حمض اليوديك
| |||
|
| |||
| الأسماء | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| أسماء أخرى
Iodic(V) acid
| |||
| المُعرِّفات | |||
| رقم CAS | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.056 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| الخصائص | |||
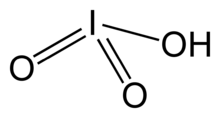
| الصيغة الجزيئية | HIO3 | ||
| كتلة مولية | 175.91 g/mol | ||
| المظهر | White solid | ||
| الكثافة | 4.62 g/cm3, solid | ||
| نقطة الانصهار | |||
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | 269 g/100 mL (20 °C) | ||
| الحموضة (pKa) | 0.75 | ||
| القابلية المغناطيسية | −48.0·10−6 cm3/mol | ||
| المخاطر | |||
| خطر رئيسي | acid, corrosive, oxidant | ||
| ن.م.ع. مخطط تصويري |  
| ||
| ن.م.ع. كلمة الاشارة | Danger | ||
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |||
| نقطة الوميض | Non-flammable | ||
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |||
كاتيونات أخرى
|
Lithium iodate Potassium iodate | ||
| حمض الكلوريك حمض البروميك | |||
مركـّبات ذات علاقة
|
حمض اليوديك المائي Iodine pentoxide Periodic acid | ||
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |||
| مراجع الجدول | |||
حمض اليوديك Iodic acid، HIO3، يمكن الحصول عليه كمادة صلبة بيضاء أو شبه بيضاء. It dissolves in water very well, but it also exists in the pure state, as opposed to chloric acid or bromic acid. Iodic acid contains iodine in the oxidation state +5 and it is one of the most stable oxo-acids of the halogens in its pure state. When iodic acid is carefully heated, it dehydrates to iodine pentoxide. On subsequent heating, the iodine pentoxide further decomposes, giving a mix of iodine, oxygen and lower oxides of iodine.
التحضير
Iodic acid can be produced by oxidizing I2 with strong oxidizers such as Nitric acid HNO 3, Chlorine Cl 2, حمض الكلوريك HClO 3 or Hydrogen peroxide H 2O 2,[2] for example :
البنية
Iodic acid crystallises from acidic solution as orthorhombic α-HIO 3 in space group P212121. The structure consists of pyramidal molecules linked by hydrogen bonding and intermolecular iodine-oxygen interactions. The I=O bond lengths are 1.81 Å while the I–OH distance is 1.89 Å.[3][4][5] Several other polymorphs have been reported, including an orthorhombic γ form in space group Pbca[6] and an orthorhombic δ form in space group P212121.[7] All of the polymorphs contain pyramidal molecules, hydrogen bonding and I···O interactions, but differ in packing arrangement.
الخصائص
Iodic acid is a relatively strong acid with a pKa of 0.75. It is strongly oxidizing in acidic solution, less so in basic solution. When iodic acid acts as oxidizer, then the product of the reaction is either iodine, or iodide ion. Under some special conditions (very low pH and high concentration of chloride ion, e.g. in concentrated hydrochloric acid), iodic acid is reduced to iodine trichloride, a golden yellow compound in solution and no further reduction occurs. In the absence of chloride ions, when there is an excess amount of reductant, then all iodate is converted to iodide ion. When there is an excess amount of iodate, then part of the iodate is converted to iodine.It may be used in preparation of ionization to form alkyl halide
الاستخدامات
Iodic acid is used as a strong acid in analytical chemistry. It may be used to standardize solutions of both weak and strong bases, with methyl red or methyl orange as the indicator.
الاستخدام في صناعة الملح
Iodic acid can be used to synthesize sodium or potassium iodate for increasing iodine content of salt.[بحاجة لمصدر]
الأحماض الأكسجينية الأخرى
Iodate is part of a series of oxyacids in which iodine can assume oxidation states of −1, +1, +3, +5, or +7. A number of neutral iodine oxides are also known.
| Iodine oxidation state | −1 | +1 | +3 | +5 | +7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Hydrogen iodide | Hypoiodous acid | Iodous acid | Iodic acid | Periodic acid |
| Formula | HI | HIO | HIO2 | HIO3 | HIO4 or H5IO6 |
الهامش
- ^ "Iodic acid" (PDF) (in الإنجليزية).
- ^ (بالألمانية) Arnold F. Holleman, Nils Wiberg, « Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie », 102. Auflage, Berlin, 2007. ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 863. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Rogers, Max T.; Helmholz, Lindsay (1941). "The Crystal Structure of Iodic Acid". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 63 (1): 278–284. doi:10.1021/ja01846a068.
- ^ Ståhl, Kenny; Szafranski, Marek (1992). "A Single-Crystal Neutron Diffraction Study of HIO3 at 295 and 30 K and of DIO3 at 295 K". Acta Chem. Scand. 46: 1146–1148. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.46-1146.
- ^ Fischer, Andreas; Lindsjö, Martin (2005). "γ-HIO3 – a Metastable, Centrosymmetric Polymorph of Iodic Acid". Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 631 (9): 1574–1576. doi:10.1002/zaac.200500099.
- ^ Wu, Tao; Zavalij, Peter Y.; Zachariah, Michael R. (2017). "Crystal structure of a new polymorph of iodic acid, δ-HIO3, from powder diffraction". Powder Diffraction. 32 (4): 261–264. Bibcode:2017PDiff..32..261W. doi:10.1017/S0885715617000859. S2CID 104100313.
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Chembox
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Articles with unsourced statements from June 2010
- مركبات الهيدروجين
- يودات
- Analytical standards
- أحماض مؤكسدة
- عوامل مؤكسدة
- أحماض معدنية
- مركبات اليود



