أكسيد النحاس الثنائي

| |
| |
| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك
Copper(II) oxide
| |
| أسماء أخرى
Cupric oxide
| |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.882 |
| رقم EC |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| رقم RTECS |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | CuO |
| كتلة مولية | 79.545 g/mol |
| المظهر | black to brown powder |
| الكثافة | 6.315 g/cm3 |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| نقطة الغليان | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | insoluble |
| قابلية الذوبان | soluble in ammonium chloride, potassium cyanide insoluble in alcohol, ammonium carbonate |
| الفجوة الحزمية | 1.2 eV |
| القابلية المغناطيسية | +238.9·10−6 cm3/mol |
| معامل الانكسار (nD) | 2.63 |
| البنية | |
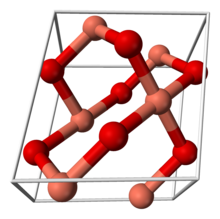
| البنية البلورية | monoclinic, mS8[1] |
| الزمرة الفراغية | C2/c, #15 |
| ثابت العقد | a = 4.6837, b = 3.4226, c = 5.1288 |
| ثابت العقد | α = 90°, β = 99.54°, γ = 90° |
| الكيمياء الحرارية | |
| الإنتالپية المعيارية للتشكل ΔfH |
−156 kJ·mol−1 |
| Standard molar entropy S |
43 J·mol−1·K−1 |
| المخاطر | |
| صفحة بيانات السلامة | Fisher Scientific |
| ن.م.ع. مخطط تصويري | 
|
| ن.م.ع. كلمة الاشارة | Warning |
| H410 | |
| P273, P391, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |
| نقطة الوميض | Non-flammable |
| حدود التعرض الصحية بالولايات المتحدة (NIOSH): | |
PEL (المسموح)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
REL (الموصى به)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
IDLH (خطر عاجل)
|
TWA 100 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |
أنيونات أخرى
|
Copper(II) sulfide |
كاتيونات أخرى
|
Nickel(II) oxide Zinc oxide |
مركـّبات ذات علاقة
|
Copper(I) oxide |
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
أكسيد النحاس الثنائي Copper(II) oxide مركب كيميائي له الصيغة CuO ، ويكون على شكل مسحوق أسود .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الخواص
- لا ينحل مركب أكسيد النحاس الثنائي لا في الماء ولا في الإيثانول. ينحل في الأحماض مشكلاً أملاح النحاس الثنائي الموافقة.
التحضير
يحضر أكسد النحاس الثنائي بتسخين فلز النحاس حتى الاحمرار عند درجة حرارة تراوح 800°س، ثم بتمرير الهواء على الفلز المحمر (أكسدة هوائية) حسب المعادلة:
- Cu + 1/2 O2 → CuO
يمكن تحضيره أيضاً من ترسيب هيدروكسيد النحاس الثنائي من تفاعل كبريتات النحاس مع الصود الكاوي (هيدروكسيد الصوديوم)، ثم بتسخيه في المحلول الناتج حتى الغليان فيترسب أكسيد النحاس الثنائي الأسود.
- CuSO4 + 2NaOH → Cu(OH)2 + Na2SO4
- Cu(OH)2 → CuO + H2O
يحصل على أنقى شكل من أكسيد النحاس الثنائي بالتفكك الحراري لنترات النحاس.
الاستخدامات
- يستخدم في تلوين الزجاج مثل النظارات الشمسية، وفي تلوين البورسلين.
- يستعمل كحفاز في الاصطناع العضوي.
- كما يدخل في تحضير مركبات النحاس الأخرى.
As a significant product of copper mining, copper(II) oxide is the starting point for the production of other copper salts. For example, many wood preservatives are produced from copper oxide.[3]
Cupric oxide is used as a pigment in ceramics to produce blue, red, and green, and sometimes gray, pink, or black glazes.
It is incorrectly used as a dietary supplement in animal feed.[4] Due to low bioactivity, negligible copper is absorbed.[5]
It is used when welding with copper alloys.[6]
A copper oxide electrode formed part of the early battery type known as the Edison–Lalande cell. Copper oxide was also used in a lithium battery type (IEC 60086 code "G").
Pyrotechnics and fireworks
Used as moderate blue coloring agent in blue flame compositions with additional chlorine donors and oxidizers such as chlorates and perchlorates. Providing oxygen it can be used as flash powder oxidizer with metal fuels such as magnesium, aluminium, or magnalium powder. Sometimes it is used in strobe effects and thermite compositions as crackling stars effect.
انظر أيضاً
المصادر
- ^ The effect of hydrostatic pressure on the ambient temperature structure of CuO, Forsyth J.B., Hull S., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 3 (1991) 5257–5261 , DOI:10.1088/0953-8984/3/28/001. Crystallographic point group: 2/m or C2h. Space group: C2/c. Lattice parameters: a = 4.6837(5), b = 3.4226(5), c = 5.1288(6), α = 90°, β = 99.54(1)°, γ = 90°.
- ^ أ ب ت NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards 0150
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةUllmann - ^ "Uses of Copper Compounds: Other Copper Compounds". Copper Development Association. 2007. Retrieved 2007-01-27.
- ^ Cupric Oxide Should Not Be Used As a Copper Supplement for Either Animals or Humans, Baker, D. H., J. Nutr. 129, 12 (1999) 2278-2279
- ^ "Cupric Oxide Data Sheet". Hummel Croton Inc. 2006-04-21. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
وصلات خارجية
| Copper(II) oxide
]].
