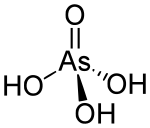
حمض الزرنيخ
| |
| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك
Arsenic acid, arsoric acid
| |
| أسماء أخرى
Arsenic acid
Orthoarsenic acid Desiccant L-10 Zotox | |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.001 |
| رقم EC |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| رقم RTECS |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1553, 1554 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | H3AsO4 |
| كتلة مولية | 141.94 g/mol |
| المظهر | White translucent crystals, hygroscopic. |
| الكثافة | 2.5 g/cm3 |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| نقطة الغليان | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | 16.7 g/100 mL |
| قابلية الذوبان | soluble in alcohol |
| ضغط البخار | 55 hPa (50 °C) |
| الحموضة (pKa) | 2.19, 6.94, 11.5 |
| البنية | |
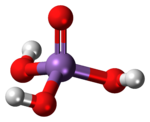
| الشكل الجزيئي | Tetrahedral |
| المخاطر | |
| خطر رئيسي | Extremely toxic, carcinogenic, corrosive |
| ن.م.ع. مخطط تصويري |     
|
| ن.م.ع. كلمة الاشارة | Danger |
| H301, H312, H314, H331, H350, H361, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P281, P301+P310, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |
| نقطة الوميض | Non-flammable |
| الجرعة أو التركيز القاتل (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (الجرعة الوسطى)
|
48 mg/kg (rat, oral)
6 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) |
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |
أنيونات أخرى
|
حامض الفوسفوريك |
كاتيونات أخرى
|
زرنيخات الصوديوم |
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
حمض الزرنيخ Arsenic acid مركب كيميائي له الصيغة H3AsO4 ، كما يكتب على الشكل AsO(OH)3 .
الخواص
التحضير
Arsenic acid is prepared by treating arsenic trioxide with concentrated nitric acid. Dinitrogen trioxide is produced as a by-product.[1]
- As2O3 + 2 HNO3 + 2 H2O → 2 H3AsO4 + N2O3
The resulting solution is cooled to give colourless crystals of the hemihydrate H3AsO4·1⁄2H2O, although the dihydrate H3AsO4·2H2O is produced when crystallisation occurs at lower temperatures.[1]
سبل أخرى
Arsenic acid is slowly formed when arsenic pentoxide is dissolved in water, and when meta- or pyroarsenic acid is treated with cold water. Arsenic acid can also be prepared directly from elemental arsenic by moistening it and treating with ozone.
- 2 As + 3 H2O + 5 O3 → 2 H3AsO4 + 5 O2
الاستخدامات
Commercial applications of arsenic acid are limited by its toxicity. It is a precursor to a variety of pesticides. It has found occasional use as a wood preservative, a broad-spectrum biocide, a finishing agent for glass and metal, and a reagent in the synthesis of some dyestuffs and organic arsenic compounds.[2]
السلامة
Arsenic acid is extremely toxic and carcinogenic, like all arsenic compounds. Corrosive. The ج.م.50 in rabbits is 6 mg/kg (0.006 g/kg).[3]
المصادر
- ^ أ ب G. Brauer, ed. (1963). "Arsenic Acid". Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 1 (2nd ed.). New York: Academic Press. p. 601.
- ^ Minerals Yearbook, 2008, V. 1, Metals and Minerals. Government Printing Office. 2010. pp. 6–. ISBN 978-1-4113-3015-3.
- ^ Grund, Sabina C.; Hanusch, Kunibert; Wolf, Hans Uwe (2008). "Arsenic and Arsenic Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_113.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
