 730 - عقد 740 - عقد 750 عقد 760 عقد 770 |
| السنوات: | 742 743 744 - 745 - 746 747 748 |
| 745 حسب الموضوع | |
| السياسة | |
| زعماء الدول – الدول ذات السيادة | |
| تصنيفات المواليد والوفيات | |
| المواليد – الوفيات | |
| تصنيفات التأسيسات والانحلالات | |
| تأسيسات – انحلالات | |
| التقويم الگريگوري | 745 DCCXLV |
| آب أوربه كونديتا | 1498 |
| التقويم الأرمني | 194 ԹՎ ՃՂԴ |
| التقويم الآشوري | 5495 |
| التقويم البهائي | −1099 – −1098 |
| التقويم البنغالي | 152 |
| التقويم الأمازيغي | 1695 |
| سنة العهد الإنگليزي | N/A |
| التقويم البوذي | 1289 |
| التقويم البورمي | 107 |
| التقويم البيزنطي | 6253–6254 |
| التقويم الصيني | 甲申年 (الخشب القرد) 3441 أو 3381 — إلى — 乙酉年 (الخشب الديك) 3442 أو 3382 |
| التقويم القبطي | 461–462 |
| التقويم الديسكوردي | 1911 |
| التقويم الإثيوپي | 737–738 |
| التقويم العبري | 4505–4506 |
| التقاويم الهندوسية | |
| - ڤيكرام سامڤات | 801–802 |
| - شاكا سامڤات | 667–668 |
| - كالي يوگا | 3846–3847 |
| تقويم الهولوسين | 10745 |
| تقويم الإگبو | −255 – −254 |
| التقويم الإيراني | 123–124 |
| التقويم الهجري | 127–128 |
| التقويم الياباني | Tenpyō 17 (天平17年) |
| تقويم جوچى | N/A |
| التقويم اليوليوسي | 745 DCCXLV |
| التقويم الكوري | 3078 |
| تقويم مينگوو | 1167 قبل جمهورية الصين 民前1167年 |
| التقويم الشمسي التايلندي | 1288 |
Year 745 (DCCXLV) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 745 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
أحداث
حسب المكان
الدولة الأموية
- التوسع الإسلامي: الخليفة الأموي إبراهيم يطيح به مروان الثاني.
الإمبراطورية البيزنطية
- Bubonic plague in Asia Minor kills 1/3 of the population, and subsequently sweeps through the Peloponnese (Balkan Peninsula) (تاريخ تقريبي).
- Invasion of Syria by Constantine V. Capture of Northern Syria.
- Genesius (Gegnœsius), leader of the Paulicians, dies of the plague . 3 The sect is divided between his successors Zechariah and Joseph, who leads his followers back to eastern Anatolia
أوروبا
- Hunald I, duke of Aquitaine, retires to a monastery, probably on Île de Ré.[1] He is succeeded by his son Waifar, who struggles during his rule for independence against the Frankish Kingdom.
- Carantania (modern Austria) loses its independence and becomes part of the Frankish Kingdom, due to the pressing danger posed by Avar tribes from the east (تاريخ تقريبي).
آسيا
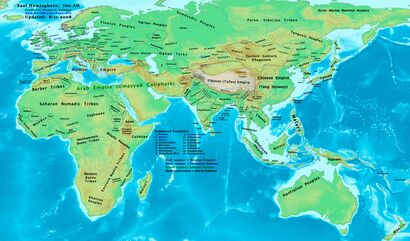 خريطة Turkish Empire (القرن الثامن) |
- الصين has accomplishments in poetry, painting and printing, but its monarchical system tends toward failure. Emperor Xuan Zong has fallen under the spell of his son's wife Yang Guifei (one of the Four Beauties of Ancient China), a Taoist priestess. He is ignoring the economy and the Tang dynasty is declining.
- Beginning of the reign of Bayan Chor (Mountchur 1 ), Kaghan of the Uighurs (end in 759 ). The newly founded Uyghur Empire controls most of the former Turkic Empire territory, مما خلق إمبراطورية امتدت من بحيرة بلكاش (قزخستان الحديثة) إلى بحيرة بايكال (منغوليا)، and is subject to Chinese suzerainty (تاريخ تقريبي).
حسب الموضوع
الدين
مواليد
- إدريس الأول، emir and founder of the Idrisid dynasty (d. 791)
- أبو عبد الله محمد المهدي، ثالث الخلفاء العباسيين (أو 744)
- موسى الكاظم، seventh Twelver Shī‘ah imām (ت. 799)
- Wei Gao, general of the Tang dynasty (d. 805)
- Willehad, bishop of Bremen (approximate date)
- Yaoshan Weiyan, Chinese Buddhist monk (d. 827)
- Zhang Jianfeng, statesman of the Tang dynasty (d. 800)
وفيات
- Cathal Maenmaighe, king of Uí Maine (Ireland)
- Daniel, bishop of Winchester
- Herlindis of Maaseik, Frankish abbess (or 753)
- عاصم بن أبي النجود، الخامس بين أشهر مقرئي القرآن.
- السدي، خطيب ومفسر للقرآن.
- جهم بن صفوان، صاحب العقيدة الجهمية.
- ثابت البناني، محدث وصوفي مسلم.
- Ingwald, bishop of London
- Kadobe, Japanese prince
- Kulun Beg, ruler (khagan) of the Turkish Empire
- Thrasimund II, duke of Spoleto
- Wilfrid, bishop of York
- يوسف بن عمر الثقفي، والي مسلم
المراجع
- ^ Pierre Riche, The Carolingians: A Family who forged Europe, pp. 51–52.
- ^ Grapard, Allan G. (1992). The Protocol of the Gods: A Study of the Kasuga Cult in Japanese History, p. 67; excerpt, "We have no information concerning Genbō's exile; the Shoku-Nihongi states simply that Genbō behaved in a manner that did not befit his ecclesiastic position and that he died in 746 as he was trying to escape."; Matsunaga, p. 125; excerpt, "...the degree of Genbō's corruption remains equivocal."