معاهدة نرچنسك
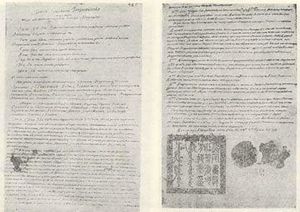 A copy of the Treaty of Nerchinsk in Latin | |
| النوع | Border treaty |
|---|---|
| وُقـِّعت | 27 أغسطس 1689 |
| المكان | نرچنسك |
| انتهاء الصلاحية | مايو 28, 1858 |
| المفاوضون | |
| الموقعون | |
| الأطراف | |
| اللغات | |

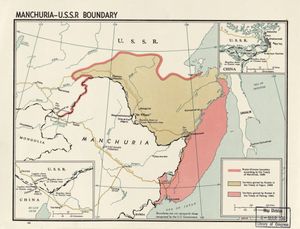
معاهدة نرچنسك Treaty of Nerchinsk في 1689 كانت أول معاهدة بين روسيا والصين في عهد أسرة تشينگ. تخلى الروس عن المنطقة شمال نهر آمور حتى سلسلة جبال ستانوڤوي واحتفظوا بالمنطقة بين نهر أرگون و بحيرة بايكال. هذه الحدود بطول نهر أرگون وسلسلة جبال ستانوڤوي استمرت حتى استحواذ الآمور في 1858 و 1860. وقد فتحت الأسواق للبضائع الروسية في الصين، ومنحت الروس إمدادات وكماليات صينية.
لخلفية الموضوع، انظر تاريخ العلاقات الروسية الصينية. الاتفاقية وُقـِّعت في نرچنسك في 27 أغسطس 1689.[1] The signatories were Songgotu on behalf of the الامبراطور كانگشي and Fyodor Golovin on behalf of the Russian tsars Peter I and Ivan V.
النص الحاكم للمعاهدة هو المكتوب باللاتينية، بترجمات إلى الروسية والمنچو، ولكن تلك النسخ تفاوتت بدرجة كبيرة. There was no official Chinese text for another two centuries,[2] but the border markers were inscribed in Chinese along with Manchu, Russian and Latin.[3]
Later, in 1727, the Treaty of Kiakhta fixed what is now the border of Mongolia west of the Argun and opened up the caravan trade. In 1858 (Treaty of Aigun) Russia annexed the land north of the Amur and in 1860 (Treaty of Beijing) took the coast down to Vladivostok. The current border runs along the Argun, Amur and Ussuri Rivers.
الأسماء
معاهدة نرچنسك تـُكتَب باللغات الأخرى كالتالي:
- إنگليزية: Treaty of Nerchinsk
- لاتينية: Tractatus pacis de Nipkoa
- روسية: Нерчинский договор (transliteration: Nerčinskij dogovor)
- Manchu: ᠨᡳᠪᠴᡠ ᡳ
ᠪᠣᠵᡳ
ᠪᡳᡨᡥᡝ, (Möllendorff transliteration: nibcoo-i bade bithe) - simplified Chinese: 尼布楚条约; traditional Chinese: 尼布楚條約; pinyin: Níbùchǔ Tiáoyuē
التاريخ

From about 1640, Russians entered the Amur basin from the north, into land claimed by the Manchus who at this time were just beginning their conquest of China. The Manchus had, by the 1680s, completed the conquest of China and eliminated the last Ming successor states in the south.[4] With the Manchu Qing dynasty now firmly in control of the South, it was in a position to deal with what they saw as Russian encroachment in Manchuria, the dynasty's ancient homeland.[5] By 1685 most of the Russians had been driven out of the area. See Sino–Russian border conflicts for details.
After their first victory at Albazin in 1685, the Qing government sent two letters to the Tsar (in Latin) suggesting peace and demanding that Russian freebooters leave the Amur. The Russian government, knowing that the Amur could not be defended and being more concerned with events in the west, sent Fyodor Golovin east as plenipotentiary. Golovin left Moscow in January 1686 with 500 streltsy and reached Selenginsk near Lake Baikal in October 1687, from whence he sent couriers ahead. It was agreed the meeting would be in Selenginsk in 1688. At this point the Oirats (western Mongols) under Galdan attacked the eastern Mongols in the area between Selenginsk and Peking and negotiations had to be delayed. To avoid the fighting Golovin moved east to Nerchinsk where it was agreed that talks would take place. The Manchus with 3,000 to 15,000 soldiers under Songgotu left Peking on June 1689 and arrived in July. Talks went on from August 22 to September 6.
The language used was Latin, the translators being, for the Russians, a Pole named Andrei Bielobocki and for the Chinese the Jesuits Jean-Francois Gerbillon and Thomas Pereira. To avoid problems of precedence, tents were erected side by side so that neither side would be seen as visiting the other. Russian acceptance of the treaty required a relaxation of what had been, in Ming (the former dynasty) times, an iron rule of Chinese diplomacy, requiring the non-Chinese party to accept language which characterized the foreigner as an inferior or tributary.[6][7] The conspicuous absence of such linguistic gamesmanship from the Treaty of Nerchinsk,[8] together with the equally conspicuous absence of Chinese language or personnel, suggests that the Kangxi emperor was using the Manchu language as a deliberate end-run around his more conservative Han bureaucracy. The Yuan Empire's rule of Mongol tribes living around Lake Baikal was claimed by the Qing, who incited the defection of the Nerchinsk Onggut and Buryat Mongols away from the Russians.[9]
The Manchus wished to remove the Russians from the Amur. They were interested in the Amur since it was the northern border of the original Manchu heartland. They could ignore the area west of the Argun since it was then controlled by the Oirats. The Kangxi Emperor (i.e. the reigning Qing (Manchu) dynasty emperor of China) also wished to settle with Russia in order to free his hands to deal with the Dzungar Mongols of Central Asia, to his northwest.[10][11] The Manchus also wanted a delineated frontier to keep nomads and outlaws from fleeing across the border.[12]
The Russians, for their part, knew that the Amur was indefensible and were more interested in establishing profitable trade, which the Kangxi Emperor had threatened to block unless the border dispute were resolved.[13] Golovin accepted the loss of the Amur in exchange for possession of Trans-Baikalia and access to Chinese markets for Russian traders. The Russians were also concerned with the military strength of the Manchus, who had demonstrated their capability, in 1685 and 1686, by twice overrunning the Russian outpost at Albazin.[14]
The Crimean Tatars were defeating the Russians and the Qing's enemies, the Dzungars under Galdan, were seizing Mongolia, so both the Russians and Qing were eager to end the conflict.[15]
الحدود
The agreed boundary was the Argun River north to its confluence with the Shilka River, up the Shilka to the "Gorbitsa River", up the Gorbitsa to its headwaters, then along the east-west watershed through the Stanovoy Mountains and down the Uda River (Khabarovsk Krai) to the Sea of Okhotsk at its southwest corner.
The border west of the Argun was not defined (at the time, this area was controlled by the Oirats). Neither side had very exact knowledge of the course of the Uda River. The Gorbitsa is hard to find on modern maps.
تفاصيل المعاهدة
The treaty had six paragraphs: 1 and 2: definition of the border, 3. Albazin to be abandoned and destroyed. 4. Refugees who arrived before the treaty to stay, those arriving after the treaty to be sent back. 5. Trade to be allowed with proper documents. 6. Boundary stones to be erected, and general exhortations to avoid conflict.
الأبعاد الاقتصادية
The treaty was "a triumph of intercultural negotiation" that gave Russians access to Chinese markets for expensive furs; Russians purchased porcelain, silk, gold, silver, and tea as well as with provisions for the northern garrisons.[16] The cross-border trade created a multiethnic character to Nerchinsk and Kyakhta in Siberia. They became locales for the interaction of Russian, Central Asian, and Chinese cultures. The trade extended European economic expansion deep into Asia. Profitable trade fell off in the 1720s because the policies of Peter I limited private initiative and ended Siberia's role as a major economic link between the West and East.[17]
التطورات اللاحقة
Russian interest in the Amur River was revived in the 1750s. In 1757 Fedor Ivanovich Soimonov was sent to map the area. He mapped the Shilka, which was partly in Chinese territory, but was turned back when he reached its confluence with the Argun. In 1757 Vasili Fedorovich Bradishchev was sent to Peking to investigate the possibility of using the Amur. He was received cordially and given a definite no. After that the matter was dropped.[18]
In 1799, when Adam Johann von Krusenstern visited Canton he saw an English ship that had brought furs from Russian America in five months as opposed to the two years or more for the Okhotsk–Yakutsk–Kyakhta route. He saw that this could replace the overland trade. He submitted a memoir to the Naval Ministry which led to his command of the first Russian circumnavigation. He was able to sell American furs at Canton after some official resistance. Only when he returned to Kronstadt did he learn that his presence in Canton had provoked an edict making clear that Russian trade with the Middle Kingdom would be confined to Kyakhta.[19]
للباقي، انظر معاهدة كياختا و استحواذ الآمور.
انظر أيضاً
الهامش
- ^ Krausse, Alexis Sidney (1899). Russia in Asia: a record and a study, 1558-1899. G. Richards. pp. 330–31. Retrieved 26 August 2011.
- ^ On the difference between version of the treaty, see V. S. Frank, "The Territorial Terms of the Sino-Russian Treaty of Nerchinsk, 1689", The Pacific Historical Review 16, No. 3 (August 1947), 265–170.
- ^ Journal of the Royal Central Asian Society, 281.
- ^ Elman, Benjamin A (2007), "Ming-Qing border defense, the inward turn of Chinese Cartography, and Qing expansion in Central Asia in the Eighteenth Century", in Diana Lary (ed.) Chinese State at the Borders. Univ. Wash. Press, pp. 29–56.
- ^ Ellman (2007: 47)
- ^ Fairbank, John K (1986), The Great Chinese Revolution: 1800-1985. Harper & Row, pp. 36-37.
- ^ Keay, John (2009), China: a History. Basic Books, pp. 439-440
- ^ Elman 2007:50-51)
- ^ Peter C Perdue (30 June 2009). China Marches West: The Qing Conquest of Central Eurasia. Harvard University Press. pp. 167–169. ISBN 978-0-674-04202-5.
- ^ Elman 2007: 50)
- ^ Perdue, Peter C (1996), "Military mobilization in Seventeenth and Eighteenth-Century China, Russia, and Mongolia". Modern Asian Studies 30: 757-793, 763-764.
- ^ Gang Zhao (2006), "Reinventing China: Imperial Qing ideology and the rise of modern Chinese national identity in the early Twentieth Century". Modern China 32: 3-30, 14.
- ^ Elman 2007: 47)
- ^ Black, Jeremy (1999), War in the Early Modern World: 1450-1815. UCL Press., p. 98.
- ^ Christopher I. Beckwith (16 March 2009). Empires of the Silk Road: A History of Central Eurasia from the Bronze Age to the Present. Princeton University Press. pp. 235–. ISBN 1-4008-2994-1.
- ^ Peter C. Perdue, "Nature and Power: China and the Wider World." Social Science History 37.3 (2013): 373-391.
- ^ Eva-Maria Stolberg, "Interracial Outposts in Siberia: Nerchinsk, Kiakhta, and the Russo-Chinese Trade in the Seventeenth/Eighteenth Centuries." Journal of Early Modern History 4#3-4 (2000): 322-336.
- ^ Foust, Muscovite and Mandarin p. 245-250
- ^ Foust, page 319-32
المراجع
- Bao, Muping. "trade centres (maimaicheng) in Mongolia, and their function in Sino–Russian trade networks." International Journal of Asian Studies 3.2 (2006): 211-237.
- Chen, Vincent. Sino Russian Relations in the Seventeenth Century. (Martinus Nijhoff, 1966).
- Frank, V.S. "The Territorial Terms of the Sino-Russian Treaty of Nerchinsk, 1689". The Pacific Historical Review (August 1947): 265-170.0
- Gardener, William. "China and Russia: The Beginnings of Contact" History Today, 27 (January 1977): 22-30.
- Maier, Lothar. "Gerhard Friedrich Müller's memoranda on Russian relations with China and the reconquest of the Amur." Slavonic and East European Review (1981): 219-240. online
- Mancall, Mark. Russia and China: Their Diplomatic Relations to 1728. Harvard University Press, 1971.
- March, G. Patrick (1996), Eastern Destiny: Russia in Asia and the North Pacific, ISBN 0-275-95566-4, https://books.google.com/books?id=ujht5Y_yQooC
- Perdue, Peter C. China Marches West: The Qing Conquest of Central Eurasia. Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, 2005.
- Perdue, Peter C. "Boundaries and trade in the early modern world: Negotiations at Nerchinsk and Beijing." Eighteenth-Century Studies (2010): 341-356. online
- Perdue, Peter C. "Nature and Power: China and the Wider World." Social Science History 37.3 (2013): 373-391.
- Perdue, Peter C. "Military Mobilization in Seventeenth and Eighteenth-Century China, Russia, and Mongolia." Modern Asian Studies 30.4 (1996): 757-793. online
- Stolberg, Eva-Maria. "Interracial Outposts in Siberia: Nerchinsk, Kiakhta, and the Russo-Chinese Trade in the Seventeenth/Eighteenth Centuries." Journal of Early Modern History 4#3-4 (2000): 322-336.
- Zhao, Gang (January 2006), "Reinventing China Imperial Qing Ideology and the Rise of Modern Chinese National Identity in the Early Twentieth Century", Modern China 32 (1): 3–30, doi:, https://web.archive.org/web/20140420022354/http://mcx.sagepub.com/content/32/1/3.abstract
وصلات خارجية
- Articles containing إنگليزية-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Articles containing لاتينية-language text
- Articles containing روسية-language text
- Articles containing simplified Chinese-language text
- Articles containing traditional Chinese-language text
- تاريخ منشوريا
- 1689 في الصين
- 1689 في روسيا
- معاهدات 1689
- المعاهدات الروسية الصينية
- أسرة تشينگ
- معاهدات قيصرية روسيا
- معاهدات أسرة تشينگ