تضخم الأطراف
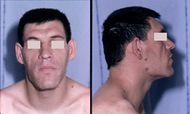
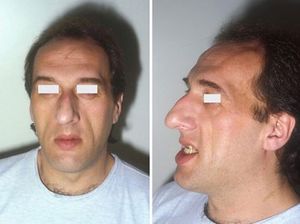
| Facial aspect of a patient with acromegaly. The nose is widened and thickened, the cheekbones are obvious, the forehead bulges, the lips are thick and the facial lines are marked. The forehead and overlying skin is thickened, which may lead to frontal bossing (an unusually prominent forehead sometimes with a heavy brow ridge). | |
| ICD-10 | E22.0 |
| ICD-9 | 253.0 |
| OMIM | 102200 |
| DiseasesDB | 114 |
| MedlinePlus | 000321 |
| eMedicine | med/27 derm/593 |
| MeSH | D000172 |
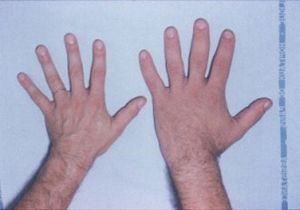
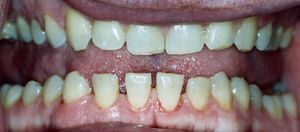
تضخم الأطراف Acromegaly هى حالة ينَتجُ عنها تمدد في عظام الوجه والقدمين واليدين. ومعظم حالات تضخم الأَطراف يُسبِّبها تورم الغدَّة النُّخاميَّة، وتحدث عند الأَشخاص ذوي الطول الطبيعي.
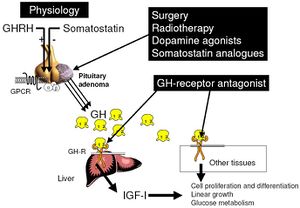
وإذا بدأ العلاج خلال فترة الطفولة يُمكن السَّيطرة على العملاقيَّة بزيادة نشاط الغدة النُّخاميَّة عن طريق العلاج بالإشْعاع. وفي بعض الحالات تزال أورام الغدَّة عن طريق الجراحة. وبإِمكان الجرَّاح أن يصل إلى الورم من خلال التجويف الأنفي، قاطعًا خلال قاع الجمجمة ليصل إِلى الغدَّة النُّخاميَّة. ولاتبدو على المريض أي آثار ندبات بعد إِجراء العملية.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
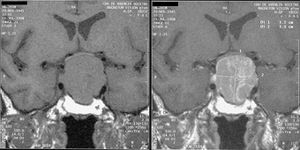
التشخيص

انظر أيضا
المصادر
وصلات خارجية
- AcromegalyAnswersWebinar.com A valuable webinar series that teaches you what you need to know about acromegaly, its impact, and available treatment options
- AcromegalyAnswersBlog.com A place to learn more about acromegaly, read others’ perspectives, receive helpful hints, and share your thoughts
- www.AcromegalyCommunity.com Emotional and communal support for those touched by Acromegaly
- acromegaly.org A satellite site of the Pituitary Network Association
- Acromegaly and Gigantism (a very comprehensive article)
- Acromegaly and Gigantism (Image of a patient with macroglossia - enlargement of the tongue)
- Patient community for acromegaly