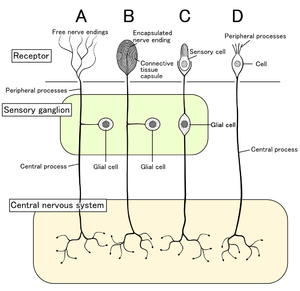
عصبون حسي
في جهاز الحس، المستقبل الحسي sensory receptor، هو نهاية العصب الحسي[1] الذي يستجيب المنبهات الموجودة في البيئة الداخلية أو الخارجية للكائن الحي.
الوظائف
التصنيف
حسب المنبه التحفيزي
- Ampullae of Lorenzini respond to electric fields, salinity, and to temperature, but function primarily as electroreceptors
- Baroreceptors respond to pressure in blood vessels
- Chemoreceptors respond to chemical stimuli
- Hydroreceptors respond to changes in humidity
- Mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical stress or mechanical strain
- Nociceptors respond to damage to body tissues leading to pain perception
- Osmoreceptors respond to the osmolarity of fluids (such as in the hypothalamus)
- Photoreceptors respond to light
- Proprioceptors provide the sense of position
- Thermoreceptors respond to temperature, either heat, cold or both
- Electromagnetic receptors respond to electromagnetic waves
حسب الموقع
- Cutaneous receptors are sensory receptors found in the dermis or epidermis.[2]
- Muscle spindles contain mechanoreceptors that detect stretch in muscles.
حسب الشكل الخارجي
Somatic sensory receptors near the surface of the skin can usually be divided into two groups based on morphology:
- Free nerve endings characterize the nociceptors and thermoreceptors and are called thus because the terminal branches of the neuron are unmyelinated and spread throughout the dermis and epidermis.
- Encapsulated receptors consist of the remaining types of cutaneous receptors. Encapsulation exists for specialized functioning.
حسب سرعة الاستجابة
- A tonic receptor is a sensory receptor that adapts slowly to a stimulus[3] and continues to produce action potentials over the duration of the stimulus.[4] In this way it conveys information about the duration of the stimulus.
Some tonic receptors are permanently active and indicate a background level. Examples of such tonic receptors are pain receptors, joint capsule, and muscle spindle.[5]
- A phasic receptor is a sensory receptor that adapts rapidly to a stimulus. The response of the cell diminishes very quickly and then stops.[3] It does not provide information on the duration of the stimulus[4]; instead some of them convey information on rapid changes in stimulus intensity and rate.[5] An example of a phasic receptor is the Pacinian corpuscle.
التعصيب
انظر أيضاً
المصادر
- ^ http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1O87-sensoryreceptor.html
- ^ http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Cutaneous+receptor
- ^ أ ب http://caspar.bgsu.edu/~courses/Glossary.htm
- ^ أ ب mentor.lscf.ucsb.edu/course/fall/eemb157/lecture/Lectures%2016,%2017%2018.ppt
- ^ أ ب http://frank.mtsu.edu/~jshardo/bly2010/nervous/receptor.html
وصلات خارجية
All content in this article is created by Marefa contributors and is © Marefa. All rights reserved.