740
► | قرن 7 | << قرن 8 >> | قرن 9 | ◄
► | عقد 710 | عقد 720 | عقد 730 | << عقد 740 >> | عقد 750 | عقد 760 | عقد 770 | ◄
► | ► | 735 | 736 | 737 | 738 | 739 | << 740 >> | 741 | 742 | 743 | 744 | 745 | ◄ | ◄
تحويل 1-1-740م الى هجري (وصلة خارجية) | تحويل 31-12-740م الى هجري (وصلة خارجية) | ابحث في الموسوعة عن مواضيع متعلقة بسنة 740
| الألفية: | الألفية 1 |
|---|---|
| القرون: | القرن 7 - القرن 8 - القرن 9 |
| العقود: | عقد 710 عقد 720 عقد 730 - عقد 740 - عقد 750 عقد 760 عقد 770 |
| السنوات: | 737 738 739 - 740 - 741 742 743 |
| 740 حسب الموضوع | |
| السياسة | |
| زعماء الدول – الدول ذات السيادة | |
| تصنيفات المواليد والوفيات | |
| المواليد – الوفيات | |
| تصنيفات التأسيسات والانحلالات | |
| تأسيسات – انحلالات | |
| التقويم الگريگوري | 740 DCCXL |
| آب أوربه كونديتا | 1493 |
| التقويم الأرمني | 189 ԹՎ ՃՁԹ |
| التقويم الآشوري | 5490 |
| التقويم البهائي | −1104 – −1103 |
| التقويم البنغالي | 147 |
| التقويم الأمازيغي | 1690 |
| سنة العهد الإنگليزي | N/A |
| التقويم البوذي | 1284 |
| التقويم البورمي | 102 |
| التقويم البيزنطي | 6248–6249 |
| التقويم الصيني | 己卯年 (التراب الأرنب) 3436 أو 3376 — إلى — 庚辰年 (المعدن التنين) 3437 أو 3377 |
| التقويم القبطي | 456–457 |
| التقويم الديسكوردي | 1906 |
| التقويم الإثيوپي | 732–733 |
| التقويم العبري | 4500–4501 |
| التقاويم الهندوسية | |
| - ڤيكرام سامڤات | 796–797 |
| - شاكا سامڤات | 662–663 |
| - كالي يوگا | 3841–3842 |
| تقويم الهولوسين | 10740 |
| تقويم الإگبو | −260 – −259 |
| التقويم الإيراني | 118–119 |
| التقويم الهجري | 122–123 |
| التقويم الياباني | Tenpyō 12 (天平12年) |
| تقويم جوچى | N/A |
| التقويم اليوليوسي | 740 DCCXL |
| التقويم الكوري | 3073 |
| تقويم مينگوو | 1172 قبل جمهورية الصين 民前1172年 |
| التقويم الشمسي التايلندي | 1283 |
Year 740 (DCCXL) was a leap year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 740 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
أحداث
حسب المكان
الدولة الأموية
- 6 يناير - الإمام زيد بن علي، حفيد الحسين، was captured by Syrian soldiers who perform it with arrows in Kufa ( Iraq ) after ten months of revolt 1 . After the failure of his revolt, he leaves his name to a movement, Zaydism , whose doctrine will be important.
الامبراطورية البيزنطية
- Battle of Akroinon: Following the disastrous Battle of Sebastopolis (see 692), Emperor Leo III has largely confined himself to a defensive strategy, while the Umayyad armies regularly launch raids into Byzantine-held Anatolia.[1] Caliph Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik assembles an expeditionary force (90,000 men) under his son Sulayman ibn Hisham. One of these armies, 20,000 men strong under Abdallah al-Battal, is defeated at Akroinon (modern-day Afyon) by the Byzantines, led by Leo and his son, the future emperor Constantine V. About 6,800 Muslim Arabs, however, resist and manage to conduct an orderly retreat to Synnada (Phrygia).[2]
- October 26 – An earthquake strikes Constantinople and the surrounding countryside, causing destruction to the city's land walls and buildings.
أوروبا
- قبائل الأمازيغ في المنطقة حديثة الفتح گاليسيا (شمال غرب اسبانيا) rebel. This facilitates the establishment of an independent kingdom in the Cantabrian Mountains under King Alfonso I of Asturias.[3]
- Duke Thrasimund II recovers the duchy of Spoleto and kills Hilderic with Papal-Beneventian aid.[4] He does not return the confiscated papal cities, and his alliance with Pope Gregory III ruptures.
- ديسمبر - الملك Liutprand of the Lombards attempts to counter the growing independence of الدوقيات اللومباردية في جنوب إيطاليا.
بريطانيا
- الملك Eadberht of Northumbria marches his army north to attack the Picts. King Æthelbald of Mercia takes advantage of his absence, and ravages مدينة يورك. Internal struggles re-emerge in Northumbria with the murder of Eardwine, probably the son of the late usurping king Eadwulf I.[5]
- الملك Æthelheard of Wessex dies after a 14-year reign. He is succeeded by his brother (and probably distant relative) Cuthred. Æthelbald of Mercia takes control of Berkshire من وسكس.
أفريقيا
- معركة النبلاء: The Berber rebels under chieftain Khalid ibn Hamid al-Zanati defeat and overwhelm the Umayyad forces of Khalid ibn Abi Habib al-Fihri, near Tangier (شمال المغرب)، undermining Arab domination in Islamic North Africa. The rebellion spreads in Al-Andalus (Spain), causing governor Ubayd Allah ibn al-Habhab to withdraw Moorish troops from many garrisons north of the Pyrenees.[6]
- ثورة خوارج الأمازيغ: The Berber leader Maysara with his followers Kharidjites seizes Tangier , kills the governor Omar Ibn Abdallah and proclaims caliph. He succeeded in preventing the landing of an Arab army sent from Spain . The governor of Spain Uqba ibn al-Hajjaj intervenes in person but fails to take back Tangier, while Maysara seizes the Souss which he kills the governor. Then Maysara, behaving like a tyrant, is deposed and killed by his own, and replaced by Khalid ibn Hamid al-Zanati . Under his command, the Berbers were victorious in the Battle of the Nobles , on the banks of Chelif
آسيا
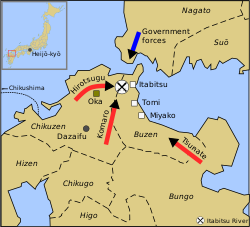
خريطة تبين الأحداث الرئيسية في تمرد فوجيوارا نو هيروتسوگو (740)
- Much to the delight of the citizens of Chang'an, the Chinese government of the Tang Dynasty orders fruit trees to be planted along every main avenue of the city, which enriches not only the diets of the people but also the surroundings (تاريخ تقريبي)
- تمرد فوجيوارا نو هيروتسوگو: عشيرة فوجيوارا بقيادة فوجيوارا نو هيروتسوگو، غير الراضية عن القوى السياسية في اليابان، تجمع جيشاً في Dazaifa (كيوشو) إلا أنها تُهزم أمام قوات الحكومة.
- في الهند، the Châlukya take Kanchi and then submit the southern dynasties. After the victory of Vikramaditya II (in) , many Pallava craftsmen are deported by the Châlukya, which induces a mixed style architecture, both Northern and Dravidian ( Virūpākṣa temple and Papanâtha temple in Pattadakal in 746 and 747).
- Early reign of Maravarman Rajasimha I first king Pandya (ending in 765 ). He fights the Pallava and the Châlukya 5 .
- 740-786 - ملك التبت تيسرون-دبتسان. صياغة النسخة التبتية من البوذية على يد الراهب الهندي پادما سامبهاڤا.
Ecloga of the Byzantine Emperor Leo III , associated with his son قسطنطين الخامس (the text is also dated 726 ).
- أول ذكر للتراقيين.
حسب الموضوع
الدين
- الخزر، الأمة على سهوب البحر الأسود، بالرغم من أنهم ليسو من العرق اليهودي، إلا أنهم يعتنقون اليهودية.
- Cuthbert becomes archbishop of Canterbury after the death of Nothhelm (انظر 739).
مواليد
- Aurelius, king of Asturias (تاريخ تقريبي)
- Gao Ying, chancellor of the Tang Dynasty (ت. 811)
- Layman Pang, Chinese Chán (Zen) Buddhist (ت. 808)
- ما شاء الله اليهودي، منجم وفلكي يهودي عربي (ت. 815)
- Waldo of Reichenau, Frankish abbot (تاريخ تقريبي)
- كمالاشيلا، مؤلف ودارس هندي († 795 )
- ح. 740 - أوكيت كان لك توك، حاكم المايا على مدينة إك بلم (ت. 801)
وفيات
- عبد الله البطال، قائد عسكري عربي
- Æthelburg، ملكة وسكس
- Æthelheard، ملك وسكس
- Æthelwold, bishop of Lindisfarne
- Acca, bishop of Hexham (or 742)
- Anna, wife of Artabasdos
- Frithugyth, queen of Wessex
- Gregory, duke of Benevento
- Hilderic, duke of Spoleto
- خالد بن أبي حبيب الفهري، قائد عسكري عربي
- ميسرة المطغري، قائد أمازيغي متمرد
- Meng Haoran, Chinese poet
- Rhain ap Cadwgan, king of Dyfed and Brycheiniog
- عقبة بن الحجاج، والي عربي.
- زيد بن علي، إمام عربي وحفيد الحسين بن علي (و. 695)
- Zhang Jiuling, chancellor of the Tang Dynasty (و. 673)
المراجع
- ^ Blankinship 1994, pp. 104–105, 117
- ^ Blankinship 1994, p. 170
- ^ de Oliviera Marques, A. H. (1993). "O Portugal Islâmico". In Joel Serrão and A. H. de Oliverira Marques (ed.). Hova Historia de Portugal. Portugal das Invasões Germânicas à Reconquista. Lisbon: Editorial Presença. p. 123.
- ^ Hartmann, chapter II (pp. 2, 139)
- ^ Kirby, pp. 150 & 154; Yorke, Kings, p. 89
- ^ David Nicolle (2008). Poitiers AD 732, Charles Martel turns the Islamic tide (p. 19). ISBN 978-184603-230-1
الكلمات الدالة:
