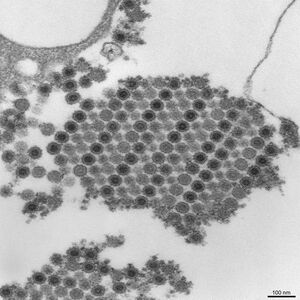
تشيكونگونيا
| تشيكونگونيا Chikungunya | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Rash from chikungunya | |
| النطق | |
| التخصص | Infectious disease |
| الأعراض | Fever, joint pain[2] |
| المضاعفات | Long term joint pain[2] |
| البداية المعتادة | 2 to 14 days after exposure[3] |
| المدة | Usually less than a week[2] |
| المسببات | Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) spread by mosquitoes[3] |
| الطريقة التشخيصية | Blood test for viral RNA or antibodies[3] |
| التشخيص المفاضل | Dengue fever, Zika fever[3] |
| الوقاية | Mosquito control, avoidance of bites[4] |
| العلاج | Supportive care[3] |
| Prognosis | Risk of death ~ 1 in 1,000[4] |
| التردد | > 1 million (2014)[3] |
تشيكونگونيا Chikungunya (في لغة ماكوندى "ذلك الذي يثني") الڤيروس (CHIKV) هو ڤيروس تحمله الحشرات، من جنس ألفاڤيروس، الذي ينتقل إلى البشر عن طريق بعوضة إيديس Aedes الحاملة للفيروس.[5] وقد كانت هناك مؤخراً موجات تفشي للفيروس مصحوبة بحالة مرضية شديدة. وقد تسبب الفيروس CHIKV في حالة مرضية لها أعراض شبيهة بحمى الدنگ. ويتميز فيروس CHIKV بطور حمى حادة من المرض يستمر من يومين إلى 5 أيام، يتبعه مرض ألم مفصلي لفترة طويلة ويؤثر على مفاصل الأطراف. الألم المصاحب لعدوى الفيروس CHIKV في المفاصل يبقى لأسابيع أو شهور، بل وفي بعض الحالات لأعوام.[6][7]
تشيكونگونيا هو أحد أنواع الحميات النزفية التي تصيب الإنسان جراء التعرض للدغات نوع معين من البعوض، يعرف ببعوض «أيديس - Aedes». ومصدر الاسم هو لغة قبيلة «الماكونده»، التي تنتشر في تنزانيا وموزمبيق، ويعني بلغتهم المحلية «المرض الذي يسبب الانحناء»، فيما يرمي إلى أحد أشهر الأعراض التي يسببها المرض من آلام شديدة في العظام والمفاصل تؤدي إلى انحناء الظهر. وليس للاسم أي علاقة حقيقية من قريب أو بعيد بالدجاج أو بدولة غينيا، حيث تنتشر قراءة خاطئة له تدعوه «Chicken Guinea».
ورغم عدم شهرة المرض واسمه بين العامة، كما أنه ليس مرضا خطيرا بالمفاهيم الطبية، فإن تفشيه في عام 2006 في جزيرة رينيون (Reunion)، المستعمرة الفرنسية في المحيط الهندي التي تقع شرق مدغشقر، قد أسفر عن إصابة ما يربو على 260 ألف شخص وتسبب في مقتل نحو 300 منهم، الأمر الذي أقلق الباحثين مع تعدد مرات انتشاره، وتجاوزه القارة الأفريقية في مرات كثيرة مثلما حدث سابقا في شمال إيطاليا أو جنوب تايلاند أخيرا في مايو (أيار) 2009.[8]
الأعراض
فترة حضانة التشيكونگونيا تتراوح من يومين إلى أربعة أيام. أهم أعراض المرض هي الحمى، حيث ترتفع الحرارة حتى 40 درجة مئوية وتنتهي فجأة بعد يومين، والنزيف النقطي تحت الجلد، والتهاب المفاصل الذي يتسبب في آلام حادة، تستمر لأسابيع طويلة وقد تمتد لسنوات.
السبب
علم الفيروسات
| Chikungunya virus | |
|---|---|
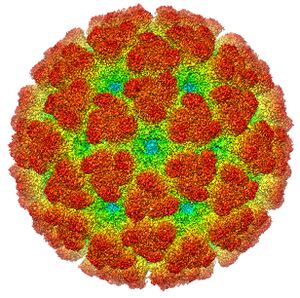
| |
| Cryoelectron microscopy reconstruction of Chikungunya virus. From EMDB entry EMD-5577[9] | |
| تصنيف الفيروسات | |
| أصنوفة غير معروفة (أصلحها): | Alphavirus |
| Species: | Chikungunya virus
|
فيروس تشيكونگونيا (Chikungunya virus ؛ CHIKV), is a member of the genus Alphavirus, and family Togaviridae. It was first isolated in 1953 in Tanzania and is an RNA virus with a positive-sense single-stranded genome of about 11.6kb.[10] It is a member of the Semliki Forest virus complex and is closely related to Ross River virus, O'nyong'nyong virus, and Semliki Forest virus.[11] Because it is transmitted by arthropods, namely mosquitoes, it can also be referred to as an arbovirus (arthropod-borne virus). In the United States, it is classified as a category B priority pathogen,[12] and work requires biosafety level III precautions.[13] موطنه هو أفريقيا وآسيا الإستوائيتان، وينتقل للبشر عبر عضة بعوضة، غالباً ما تكون من جنس الإيديس.
النقل
Chikungunya is generally transmitted from mosquitoes to humans. Less common modes of transmission include vertical transmission, which is transmission from mother to child during pregnancy or at birth. Transmission via infected blood products and through organ donation is also theoretically possible during times of outbreak, though no cases have yet been documented.[14] The incubation period ranges from one to twelve days, and is most typically three to seven.[15]
Chikungunya is related to mosquitoes, their environments, and human behavior. The adaptation of mosquitoes to the changing climate of North Africa around 5,000 years ago made them seek out environments where humans stored water. Human habitation and the mosquitoes' environments were then very closely connected. During periods of epidemics humans are the reservoir of the virus. Because high amounts of virus are present in the blood in the beginning of acute infection, the virus can be spread from a viremic human to a mosquito, and back to a human.[16] During other times, monkeys, birds and other vertebrates have served as reservoirs.[17] Three genotypes of this virus have been described, each with a distinct genotype and antigenic character: West African, East/Central/South African, and Asian genotypes.[18] The Asian lineage originated in 1952 and has subsequently split into two lineages – India (Indian Ocean Lineage) and South East Asian clades. This virus was first reported in the Americas in 2014. Phylogenetic investigations have shown that there are two strains in Brazil – the Asian and East/Central/South African types – and that the Asian strain arrived in the Caribbean (most likely from Oceania) in about March 2013.[19] The rate of molecular evolution was estimated to have a mean rate of 5 × 10−4 substitutions per site per year (95% higher probability density 2.9–7.9 × 10−4).[19]
Chikungunya is spread through bites from Aedes mosquitoes, and the species A. aegypti was identified as the most common vector, though the virus has recently been associated with many other species, including A. albopictus.[14] Research by the Pasteur Institute in Paris has suggested Chikungunya virus strains in the 2005–2006 Reunion Island outbreak incurred a mutation that facilitated transmission by the Asian tiger mosquito (A. albopictus).[20] Other species potentially able to transmit Chikungunya virus include Ae. furcifer-taylori, Ae. africanus, and Ae. luteocephalus.[14]
الآلية
Chikungunya virus is passed to humans when a bite from an infected mosquito breaks the skin and introduces the virus into the body. The pathogenesis of chikungunya infection in humans is still poorly understood, despite recent outbreaks. It appears that in vitro, Chikungunya virus is able to replicate in human epithelial and endothelial cells, primary fibroblasts, and monocyte-derived macrophages. Viral replication is highly cytopathic, but susceptible to type-I and -II interferon.[21] In vivo, in studies using living cells, chikungunya virus appears to replicate in fibroblasts, skeletal muscle progenitor cells, and myofibers.[22][23][24]
The type-1 interferon response seems to play an important role in the host's response to chikungunya infection. Upon infection with chikungunya, the host's fibroblasts produce type-1 alpha and beta interferon (IFN-α and IFN-β).[25][23] In mouse studies, deficiencies in INF-1 in mice exposed to the virus cause increased morbidity and mortality.[23][26][27] The chikungunya-specific upstream components of the type-1 interferon pathway involved in the host's response to chikungunya infection are still unknown.[28] Nonetheless, mouse studies suggest that IPS-1 is an important factor,[28] and that IRF3 and IRF7 are important in an age-dependent manner.[29][30] Mouse studies also suggest that chikungunya evades host defenses and counters the type-I interferon response by producing NS2, a nonstructural protein that degrades RBP1 and turns off the host cell's ability to transcribe DNA.[31] NS2 interferes with the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and prevents STAT from becoming phosphorylated.[32]
In the acute phase of chikungunya, the virus is typically present in the areas where symptoms present, specifically skeletal muscles, and joints. In the chronic phase, it is suggested that viral persistence (the inability of the body to entirely rid itself of the virus), lack of clearance of the antigen, or both, contribute to joint pain. The inflammation response during both the acute and chronic phase of the disease results in part from interactions between the virus and monocytes and macrophages.[33] Chikungunya virus disease in humans is associated with elevated serum levels of specific cytokines and chemokines. High levels of specific cytokines have been linked to more severe acute disease: interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1β, RANTES, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), monokine induced by gamma interferon (MIG), and interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP-10). Cytokines may also contribute to chronic Chikungunya virus disease, as persistent joint pain has been associated with elevated levels of IL-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF).[16] In those with chronic symptoms, a mild elevation of C-reactive protein (CRP) has been observed, suggesting ongoing chronic inflammation. However, there is little evidence linking chronic Chikungunya virus disease and the development of autoimmunity.[بحاجة لمصدر][34]
النسخ الفيروسي
هذا section يفتقد معلومات عن replication organelle called spherules ("small spheres"), see PubMed and very recent EM work in DOI:10.1101/2022.04.08.487651. (April 2022) |
The virus consists of four nonstructural proteins and three structural proteins.[33] The structural proteins are the capsid and two envelope glycoproteins: E1 and E2, which form heterodimeric spikes on the viron surface. E2 binds to cellular receptors in order to enter the host cell through receptor-mediated endocytosis. E1 contains a fusion peptide which, when exposed to the acidity of the endosome in eukaryotic cells, dissociates from E2 and initiates membrane fusion that allows the release of nucleocapsids into the host cytoplasm, promoting infection.[35] The mature virion contains 240 heterodimeric spikes of E2/E1, which after release, bud on the surface of the infected cell, where they are released by exocytosis to infect other cells.[10]
التشخيص
Chikungunya is diagnosed on the basis of clinical, epidemiological, and laboratory criteria. Clinically, acute onset of high fever and severe joint pain would lead to suspicion of chikungunya. Epidemiological criteria consist of whether the individual has traveled to or spent time in an area in which chikungunya is present within the last twelve days (i.e.) the potential incubation period). Laboratory criteria include a decreased lymphocyte count consistent with viremia. However a definitive laboratory diagnosis can be accomplished through viral isolation, RT-PCR, or serological diagnosis.[36]
The differential diagnosis may include other mosquito-borne diseases, such as dengue or malaria, or other infections such as influenza. Chronic recurrent polyarthralgia occurs in at least 20% of chikungunya patients one year after infection, whereas such symptoms are uncommon in dengue.[37]
Virus isolation provides the most definitive diagnosis, but takes one to two weeks for completion and must be carried out in biosafety level III laboratories.[38] The technique involves exposing specific cell lines to samples from whole blood and identifying Chikungunya virus-specific responses. RT-PCR using nested primer pairs is used to amplify several chikungunya-specific genes from whole blood, generating thousands to millions of copies of the genes in order to identify them. RT-PCR can also be used to quantify the viral load in the blood. Using RT-PCR, diagnostic results can be available in one to two days.[38] Serological diagnosis requires a larger amount of blood than the other methods, and uses an ELISA assay to measure chikungunya-specific IgM levels in the blood serum. One advantage offered by serological diagnosis is that serum IgM is detectable from 5 days to months after the onset of symptoms, but drawbacks are that results may require two to three days, and false positives can occur with infection due to other related viruses, such as o'nyong'nyong virus and Semliki Forest virus.[38]
Presently, there is no specific way to test for chronic signs and symptoms associated with Chikungunya fever although nonspecific laboratory findings such as C reactive protein and elevated cytokines can correlate with disease activity.[39]
العلاج
ولا يوجد علاج معروف ومحدد لهذا المرض حتى اليوم، وإن كان الاتجاه المستخدم طبيا هو الرعاية الطبية المكثفة مع خافضات الحرارة ومسكنات الآلام.
يوجد اختبار مصلي للتشيكونگونيا من جامعة مالايا في كوالا لمپور، ماليزيا.
اللقاح قيد التطوير
تمكن العلماء من تصنيع جزيئات غير ناقلة للمرض تشبه الغطاء الخارجي للفيروس، وحققت التجربة نجاحا باهرا في تنشيط الجهاز المناعي لقردة الريسس (Rhesus monkeys)، أحد أقرب الكائنات جينيا إلى الإنسان، ليصنع بدوره أجساما مضادة تحارب الفيروس. وتعد خطوة تجربة العقاقير على حيوانات التجارب، وبخاصة الشبيهة بالإنسان جينيا مثل القردة أو الخنازير، الخطوة قبل الأخيرة في إطار تصنيع اللقاحات، حيث لا يتبقى بعدها سوى تجربتها على الإنسان قبل الحكم على صلاحية استخدامها، من عدمه.
الفرق بين المصل واللقاح
من الأخطاء الشائعة بين عامة الناس، الخلط بين الأمصال واللقاحات. فالمصل هو الأجسام المضادة سابقة التجهيز، التي يتم استخلاصها من «مصل» الدم سواء من شخص أصيب سابقا بالمرض وأعد جهازه المناعي هذه الأجسام المضادة، أو من بعض الحيوانات التي تم تعريضها للمرض، أو حديثا عن طريق الهندسة الوراثية. ويعبر المصل عن تفاعل مناعي سلبي، حيث يجري حقن الأجسام المضادة الجاهزة لمقاومة المرض. وهو يستخدم غالبا في حالة الإصابة الفعلية بالمرض وليس في حالة الوقاية. أما اللقاح، فهو حقن جزء غير معد أو مضر من الميكروب، سواء كان بكتريا أو فيروسا، حتى يتعرف إليه الجهاز المناعي ويعد ضده أجساما مضادة تقوم بحماية الجسم مستقبلا في حال التعرض للميكروب الفعلي.
ومن المشكلات الرئيسية التي تواجه إعداد اللقاح، إيجاد جزيء ثابت وغير متغير في غلافه الخارجي يمكن للجهاز المناعي التعرف عليه، وهي مشكلة فيروسات الإنفلونزا على سبيل المثال التي يتحور شكلها من آن إلى آخر بما لا يسمح بإنتاج لقاح دائم لها.
كما يشترط أن يكون هذا الجزيء لا يشبه جزيئات الخلايا البشرية العادية، فلو كان كذلك فإن أمام الجهاز المناعي حلا من اثنين، إما إهمال التفاعل مع هذا الجزيء باعتباره جزءا طبيعيا من تكوين الجسم البشري، أو التفاعل معه مناعيا، وهي كارثة بحق تعرف باسم التفاعل المناعي الشخصي (AutoImmune crisis)، حين يهاجم الجهاز المناعي خلايا الجسم ذاته، ولا يكف عن ذلك إلا مع تدميرها كلياً أو عند تناول المواد المثبطة للمناعة مثل الكورتيزون.
الوبائيات

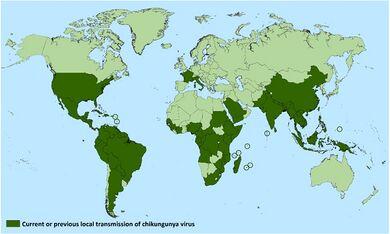
Historically, chikungunya has been present mostly in the developing world. The disease causes an estimated 3 million infections each year.[40] Epidemics in the Indian Ocean, Pacific Islands, and in the Americas, continue to change the distribution of the disease.[41] In Africa, chikungunya is spread by a sylvatic cycle in which the virus largely cycles between other non-human primates, small mammals, and mosquitos between human outbreaks.[6] During outbreaks, due to the high concentration of virus in the blood of those in the acute phase of infection, the virus can circulate from humans to mosquitoes and back to humans.[6] The transmission of the pathogen between humans and mosquitoes that exist in urban environments was established on multiple occasions from strains occurring on the eastern half of Africa in non-human primate hosts.[33] This emergence and spread beyond Africa may have started as early as the 18th century.[33] Currently, available data does not indicate whether the introduction of chikungunya into Asia occurred in the 19th century or more recently, but this epidemic Asian strain causes outbreaks in India and continues to circulate in Southeast Asia.[33] In Africa, outbreaks were typically tied to heavy rainfall causing increased mosquito population. In recent outbreaks in urban centers, the virus has spread by circulating between humans and mosquitoes.[14]
Global rates of chikungunya infection are variable, depending on outbreaks. When chikungunya was first identified in 1952, it had a low-level circulation in West Africa, with infection rates linked to rainfall. Beginning in the 1960s, periodic outbreaks were documented in Asia and Africa. However, since 2005, following several decades of relative inactivity, chikungunya has re-emerged and caused large outbreaks in Africa, Asia, and the Americas. In India, for instance, chikungunya re-appeared following 32 years of absence of viral activity.[42] Outbreaks have occurred in Europe, the Caribbean, and South America, areas in which chikungunya was not previously transmitted. Local transmission has also occurred in the United States and Australia, countries in which the virus was previously unknown.[14] In 2005, an outbreak on the island of Réunion was the largest then documented, with an estimated 266,000 cases on an island with a population of approximately 770,000.[43] In a 2006 outbreak, India reported 1.25 million suspected cases.[44] Chikungunya was introduced to the Americas in 2013, first detected on the French island of Saint Martin,[45] and for the next two years in the Americas, 1,118,763 suspected cases and 24,682 confirmed cases were reported by the PAHO.[46]
An analysis of the genetic code of Chikungunya virus suggests that the increased severity of the 2005–present outbreak may be due to a change in the genetic sequence which altered the E1 segment of the virus' viral coat protein, a variant called E1-A226V. This mutation potentially allows the virus to multiply more easily in mosquito cells.[47] The change allows the virus to use the Asian tiger mosquito (an invasive species) as a vector in addition to the more strictly tropical main vector, Aedes aegypti.[48] Enhanced transmission of Chikungunya virus by A. albopictus could mean an increased risk for outbreaks in other areas where the Asian tiger mosquito is present.[49] A albopictus is an invasive species which has spread through Europe, the Americas, the Caribbean, Africa and the Middle East.[بحاجة لمصدر]
After the detection of zika virus in Brazil in April 2015, the first ever in the Western Hemisphere,[50][51] it is now thought some chikungunya and dengue cases could in fact be zika virus cases or coinfections.
التاريخ
The disease was first described by Marion Robinson[52] and W.H.R. Lumsden[53] in a pair of 1955 papers, following an outbreak in 1952 on the Makonde Plateau, along the border between Mozambique and Tanganyika (the mainland part of modern-day Tanzania). Since then outbreaks have occurred occasionally in Africa, South Asia, and Southeast Asia; recent outbreaks have spread the disease over a wider range.[بحاجة لمصدر]
The first recorded outbreak may have been in 1779.[54] This is in agreement with the molecular genetics evidence that suggests it evolved around the year 1700.[55]
According to the original paper by Lumsden, the term 'chikungunya' is derived from the Makonde root verb kungunyala, meaning to dry up or become contorted. In concurrent research, Robinson[بحاجة لمصدر] glossed the Makonde term more specifically as "that which bends up". It is understood to refer to the contorted posture of people affected with the severe joint pain and arthritic symptoms associated with this disease.[56] Subsequent authors apparently overlooked the references to the Makonde language and assumed the term to have been derived from Swahili, the lingua franca of the region. The erroneous attribution to Swahili has been repeated in numerous print sources.[57] Erroneous spellings of the name of the disease are also in common use.[بحاجة لمصدر]
انظر أيضاً
- Chikungunya outbreaks: outbreaks of the disease, 2004 to present.
- DEET
- O'nyong'nyong virus: a similar virus.
للاستزادة
- "Chikungunya — Fact sheet". European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 2008-01-23. Retrieved 2008-03-19.
الهامش
- ^ "chikungunya". Oxford Learner's Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 4 November 2014. Retrieved 4 November 2014.
- ^ أ ب ت خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةCDC2016Sym - ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةWHO2016 - ^ أ ب خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةCag2013 - ^ {{Lahariya C, Pradhan SK. Emergence of chikungunya virus in Indian subcontinent after 32 years: a review. J Vect Borne Dis. 2006 Dec;43(4):151-60. accessible at http://www.mrcindia.org/journal/issues/434151.PDF }}
- ^ أ ب ت Powers AM, Logue CH (2007). "Changing patterns of chikungunya virus: re-emergence of a zoonotic arbovirus" (PDF). J. Gen. Virol. 88 (Pt 9): 2363–77. doi:10.1099/vir.0.82858-0. PMID 17698645. Retrieved 2008-03-19. خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صالح؛ الاسم "Powers" معرف أكثر من مرة بمحتويات مختلفة. - ^ Sourisseau M, Schilte C, Casartelli N; et al. (2007). "Characterization of reemerging chikungunya virus". PLoS Pathog. 3 (6): e89. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030089. PMC 1904475. PMID 17604450.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ أحمد الغمراوي. "التشيكونغونيا المرض الذي يسبب الانحناء". جريدة الشرق الأوسط. Retrieved 2010-03-14.
- ^ Sun S, Xiang Y, Akahata W, Holdaway H, Pal P, Zhang X, et al. (April 2013). "Structural analyses at pseudo atomic resolution of Chikungunya virus and antibodies show mechanisms of neutralization". eLife. 2: e00435. doi:10.7554/eLife.00435. PMC 3614025. PMID 23577234.
- ^ أ ب Weaver SC, Osorio JE, Livengood JA, Chen R, Stinchcomb DT (September 2012). "Chikungunya virus and prospects for a vaccine". Expert Review of Vaccines. 11 (9): 1087–101. doi:10.1586/erv.12.84. PMC 3562718. PMID 23151166.
- ^ Powers AM, Brault AC, Shirako Y, Strauss EG, Kang W, Strauss JH, Weaver SC (November 2001). "Evolutionary relationships and systematics of the alphaviruses". Journal of Virology. 75 (21): 10118–31. doi:10.1128/JVI.75.21.10118-10131.2001. PMC 114586. PMID 11581380.
- ^ "NIAID Category A, B, and C Priority Pathogens". Archived from the original on 5 January 2014. Retrieved 23 July 2020.
- ^ "Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories (BMBL) Fifth Edition" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 October 2014. Retrieved 1 January 2014.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج Burt FJ, Rolph MS, Rulli NE, Mahalingam S, Heise MT (February 2012). "Chikungunya: a re-emerging virus". Lancet. 379 (9816): 662–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60281-X. PMID 22100854. S2CID 33440699.
- ^ Thiberville, Simon-Djamel; Moyen, Nanikaly; Dupuis-Maguiraga, Laurence; Nougairede, Antoine; Gould, Ernest A.; Roques, Pierre; de Lamballerie, Xavier (2013-09-01). "Chikungunya fever: Epidemiology, clinical syndrome, pathogenesis and therapy". Antiviral Research. 99 (3): 345–370. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.009. ISSN 0166-3542. PMC 7114207. PMID 23811281.
- ^ أ ب خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةMorrison2014 - ^ Ng LC, Hapuarachchi HC (October 2010). "Tracing the path of Chikungunya virus--evolution and adaptation". Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 10 (7): 876–85. Bibcode:2010InfGE..10..876N. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2010.07.012. PMID 20654736.
- ^ Powers AM, Brault AC, Tesh RB, Weaver SC (February 2000). "Re-emergence of Chikungunya and O'nyong-nyong viruses: evidence for distinct geographical lineages and distant evolutionary relationships". The Journal of General Virology. 81 (Pt 2): 471–9. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-81-2-471 (inactive 31 January 2024). PMID 10644846.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of يناير 2024 (link) - ^ أ ب Sahadeo NS, Allicock OM, De Salazar PM, Auguste AJ, Widen S, Olowokure B, Gutierrez C, Valadere AM, Polson-Edwards K, Weaver SC, Carrington CV (2017). "Understanding the evolution and spread of chikungunya virus in the Americas using complete genome sequences". Virus Evol. 3 (1): vex010. doi:10.1093/ve/vex010. PMC 5413804. PMID 28480053.
- ^ Enserink M (September 2007). "Epidemiology. Tropical disease follows mosquitoes to Europe". Science. 317 (5844): 1485. doi:10.1126/science.317.5844.1485a. PMID 17872417. S2CID 83359245.
- ^ Sourisseau M, Schilte C, Casartelli N, Trouillet C, Guivel-Benhassine F, Rudnicka D, et al. (June 2007). "Characterization of reemerging chikungunya virus". PLOS Pathogens. 3 (6): e89. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030089. PMC 1904475. PMID 17604450.

- ^ Ozden S, Huerre M, Riviere JP, Coffey LL, Afonso PV, Mouly V, et al. (June 2007). "Human muscle satellite cells as targets of Chikungunya virus infection". PLOS ONE. 2 (6): e527. Bibcode:2007PLoSO...2..527O. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000527. PMC 1885285. PMID 17565380.

- ^ أ ب ت Schilte C, Couderc T, Chretien F, Sourisseau M, Gangneux N, Guivel-Benhassine F, et al. (February 2010). "Type I IFN controls chikungunya virus via its action on nonhematopoietic cells". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 207 (2): 429–42. doi:10.1084/jem.20090851. PMC 2822618. PMID 20123960.
- ^ Rohatgi A, Corbo JC, Monte K, Higgs S, Vanlandingham DL, Kardon G, Lenschow DJ (March 2014). "Infection of myofibers contributes to increased pathogenicity during infection with an epidemic strain of chikungunya virus". Journal of Virology. 88 (5): 2414–25. doi:10.1128/JVI.02716-13. PMC 3958092. PMID 24335291.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةKril - ^ Couderc T, Chrétien F, Schilte C, Disson O, Brigitte M, Guivel-Benhassine F, et al. (February 2008). "A mouse model for Chikungunya: young age and inefficient type-I interferon signaling are risk factors for severe disease". PLOS Pathogens. 4 (2): e29. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0040029. PMC 2242832. PMID 18282093.

- ^ Partidos CD, Weger J, Brewoo J, Seymour R, Borland EM, Ledermann JP, et al. (April 2011). "Probing the attenuation and protective efficacy of a candidate chikungunya virus vaccine in mice with compromised interferon (IFN) signaling". Vaccine. 29 (16): 3067–73. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.01.076. PMC 3081687. PMID 21300099.
- ^ أ ب White LK, Sali T, Alvarado D, Gatti E, Pierre P, Streblow D, Defilippis VR (January 2011). "Chikungunya virus induces IPS-1-dependent innate immune activation and protein kinase R-independent translational shutoff". Journal of Virology. 85 (1): 606–20. doi:10.1128/JVI.00767-10. PMC 3014158. PMID 20962078.
- ^ Rudd PA, Wilson J, Gardner J, Larcher T, Babarit C, Le TT, et al. (September 2012). "Interferon response factors 3 and 7 protect against Chikungunya virus hemorrhagic fever and shock". Journal of Virology. 86 (18): 9888–98. doi:10.1128/JVI.00956-12. PMC 3446587. PMID 22761364.
- ^ Schilte C, Buckwalter MR, Laird ME, Diamond MS, Schwartz O, Albert ML (April 2012). "Cutting edge: independent roles for IRF-3 and IRF-7 in hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells during host response to Chikungunya infection". Journal of Immunology. 188 (7): 2967–71. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1103185. PMID 22371392.
- ^ Akhrymuk I, Kulemzin SV, Frolova EI (July 2012). "Evasion of the innate immune response: the Old World alphavirus nsP2 protein induces rapid degradation of Rpb1, a catalytic subunit of RNA polymerase II". Journal of Virology. 86 (13): 7180–91. doi:10.1128/JVI.00541-12. PMC 3416352. PMID 22514352.
- ^ Fros JJ, Liu WJ, Prow NA, Geertsema C, Ligtenberg M, Vanlandingham DL, et al. (October 2010). "Chikungunya virus nonstructural protein 2 inhibits type I/II interferon-stimulated JAK-STAT signaling". Journal of Virology. 84 (20): 10877–87. doi:10.1128/JVI.00949-10. PMC 2950581. PMID 20686047.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج Weaver SC, Lecuit M (March 2015). "Chikungunya virus and the global spread of a mosquito-borne disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 372 (13): 1231–9. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1406035. PMID 25806915.
- ^ Tanay A. Chikungunya virus and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017 Jul;29(4):389-393. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000396. PMID 28376065.
- ^ Voss JE, Vaney MC, Duquerroy S, Vonrhein C, Girard-Blanc C, Crublet E, et al. (December 2010). "Glycoprotein organization of Chikungunya virus particles revealed by X-ray crystallography". Nature. 468 (7324): 709–12. Bibcode:2010Natur.468..709V. doi:10.1038/nature09555. PMID 21124458. S2CID 4412764.
- ^ Cabié A, Ledrans M, Abel S (July 2015). "Chikungunya Virus Infections". The New England Journal of Medicine. 373 (1): 94. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1505501. PMID 26132958.
- ^ Morens DM, Fauci AS (September 2014). "Chikungunya at the door--déjà vu all over again?". The New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (10): 885–7. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1408509. PMID 25029435.
- ^ أ ب ت "Laboratory Diagnosis of Chikungunya Fevers". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 8 September 2012. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ Schilte C, Staikowsky F, Staikovsky F, Couderc T, Madec Y, Carpentier F, et al. (2013). "Chikungunya virus-associated long-term arthralgia: a 36-month prospective longitudinal study". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 7 (3): e2137. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002137. PMC 3605278. PMID 23556021.
- ^ Seppa N (2 June 2015). "Chikungunya is on the move". Science News. Archived from the original on 11 June 2015. Retrieved 13 June 2015.
- ^ Sam IC, Loong SK, Michael JC, Chua CL, Wan Sulaiman WY, Vythilingam I, et al. (2012). "Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of Chikungunya virus of different genotypes from Malaysia". PLOS ONE. 7 (11): e50476. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...750476S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050476. PMC 3507689. PMID 23209750.
- ^ Lahariya C, Pradhan SK (December 2006). "Emergence of chikungunya virus in Indian subcontinent after 32 years: A review" (PDF). Journal of Vector Borne Diseases. 43 (4): 151–60. PMID 17175699. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 October 2013.
- ^ Roth A, Hoy D, Horwood PF, Ropa B, Hancock T, Guillaumot L, et al. (August 2014). "Preparedness for threat of chikungunya in the pacific". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 20 (8). doi:10.3201/eid2008.130696. PMC 4111160. PMID 25062306.
- ^ Muniaraj M (March 2014). "Fading chikungunya fever from India: beginning of the end of another episode?". The Indian Journal of Medical Research. 139 (3): 468–70. PMC 4069744. PMID 24820844.
- ^ Charles, Jacqueline (1 Jun 2014). "Mosquito-borne virus knocking on Fla.'s door". Newspapers.com (in الإنجليزية). The Miami Herald. p. A17. Retrieved 22 February 2023.
- ^ "Number of cumulative cases 2013–2014". www.paho.org. Pan-American Health Organization (PAHO). 15 May 2015. Archived from the original on 21 July 2015. Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ^ Schuffenecker I, Iteman I, Michault A, Murri S, Frangeul L, Vaney MC, et al. (July 2006). "Genome microevolution of chikungunya viruses causing the Indian Ocean outbreak". PLOS Medicine. 3 (7): e263. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030263. PMC 1463904. PMID 16700631.
- ^ Tsetsarkin KA, Vanlandingham DL, McGee CE, Higgs S (December 2007). "A single mutation in chikungunya virus affects vector specificity and epidemic potential". PLOS Pathogens. 3 (12): e201. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030201. PMC 2134949. PMID 18069894.

- ^ Liumbruno GM, Calteri D, Petropulacos K, Mattivi A, Po C, Macini P, et al. (October 2008). "The Chikungunya epidemic in Italy and its repercussion on the blood system". Blood Transfusion = Trasfusione del Sangue. 6 (4): 199–210. doi:10.2450/2008.0016-08. PMC 2626913. PMID 19112735.
- ^ "Identificado vírus causador de doença misteriosa em Salvador e RMS". 2015-04-29. Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 2015-05-09.
- ^ "São Paulo já pode ter casos de Zika Vírus - Cenário da Notícia em Lucas do Rio Verde e Região". Archived from the original on 5 May 2015. Retrieved 2015-05-09.
- ^ Robinson MC (January 1955). "An epidemic of virus disease in Southern Province, Tanganyika Territory, in 1952-53. I. Clinical features". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 49 (1): 28–32. doi:10.1016/0035-9203(55)90080-8. PMID 14373834.
- ^ Lumsden WH (January 1955). "An epidemic of virus disease in Southern Province, Tanganyika Territory, in 1952-53. II. General description and epidemiology". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 49 (1): 33–57. doi:10.1016/0035-9203(55)90081-X. PMID 14373835.
- ^ Carey DE (July 1971). "Chikungunya and dengue: a case of mistaken identity?". Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences. 26 (3): 243–62. doi:10.1093/jhmas/XXVI.3.243. PMID 4938938.
- ^ Cherian SS, Walimbe AM, Jadhav SM, Gandhe SS, Hundekar SL, Mishra AC, Arankalle VA (January 2009). "Evolutionary rates and timescale comparison of Chikungunya viruses inferred from the whole genome/E1 gene with special reference to the 2005-07 outbreak in the Indian subcontinent". Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 9 (1): 16–23. Bibcode:2009InfGE...9...16C. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2008.09.004. PMID 18940268.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control Prevention (CDC) (September 2006). "Chikungunya fever diagnosed among international travelers--United States, 2005-2006". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 55 (38): 1040–2. PMID 17008866. Archived from the original on 28 May 2017.
- ^ Benjamin M (2008). "Chikungunya is NOT a Swahili word, it is from the Makonde language!".
وصلات خارجية
- WHO site on disease outbreak news
- Chikungunya and Pregnancy
- Chikungunya Infection in India and Vector Control
- Schuffenecker I, Iteman I, Michault A; et al. (2006). "Genome microevolution of chikungunya viruses causing the Indian Ocean outbreak". PLoS Med. 3 (7): e263. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030263. PMC 1463904. PMID 16700631.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Chikungunya, a debilitating illness From Reuters Alertnet
- Mosquito-borne African virus a new threat to West Update on increasing threat, from Reuters
- Information about previous outbreaks of Chikungunya
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- CS1 errors: unsupported parameter
- CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI
- CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of يناير 2024
- الصفحات بخصائص غير محلولة
- Short description matches Wikidata
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Automatic taxobox cleanup
- Articles with unsourced statements from May 2021
- مقالات ينبغي توسيعها from April 2022
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles with unsourced statements from August 2023
- Chikungunya
- أمراض ڤيروسية
- Togaviruses
- أمراض إستوائية
- أمراض تحملها الحشرات
- كوارث صحية في الهند
- أسلحة بيولوجية