حمض الفوماريك
| لهيب الشوق ساهم بشكل رئيسي في تحرير هذا المقال
|
| |
| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك
(E)-Butenedioic acid
| |
| أسماء أخرى
trans-1,2-Ethylenedicarboxylic acid
2-Butenedioic acid trans-butenedioic acid Allomaleic acid Boletic acid Donitic acid Lichenic acid | |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.404 |
| رقم EC |
|
| E number | E297 (preservatives) |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | C4H4O4 |
| كتلة مولية | 116.07 g/mol |
| المظهر | White solid |
| الكثافة | 1.635 g/cm³, solid |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | 0.63 g/100 mL |
| الحموضة (pKa) | pka1 = 3.03, pka2 = 4.44 |
| المخاطر | |
تبويب الاتحاد الاوروپي (DSD)
|
Irritant (Xi) |
| توصيف المخاطر | R36 |
| تحذيرات وقائية | (S2) S26 |
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
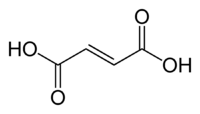
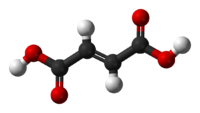
حمض الفوماريك Fumaric acid أو trans-butenedioic acid، هو مركب كيميائي يعبر عنه بصيغة HO2CCH=CHCO2H.
هذا المركب البلوري الأبيض هو أحد نظيري الأحماض الكربوكسيلية الغير مشبعة، والحمض الثاني هو حمض الماليك، wherein the carboxylic acid groups are cis. ويتميز بمذاق يشبه الفاكهة. وتعرف أملاح وإسترات حمض الفوماريك باسم فومارات.
علم الأحياء
Fumaric acid is found in fumitory (Fumaria officinalis), bolete mushrooms (specifically Boletus fomentarius var. pseudo-igniarius), lichen, and Iceland moss.
Fumarate is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle used by cells to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from food. It is formed by the oxidation of succinate by the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase. Fumarate is then converted by the enzyme fumarase to malate. Human skin naturally produces fumaric acid when exposed to sunlight.[بحاجة لمصدر]
Fumarate is also a product of the urea cycle.
الطب
Fumaric acid esters are sometimes used to treat psoriasis, as it has been suggested that the condition is caused by an impairment of fumaric acid production in the skin.[1] A starting dose is 60-105 mg daily, which may be gradually increased to as much as 1,290 mg per day. Side-effects include kidney or gastrointestinal disorders, as well as skin flushing; these are mainly caused by excess intake. Decreased white blood cell (WBC) counts have been reported with prolonged use.[بحاجة لمصدر]
الغذاء
Fumaric acid is a food acidulent used since 1946. It is non-toxic. It is generally used in beverages and baking powders for which requirements are placed on purity. It is generally used as a substitute for tartaric acid and occasionally in place of citric acid, at a rate of 1.36 g of citric acid to every 0.91 grams of fumaric acid to add sourness, similar to the way malic acid is used. It is also used as a coagulant in stovetop pudding mixes.
الكيمياء
Fumaric acid was first prepared from Succinic acid.[2] A traditional synthesis involves oxidation of furfural (from the processing of maize) using chlorate in the presence of a vanadium-based catalyst.[3] Nowadays industrial synthesis of fumaric acid is mostly based on catalytic isomerisation of maleic acid in aqueous solutions at low pH. Maleic acid is accessible in large volumes as a hydrolysis product of maleic anhydride, produced by catalytic oxidation of benzene or butane.[4]
The chemical properties of fumaric acid can be anticipated from its component functional groups. This weak acid forms a diester, it undergoes additions across the double bond, and it is an excellent dienophile.
Fumaric acid does not combust in a bomb calorimeter under conditions where maleic acid deflagrates smoothly. For teaching experiments designed to measure the difference in energy between the cis- and trans- isomers, a measured quantity of carbon can be ground with the subject compound and the enthalpy of combustion computed by difference.
استخدامات أخرى
Fumaric acid is used in the manufacture of polyester resins and polyhydric alcohols and as a mordant for dyes.
السلامة
Fumaric acid converts to the irritant maleic anhydride, upon partial combustion.
انظر أيضا
- طب الأمراض الجلدية
- Photosynthesis
- حمص الماليك, the cis-isomer of fumaric acid
المصادر
- ^ Br J Dermatol 05; 152(4):597-615), BR J Dermatol 98;138(3): 456-460
- ^ Volhard, J. "Darstellung von Maleïnsäureanhydrid" Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie 1892, volume 268, page 255-6. DOI: 10.1002/jlac.18922680108
- ^ Milas, N. A. "Fumaric Acid" Organic Synthesis 1943, Collective Volume 2, page 302. Online version
- ^ British Patent No. 775,912, publicated on the May 29, 1957, by Monsanto Chemical Company.
وصلات خارجية
- Pages using Chembox with unknown parameters
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- E number from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Chembox
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chembox image size set
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- مقالات ذات عبارات بحاجة لمصادر
- أحماض ثنائية الكربوكسيلية
- مواد مضافة غذائية
- منظمات حموضة الطعام
- Fumarates
