تعطل حركة الطيران بعد بركان إيافيالايوكل 2010
| أحداث هذه المقالة هي أحداث جارية. المعلومات المذكورة قد تتغير بسرعة مع تغير الحدث. |
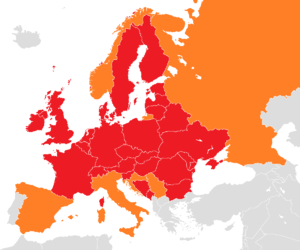
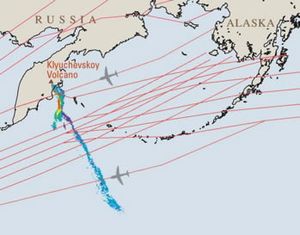
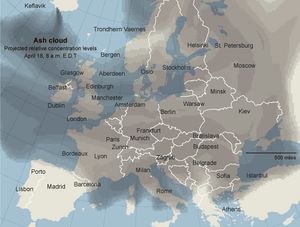
أدى الثوران الثاني لبركان إيافيالايوكل في آيسلندا في 14 أبريل 2010 إلى تعطل حركة الطيران في أجزاء واسعة من اوروبا.[1] ونتيجة لمخاوف من تناثر جسيمات بركانية في ممرات الطائرات وما يمكن أن يلحقه بأضرار في محركات الطائرات، فقد أغلقت المجالات الجوية في العديد من البلدان، وتعطل ملايين من المسافرين. ويعتبر هذا أكبر إغلاق مجالا جوي منذ الحرب العالمية الثانية.[2]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
خلفية
محاولات فتح المجال الجوي
إغلاقات المجال الجوي
| On 16 April 2010, Austro Control ceased air activities at airports in both Vienna and Linz; Salzburg and Innsbruck stopped flights at 18:00 UTC; and Graz and Klagenfurt followed at 21:00 UTC. At 00:30 on 18 April, all Austrian airports were closed until 14:00.قالب:Verification failed[3] | |
| On Saturday 17 April, the airspace over Belarus was closed.[4] | |
| Belgium's airspace closed at 14:30 UTC on 15 April. It would remain closed until 08:00 UTC on Sunday 18 April at least, but would probably remain closed until 16:00 UTC.[5] | |
| The airspace over Bosnia and Herzegovina was closed to traffic from 08:00 (06:00 UTC) until midnight (22:00 UTC) on 17 April.[6] | |
| On Sunday 18 April, all Bulgarian airports were closed.[7] However, at 14:00 local time the airports in Sofia and Plovdiv were open.[8] | |
| At 02:00 CET on 17 April, the air space over northern Croatia was closed, including Zagreb. At 08:00 CET the airports at Pula, Rijeka, Zadar and Lošinj were closed.[9][مطلوب توضيح] | |
| On 16 April Czech airspace was closed, after partial closure forced some aircraft to land at Brno. Czech airspace would remain closed at least until 12:00 on 19 April. During 16 April, approximately 400 flights to and from پراگ were cancelled. | |
| Naviair, the state-owned company controlling Danish airspace, announced that Denmark's airspace would close at 16:00 UTC on 15 April.[10]
The 70th birthday celebration of Queen Margrethe II was affected; several European royals were invited, but had to cancel because of the disruption.[11][12] | |
| On 15 April Estonian Air flights from Tallinn to Oslo, Copenhagen and لندن were cancelled due to airspace closures in Norway, Denmark and the المملكة المتحدة.[13] As the ash cloud spread over Estonia on the night of 16 April, most flights were cancelled.[14] All flights from Tallinn were cancelled until at least 00:00 UTC (03:00 local time) on 19 April.[15] | |
| Finland closed its airspace at 00:00 UTC+03 on 16 April, having previously closed northern, western and central parts of its airspace.[16] | |
| At 23:00 UTC+02 on 15 April, 24 airports, including Charles De Gaulle Airport were closed.[17] On 17 April, the Direction Générale de l'Aviation Civile extended the suspension to 35 airports, including all باريس airports, until 08:00 UTC+2 on Monday 19 April.[18] On 18 April, the closure was extended to at least 15:00 UTC+2 on Monday 19 April for the باريس airports.[19] | |
| On 16 April, all international airports in Germany were closed.[20] All airports were to remain closed until at least 18:00 UTC on Sunday 18 April.[21] | |
| Hungary's airspace was closed at 17:00 UTC on 16 April.[22] It remained closed until at least 10:00 UTC on 18 April.[23] | |
On 15 April 2010, the Irish Aviation Authority announced restrictions on flying in Irish airspace until 06:00 UTC+01 on Friday 16 April at the earliest, with the Dublin Airport Authority's Siobhan Moore describing the event as "extraordinary" on radio programme Today with Pat Kenny.[24] Restrictions were lifted on flights to and from Cork Airport, Shannon Airport and some regional airports by the day's end but restrictions remained at Dublin Airport until 11:00 UTC+1 due to reports from the Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre in London, UK saying that the ash cloud was hovering over the east coast at this point.[24] The government's emergency planning taskforce, which included several government departments (Foreign Affairs / Health and Children / Tourism, Culture and Sport / Transport), An Garda Síochána, Met Éireann, the Irish Aviation Authority and the Dublin Airport Authority, met on the evening of 15 April to discuss the unfolding emergency.[25] On 16 April, Irish air space was reopened for domestic flights from 10:00 UTC+01 and westward transatlantic flights resumed from Dublin Airport.[26] Irish flights which were scheduled to fly eastwards over UK and continental European airspace were grounded however, as the ash plume still threatened their air.[26][26] On 17 April, the ash spread to most of Ireland, and all airspace remains closed.[27] It was announced that airspace would close until 18:00 UTC+01 when the risk coverage would be further assessed.[28] It was then announced that all Irish airspace would remain closed until 13:00 on Sunday 18 April.[29] On 18 April, it was announced by the IAA that airspace would remain closed unil 13:00 GMT+01 on Monday 19 April. A further announcement will be made at 09:00 on Monday. [30] | |
| During the evening of 16 April 2010, the Italian Civil Aviation Authority has closed the Italian airspace limited to Northern Italy for the day of 17 April, excluding emergency flights and flights flying over 35,000 feet[31], from 06:00 UTC+02 until 14:00 UTC+02[32] and later extended to 20:00 UTC+02[31]. Lately the closure was extended to 08:00 UTC+02 of Monday 19 April[33].
Over 198 flights at the airports of Leonardo da Vinci-Fiumicino Airport and Rome Ciampino Airport were cancelled[34][33], 325 flights were cancelled at the Malpensa Airport,[33] 111 at the Linate Airport,[34] 104 at the Naples Airport[33] and 43 at the Catania-Fontanarossa Airport.[34] | |
| Kosovo closed its airspace at 18 April 00:00 UTC+02, cutting air access to Pristina International Airport. It will open at 18 April 14:00 UTC+02 when the ash cloud is expected to go away.[35] | |
| Latvian airspace was closed on 15 April at 21:00 UTC, cutting air access to Riga International Airport and other airports of local significance.[36]
The airspace will remain closed at least until 18 April, 12:00 UTC, but most probably until 22 April.[37] | |
| Luxembourg Airport was also closed for virtually all flights on 16 April 2010 and remained closed at least until the evening of 18 April.[38][39] | |
| Moldova's airspace was affected in the afternoon 16 April.[40] | |
| Air Traffic Services Agency of Serbia and Montenegro[41], shut down all traffic over Montenegro, part of international waters of the Adriatic Sea at 14:00 UTC, 17 April.[42] | |
| The airspace of The Netherlands closed at 17:00 UTC on 15 April.[43] and was to remain closed at least until 20:00 UTC on 18 April.[44] | |
| Air travel in Norway was suspended from 14 April. Airports throughout Nord-Trøndelag, Nordland, Troms and Finnmark were re-opened at times, as those areas were least affected by the ash. The largest of these, Trondheim Airport, Værnes, was opened for six hours on 16 April. However, it and the other four largest airports in Norway (Oslo, Bergen, Stavanger & Sandefjord) remained closed as of 13:00 UTC on 17 April.
In addition to the effects on air travel, the total closure of Norwegian airspace included the 21 search and rescue and medical aircraft and helicopters in the country. The health authorities stated that the challenges faced were unprecedented in modern history, and ambulances and medical personnel were moved north and out of the cities to decentralize the service and supplant the loss of aerial transport.[45] | |
| Poland closed the northern part of its airspace at 18:00 UTC on 15 April. On 16 April its whole airspace was shut down.[46]
The eruption also affected the funeral for the Polish president Lech Kaczyński, his wife Maria and all other passengers who died in a plane crash earlier in April 2010. Family members decided against postponing the ceremony to allow other countries' dignitaries to attend. | |
| Romania closed the north western part of its airspace on at 00:00 local time (UTC+03) on 17 April, including Oradea, Satu Mare, Baia Mare, Cluj-Napoca, Sibiu, and Timişoara airports. The two Bucharest airports were also closed. Romania's entire airspace closed at 18:00 local time (UTC+03) on 17 April until at least 12:00 on 19 April.[47][48] | |
| Air Traffic Services Agency of Serbia and Montenegro[41], shut down all traffic over Serbia at 14:00 UTC on 17 April.[49] | |
| Slovakia's airspace was closed at 15:00 UTC on 16 April.[50] | |
| Slovenia was affected by the volcanic eruption in the evening, 16 April UTC+1. The Slovenian Transport Ministry has partially closed the Slovenian airspace to the north of the 46th parallel from the ground up to the height of 35,500 feet (10,800 m) at 22:00 UTC+1, 16 April, and over the entire territory of Slovenia from the ground up to the height of 35,500 feet (10,800 m)* at 6:00 UTC+1, 17 April. The closure is planned to last till the 01:00 UTC+1, 19 April.[51] This is the first closure of Slovenian airspace since the Ten-Day War.[52] | |
| Aena decided to shut down 7 airports in northern Spain at 20:00 UTC+1 on 17 April and were planned to remain closed until 10:00 on the 18th. [53] However, one hour later, at 21:00 UTC+1 on 17th of April, they started to operate again.[54]. At 8:30 UTC+1 on 18 April 11 airports in the north of Spain were shut down including Barcelona airport (2nd largest). At 12:00 UTC+1 two more airports in the Balearic Islands were closed. All 13 airports are expected to re-open at 20:00 UTC+1 on 18 April. Other minor airports independent from Aena were shut down as well. [55]. They could, however, be re-opened a few hours later at 15:30 UTC+1 [56]. | |
| Sweden's airspace was closed at 20:00 UTC, 15 April. Updates can be found at www.lfv.se[57] | |
| Switzerland's Federal office of Civil Aviation (FOCA) issued a NOTAM[58] on 16 April at 14:15 UTC stating that the FIR Switzerland will be closed for VFR and IFR operations from 16 April, 21:59 UTC to 17 April, 18:00 UTC. Police, SAR and emergency medical helicopter flights are exempted from this measure.[59] Swiss International Air Lines informed its customers on 16 April that the Zurich, Basel, Geneva and Lugano airports would be closed, and that all flights going to those airports would be cancelled.[60] Also some minor airports, such as the one in Ambri were closed. | |
| Ministry of Transport of Ukraine closed majority of national air zones by 00:00 UTC+3 on 17 April. Only South Ukrainian airports have served air companies. Aircrafts flown from Egypt and Thailand to Kiev landed at Simferopol International Airport. All Ukrainian airspace was closed by 15:00 EEST 17 April. | |
|
Scotland was the third region in Europe, after Iceland and Norway, to be affected by the ash with all Scottish airports being closed to IFR flights by 04:00 BST on 15 April. The United Kingdom's controlled airspace was closed to IFR flights at 11:00 UTC (12:00 BST) on 15 April.[61] At 14:45 BST on Friday, 16 April, it was announced by NATS that restrictions preventing IFR flights (which includes all scheduled passenger services) in English and Welsh controlled airspace will remain in place until 13:00 BST (12:00 UTC) on 17 April at the earliest. On Saturday, 17 April, NATS extended this restriction until 01:00 BST (00:00 UTC) on Sunday, 18 April. However, later in the day, this restriction was further extended until 13:00 BST (12:00 UTC) on Sunday. Plans to lift ATC restrictions from 19:00 BST Friday 16 April over a large part of Scottish airspace including Scottish airports, Shetland, Orkney and also Northern Ireland were revoked due to deteriorating conditions.[62] However, later on Saturday, it was suggested that a few domestic flights may be able to take off from Scotland and Northern Ireland before 19:00 BST (18:00 UTC) on Saturday, although most aircraft will remain grounded.[63] At 10:00 BST (09:00 UTC) on Sunday, 18 April, it was announced by NATS that the restrictions on flights in UK airspace would be extended until 01:00 BST (00:00 UTC) on Monday, 19 April.[64][65] The ash has been photographed over the Shetland Islands.[66] The Daily Mail quoted a spokesperson for the Association of British Travel Agents saying 'We estimate there could be as many as a million British people stranded abroad,' and reported the UK will soon face shortages of fresh items that are normally shipped in by air. British tourists in Spain were being told it would be at least 10 days before they could get home even if flights resume soon.[67] There remains no restriction on VFR traffic. RAF Search and rescue aircraft continued to operate as normal, as did flights between Newquay and the Isles of Scilly which operate in uncontrolled airspace at an altitude no higher than 3,000 feet (910 m).[68] On 17 April it was reported that a low level of ash from the volcano had fallen on the Thames Valley area in southeast England. The last commercial flight to leave UK airspace before the lockdown was imposed was a 11:25 BST (10:25 UTC) Thomson Airways flight on 14 April from Cardiff Airport to Sharm el-Sheikh International Airport.[69] There remained not a single commercial airliner in UK airspace until the morning of 16 April when an Air Transat flight was given clearance to leave Glasgow International Airport for Toronto Pearson International Airport.[70] |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الأثر الاجتماعي
التأثير على المسافرين
التأثير على القوات الجوية
الخسائر الإقتصادية
أعلنت المنظمة الدولية للنقل الجوي (إياتا) أن شركات الطيران خسرت حوالي 1.7 مليارات دولار، وأن حجم الأرباح الفائتة لشركات الطيران المتضررة بلغ 400 مليون دولار في اليوم الواحد خلال ذروة الأزمة، وحذرت من إفلاس أكثر من خمس شركات متوسطة وصغيرة الحجم بسبب نقص السيولة الناتجة عن هذه الأزمة. كما طالبت جمعية الشركات الجوية الأوروبية التي تضمُّ 36 شركة، بتقديم مساعدة لشركات الطيران لتمكينها من تحمل خسائرها، وقد قدّرت الجمعية عدد الرحلات التي ألغيت في أوروبا فقط بـ 95 ألف رحلة، كما أكدت المنظمة الدولية للطيران المدني أن تأثير الأزمة على شركات الطيران وحركة المسافرين يفوق إغلاق الأجواء الذي حدث بعد أحداث 11 سبتمبر 2001. الخسائر الإقتصادية الناتجة عن هذه الأزمة لم تقتصرْ على قطاع الطيران في أوروبا فقط، حيث تضرَّرت معظم شركات الطيران العالمية من هذه الأزمة، فقد كشفت الجمعية الأمريكية لصناعة السفر عن أن الأزمة الجوية في أوروبا كلَّفت الاقتصاد الأمريكي 650 مليون دولار، وتأثرت بها ستة آلاف وظيفة في الولايات المتحدة، وذكرت الجمعية أن 78% من الرحلات بين أوروبا والولايات المتحدة تم إلغاؤها خلال الأزمة. كما أفادت الحكومة الفرنسية أن إلغاء الرحلات كلَّف القطاع السياحي 200 مليون يورو على الأقل، كما تكبَّد قطاع السياحة في إسبانيا خسائر قدرها 252 مليون يورو. عربيًّا؛ أعلنت الخطوط الجوية السعودية أنها تكبدت خسائر تقارب 33 مليون دولار نتيجة إغلاق المجال الجوي الأوروبي، وأعلنت شركة طيران الإمارات التابعة لحكومة دبي خسائر بقيمة أكثر من 65 مليون دولار، وفي مصر إنخفضت حركة الطائرات بنسبة تصل إلى 35 %، أيضًا في الكويت وصلت الخسائر الأولية لمؤسسة الخطوط الجوية الكويتية خلال ثلاثة أيام فقط أثناء الأزمة إلى حوالي مليون دينار.[71]
انظر أيضا
- رحلة 9 الخطوط الجوية البريطانية - 1982، تعطل الرحلة بسبب الغبار البركاني
- KLM Flight 867 - 1989, volcanic dust disrupted flight
- Volcanic ash plume
المصادر
- ^ "Volcanic ash spreads more travel misery across Europe". BBC News. 17 April 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- ^ "Qantas cancels flights for a third day". The Sydney Morning Herald. 18 April 2010. Retrieved 18 April 2010.
- ^ Austria starts closing airspace due to volcano ash. Business Week. 16 April 2010.
- ^ Белоруссия полностью закрыла воздушное пространство Lenta.Ru
- ^ Vliegverbod verlengd De Redactie. 17 April 2010.
- ^ [news.ph.msn.com/business/article.aspx?cp-documentid=4034696 Bosnia closes airspace to 2200 GMT: official] Agence France-Presse. 17 April 2010.
- ^ "Небето над България - блокирано". News.bg. 2010-04-18. Retrieved 2010-04-18.
- ^ http://www.dnes.bg/stranata/2010/04/18/otvoriha-letishte-sofiia-i-plovdiv.89558
- ^ Autor: Portal Jutarnji.hr (2010-04-13). "Vulkanski oblak nad sjeverom Hrvatske obustavio zračni promet". Jutarnji.hr. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ "Denmark plans to close airspace due volcanic ash". Reuters. 2009-02-09. Retrieved 2010-04-15.
- ^ "blitz.dk - Vulkan besværliggør kongeliges transport - Kongelige". Jp.dk. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ "Aske kan påvirke dronningens fødselsdag - dr.dk/Nyheder/Indland". Dr.dk. 2008-07-24. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ "Estonian Air tühistas Kopenhaageni, Oslo ja Londoni lennud". Tarbija24. 2010-04-15.
- ^ "Enamik lende Tallinna lennujaamas on tühistatud". Postimees. 2010-04-16.
- ^ "Hetkeoludest Tallinna lennujaamas / Current situation in Tallinn Airport". Tallinn Airport. 2010-04-16.
- ^ "Disruption in air traffic due to volcanic eruption in Iceland".
- ^ "Main Paris airport closing within hours due to ash". Forbes.com. 2001-09-11. Retrieved 2010-04-16.
- ^ Par Europe1.fr. "France : Pas d'avion dans le nord jusqu'à lundi". Europe1.fr. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "actu - Aéroports de Paris". Aeroportsdeparis.fr. Retrieved 2010-04-18.
- ^ The Earthtimes. "EXTRA: Ash to ground planes in Germany, Belgium, Netherlands | Earth Times News". Earthtimes.org. Retrieved 2010-04-15.
- ^ The Earthtimes (2010-04-18 06:00 UTC). "Deutsche Flughäfen bis Sonntag, 20 Uhr, geschlossenSperrung des deutschen Luftraums erneut verlängert". Deutsche Flugsicherung (German Air Traffic Control). Retrieved 2010-04-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Este hétkor lezárják a magyar légteret". Index.hu. Retrieved 2010-04-16. (مجرية)
- ^ "Meghosszabbították a magyar légtérzárat". Origo.hu. 2010-04-17. Retrieved 2010-04-17. (مجرية)
- ^ أ ب Volcanic ash grounds Irish flights. RTÉ. 15 April 2010.
- ^ Irish flights are grounded as Icelandic ash shuts airspace. The Irish Times. 15 April 2010.
- ^ أ ب ت Irish airspace restrictions lifted. RTÉ. 16 April 2010.
- ^ Irish air space closed until 6pm
- ^ Irish airspace closed until 6pm
- ^ "Irish Aviation Authority - Restrictions in Irish Airspace extended to 1300 Sunday 18th April 2010". Iaa.ie. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ http://www.iaa.ie/index.jsp?p=93&n=96&a=867
- ^ أ ب "Nube di cenere, stop ai voli nel Nord Italia fino alle 20" (in Italian). SKY TG24. 17 April 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Iceland: Italian northern air space off from 6 am TO 2 pm". AGI. 16 April 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ أ ب ت ث "Vulcano Islanda, la nube arriva in Italia Al Nord stop ai voli fino a lunedì" (in Italian). Corriere della Sera. 17 April 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ أ ب ت "Traffico aereo: è caos anche in Italia" (in Italian). Corriere della Sera. 17 April 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Aeroporti i Prishtinës mbyllet në mesnatë" (in Albanian). Telegrafi. 18 April 2010. Retrieved 18 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Īslandes vulkāna dēļ pusnaktī slēgs lidostu «Rīga»". Apollo.lv. 2010-04-15. Retrieved 2010-04-16.
- ^ "Gaisa telpu virs Latvijas slēdz līdz svētdienas plkst.15". Tvnet.lv. 2010-04-18. Retrieved 2010-04-18.
- ^ "Keine Flüge vor 14 Uhr", Luxemburger Wort. (بالألمانية) Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ "lux-Airport Accueil" (بالفرنسية) Retrieved 18 April 2010.
- ^ Noinvite - Moldova
- ^ أ ب http://www.smatsa.rs/
- ^ Vazdušni prostor zatvoren u 16h
- ^ Luchtruim dicht om aswolk, (Dutch)
- ^ (Dutch)Luchtruim zeker tot zondag 14.00 gesloten, NRC Handelsblad, 18 April 2010
- ^ "Helsevesenet får utvidede fullmakter". The Norwegian government. 2010-04-16. Retrieved 2010-04-17. (Norwegian)
- ^ "Zamknięta przestrzeń powietrzna nad północną Polską — Wiadomości — WP.PL". Wiadomosci.wp.pl. Retrieved 2010-04-16.
- ^ "Spaţiul aerian al României e închis/ Lista curselor anulate". Adevarul.ro. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ "Romania Closes Entire Airspace As Volcanic Ash Cloud Approaches". Mediafax. 2010-04-17. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ Vazdušni prostor zatvoren u 16h
- ^ "Slovakia closes its airspace". Spectator.sme.sk. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ "Zaprtje zračnega prostora Republike Slovenije" (in Slovene). Slovenia Control. 16 April 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Slovenija zapira zračni prostor" (in Slovene). 24ur.com. 17 April 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Alerts - Aena.es - Spanish airports and airspace". Aena.es. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ "Alerts - Aena.es - Spanish airports and airspace (Spanish)". Aena.es. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ "Alerts - Aena.es - Spanish airports and airspace". Aena.es. Retrieved 2010-04-18.
- ^ "Alerts - Aena.es - Spanish airports and airspace (Spanish)". Aena.es. Retrieved 2010-04-18.
- ^ "Reuters AlertNet – Sweden to shut airspace due to Iceland volcano". Alertnet.org. Retrieved 2010-04-15.
- ^ NOTAM: LSSN-A0182/10
- ^ "BAZL - Aschenwolke: Schweizer Luftraum aus Sicherheitsgründen vorübergehend geschlossen". Bazl.admin.ch. Retrieved 2010-04-16.
- ^ "Latest Flight Update". Swiss.com. Retrieved 2010-04-16.
- ^ BBC News 19:40 UTC, Thursday, 15 April 2010
- ^ Volcanic ash cloud: UK flight ban worsens
- ^ BBC TV Red Button text service, page 104.
- ^ BBC News 10:40 BST (09:40 UTC), Sunday, 18 April 2010
- ^ NATS Updates
- ^ Space photograph of ash engulfing Britain
- ^ "Volcanic ash cloud: 100,000 Britons stranded in Europe as air traffic chiefs extend lockdown to 7am | Mail Online". Dailymail.co.uk. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ "Skybus beats the gloom", Western Morning News, 16 April 2010
- ^ [ http://www.walesonline.co.uk/news/wales-news/2010/04/16/flight-from-cardiff-airport-last-to-leave-uk-as-volcanic-ash-grounds-planes-91466-26254292/ Flight from Cardiff Airport last to leave UK]
- ^ Hope for passengers? Flight arrives in Toronto from Glasgow
- ^ أوروبا تحت الحصار
وصلات خارجية
| Eyjafjöll 2010 eruption
]].- "Live: Volcanic cloud over Europe" updates on BBC News
- "The eruption that changed Iceland forever" - BBC News Magazine
- "List of airports shut down by volcano ash". The Globe and Mail. 16 April 2010.
- "UPDATED List of airports closed by volcano ash". News Provider. 17 April 2010.
معلومات ترسل للطائرات عن الرماد البركاني
- Shannon Volmet on 5505 KHz and 8957 KHz USB.
Air travel disruption after the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption
- CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list
- CS1 errors: markup
- CS1 errors: unsupported parameter
- الأحداث الجارية
- جميع الصفحات التي تحتاج تنظيف
- مقالات بالمعرفة تحتاج توضيح from April 2010
- Convert invalid options
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Pages using aviation accidents and incidents with unknown parameters
- 2010 في اوروبا
- 2010 في الطيران
- كوارث طبيعية 2010
- حواد طيران في 2010
- الطيران في اوروبا
- مخاطر الطقس