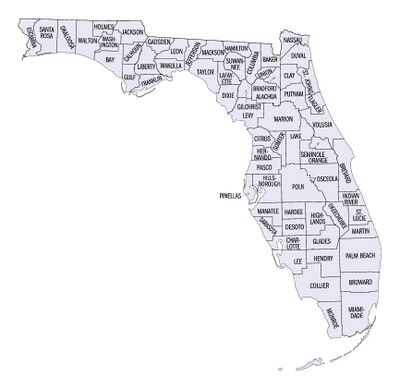
قائمة مقاطعات فلوريدا
| مقاطعات فلوريدا | |
|---|---|
| الموقع | ولاية فلوريدا |
| العدد | 67 |
| عدد السكان | 7,603 (Liberty) – 2,673,837 (Miami-Dade) |
| المساحة | 240 square miles (620 km2) (Union) – 2,034 square miles (5,270 km2) (Palm Beach) |
| الحكومة | حكومة مقاطعة |
| التقسيمات | تجمعات |
توجد 67 مقاطعة في ولاية فلوريدا، التي أصبحت إقليم تابع للولايات المتحدة في 1821 مع مقاطعتين تُكمِلان التقسيم الإقليمي المُحتفَظ به كإقليم إسپاني، Escambia to the west and St. Johns to the east. Both counties are divided by the Suwannee River. All of the other counties were apportioned from these two original counties. Florida became the 27th U.S. state in 1845, and its last county was created in 1925 with the formation of Gilchrist County from a segment of Alachua County.[1] Florida's counties are subdivisions of the state government. Florida's most populous county is Miami-Dade County, the seventh most populous county in the nation, with a population of 2,701,767 as of the 2020 census.[2]
In 1968, counties gained the power to develop their own charters.[3] All but two of Florida's county seats are incorporated municipalities: the exceptions are Crawfordville, county seat of rural Wakulla County,[4] and East Naples, located outside Naples city limits in Collier County.
The names of Florida's counties reflect its diverse cultural heritage. Some are named for Confederate political leaders and Spanish explorers, marking the influence of Spanish sovereignty, while others are named for Christian saints, Native American sites, as well as political leaders of the United States. Natural features of the region, including rivers, lakes and flora, are also commonly used for county names. Florida has counties named for participants on both sides of Second Seminole War: Miami-Dade County is partially named for Francis L. Dade, a major in the U.S. Army at the time; Osceola County is named for the war's native Muscogee-Seminole resistance leader Osceola.[5]
Population figures are based on the 2022 vintage Census population estimates. The population of Florida is 22,244,823, an increase of 3.3% from 2020. The average population of Florida's counties is 332,012; مقاطعة ميامي-ديد is the most populous (2,673,837) and Liberty County is the least (7,603). The average land area is 805 sq mi (2,085 km2). The largest county is Palm Beach County (2,034 sq mi, 5,268 km2) and the smallest is Union County (240 sq mi, 622 km2). The total area of the state is 65,795 sq miles, of which the land area constitutes 53,927 square miles (139,670 km2) while the water area constitutes 11,868 sq miles.[6]
The Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) is used by the U.S. government to uniquely identify counties, and is provided for each entry. These codes link to the United States Census Bureau's "quick facts" for each county. Florida's FIPS code of 12 is used to distinguish from counties in other states. For example, Alachua County's unique nationwide identifier is 12001.[7]
المقاطعات
| المقاطعة |
الكود [7] |
مقر المقاطعة [8] |
تأسست [5] |
تشكلت من [9] |
أصل الاسم [5] |
الكثافة |
السكان [10] |
المساحة [11][8] |
الخريطة |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
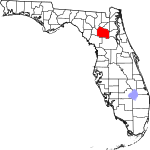
| مقاطعة Alachua | 001 | جينزفيل | 1824 | Duval and St. Johns | From a Seminole-Creek word meaning "jug", apparently in reference to the sinkholes common in the area[12] | 324.98 | 284٬030 | 874 ميل² (2٬264 كم²) |
|
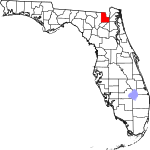
| مقاطعة Baker | 003 | Macclenny | 1861 | New River | James McNair Baker (1821–1892), a Confederate senator and later a judge in the fourth judicial district | 47.53 | 27٬803 | 585 ميل² (1٬515 كم²) |
|
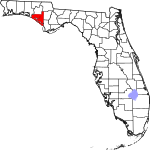
| مقاطعة Bay | 005 | Panama City | 1913 | كالهون و واشنطن | St. Andrew's Bay, the central geographic feature of the county | 242.32 | 185٬134 | 764 ميل² (1٬979 كم²) |
|
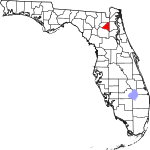
| مقاطعة Bradford | 007 | Starke | 1858 | Columbia named New River until 1861 |
Richard Bradford, the first officer from Florida to die in the Civil War; he was killed during the Battle of Santa Rosa Island | 93.22 | 27٬313 | 293 ميل² (759 كم²) |
|
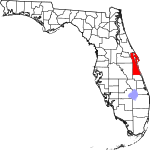
| مقاطعة Brevard | 009 | Titusville | 1844 | Hillsborough and Mosquito named St. Lucie until 1855[13] |
Theodore Washington Brevard, early settler and later state comptroller from 1853 to 1861[13] | 619.54 | 630٬693 | 1٬018 ميل² (2٬637 كم²) |
|
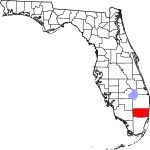
| مقاطعة Broward | 011 | Fort Lauderdale | 1915 | ميامي-ديد و Palm Beach | Napoleon Bonaparte Broward (1857–1910), 19th governor of Florida from 1905 to 1909 | 1610.44 | 1٬947٬026 | 1٬209 ميل² (3٬131 كم²) |
|
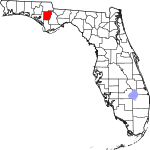
| مقاطعة Calhoun | 013 | Blountstown | 1838 | Franklin, Jackson, and Washington | John C. Calhoun (1782–1850) leading Southern politician from South Carolina | 23.75 | 13٬464 | 567 ميل² (1٬469 كم²) |
|
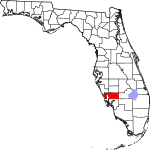
| مقاطعة Charlotte | 015 | Punta Gorda | 1921 | DeSoto | Probably a corruption of the name of the Calusa, a group of Native Americans from the area | 292.02 | 202٬661 | 694 ميل² (1٬797 كم²) |
|
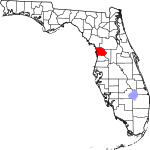
| مقاطعة Citrus | 017 | Inverness | 1887 | Hernando | The county's citrus trees | 278.30 | 162٬529 | 584 ميل² (1٬513 كم²) |
|
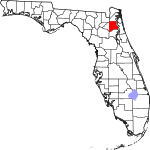
| مقاطعة Clay | 019 | Green Cove Springs | 1858 | Duval | هنري كلاي (1777–1852), Secretary of State from 1825 to 1829 under John Quincy Adams | 377.02 | 226٬589 | 601 ميل² (1٬557 كم²) |
|
| مقاطعة Collier | 021 | East Naples | 1923 | Lee | Barron Collier (1873–1939), an advertising entrepreneur who developed much of the land in southern Florida | 196.44 | 397٬994 | 2٬026 ميل² (5٬247 كم²) |
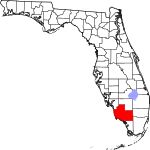
|
| مقاطعة Columbia | 023 | Lake City | 1832 | Alachua | Christopher Columbus (c. 1451–1506), explorer of the Americas | 90.22 | 71٬908 | 797 ميل² (2٬064 كم²) |
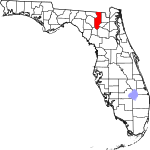
|
| مقاطعة DeSoto | 027 | Arcadia | 1887 | Manatee | Hernando de Soto (c. 1496/1497–1542), a Spanish explorer and conquistador | 55.43 | 35٬312 | 637 ميل² (1٬650 كم²) |
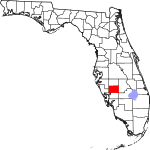
|
| مقاطعة Dixie | 029 | Cross City | 1921 | Lafayette | Dixie, the common nickname for the Southern United States | 24.32 | 17٬124 | 704 ميل² (1٬823 كم²) |
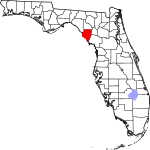
|
| مقاطعة Duval | 031 | Jacksonville | 1822 | St. Johns | William Pope Duval (1784–1854), the first governor of the Florida Territory | 1313.35 | 1٬016٬536 | 774 ميل² (2٬005 كم²) |
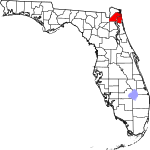
|
| مقاطعة Escambia | 033 | Pensacola | 1821 | One of the two original counties | Disputed origin; possibly from the Creek or Choctawword Shambia, meaning "clear water", or from Spanish word “cambiar”, meaning to barter | 489.27 | 324٬878 | 664 ميل² (1٬720 كم²) |
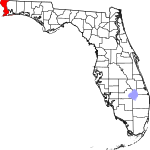
|
| مقاطعة Flagler | 035 | Bunnell | 1917 | St. Johns and Volusia | Henry Morrison Flagler (1830–1913), founder of the Florida East Coast Railway | 261.25 | 126٬705 | 485 ميل² (1٬256 كم²) |
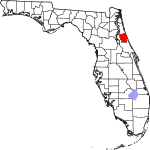
|
| مقاطعة Franklin | 037 | Apalachicola | 1832 | Gadsden and Washington | Benjamin Franklin (1706–1790), one of the Founding Fathers of the United States of America | 23.40 | 12٬498 | 534 ميل² (1٬383 كم²) |
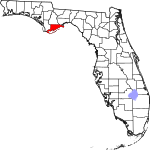
|
| مقاطعة Gadsden | 039 | Quincy | 1823 | Jackson | James Gadsden (1788–1858), American diplomat and namesake of the Gadsden Purchase | 84.11 | 43٬403 | 516 ميل² (1٬336 كم²) |
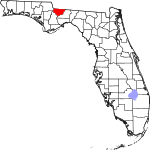
|
| مقاطعة Gilchrist | 041 | Trenton | 1925 | Alachua | Albert W. Gilchrist (1858–1926), the 20th governor of Florida | 54.42 | 18٬992 | 349 ميل² (904 كم²) |
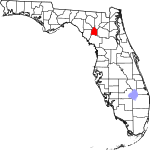
|
| مقاطعة Glades | 043 | Moore Haven | 1921 | DeSoto | The Florida Everglades | 16.09 | 12٬454 | 774 ميل² (2٬005 كم²) |
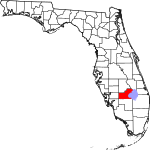
|
| مقاطعة Gulf | 045 | Port St. Joe | 1925 | Calhoun | The Gulf of Mexico | 27.10 | 15٬314 | 565 ميل² (1٬463 كم²) |
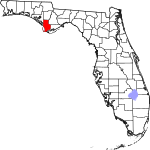
|
| مقاطعة Hamilton | 047 | Jasper | 1827 | Jefferson | Alexander Hamilton (1757–1804), the first United States Secretary of the Treasury and a Founding Father | 25.66 | 13٬217 | 515 ميل² (1٬334 كم²) |
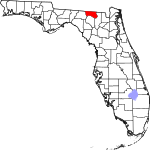
|
| مقاطعة Hardee | 049 | Wauchula | 1921 | DeSoto | Cary A. Hardee (1876–1957), governor of Florida at the time of creation of Hardee County | 40.26 | 25٬645 | 637 ميل² (1٬650 كم²) |
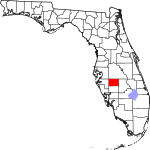
|
| مقاطعة Hendry | 051 | LaBelle | 1923 | Lee | Francis A. Hendry (1833–1917), early Floridian pioneer and politician | 35.85 | 41٬339 | 1٬153 ميل² (2٬986 كم²) |
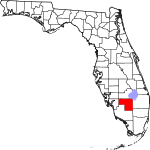
|
| مقاطعة Hernando | 053 | Brooksville | 1843 | Alachua and Hillsborough named Benton from 1844 to 1850 |
Hernando de Soto (c.1496/1497–1542), a Spanish explorer and conquistador | 432.84 | 206٬896 | 478 ميل² (1٬238 كم²) |
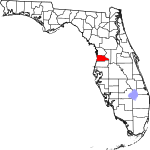
|
| مقاطعة Highlands | 055 | Sebring | 1921 | DeSoto | Named for the county's hilly terrain | 102.74 | 105٬618 | 1٬028 ميل² (2٬663 كم²) |
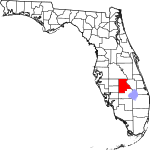
|
| مقاطعة Hillsborough | 057 | Tampa | 1834 | Alachua | Wills Hill, Earl of Hillsborough (1718–1793), former Secretary of State for the Colonies | 1439.87 | 1٬513٬301 | 1٬051 ميل² (2٬722 كم²) |
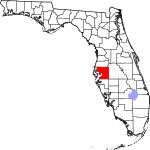
|
| مقاطعة Holmes | 059 | Bonifay | 1848 | Jackson and Walton | Holmes Creek, which forms the eastern boundary of the county | 40.77 | 19٬651 | 482 ميل² (1٬248 كم²) |
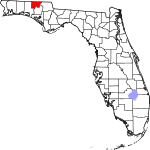
|
| مقاطعة Indian River | 061 | Vero Beach | 1925 | St. Lucie | The Indian River Lagoon, which flows through the county | 332.71 | 167٬352 | 503 ميل² (1٬303 كم²) |
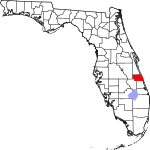
|
| مقاطعة Jackson | 063 | Marianna | 1822 | Escambia | Andrew Jackson (1767–1845), the seventh President of the United States | 52.63 | 48٬211 | 916 ميل² (2٬372 كم²) |
|
| مقاطعة Jefferson | 065 | Monticello | 1827 | Leon | Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826), the third President of the United States and principal author of the Declaration of Independence | 25.15 | 15٬042 | 598 ميل² (1٬549 كم²) |
|
| مقاطعة Lafayette | 067 | Mayo | 1856 | Madison | Gilbert du Motier, marquis de La Fayette (1757–1834), French aristocrat and general in the American Revolutionary War | 14.34 | 7٬786 | 543 ميل² (1٬406 كم²) |
|
| مقاطعة Lake | 069 | Tavares | 1887 | Orange and Sumter | Named for the many lakes in the region | 430.37 | 410٬139 | 953 ميل² (2٬468 كم²) |
|
| مقاطعة Lee | 071 | Fort Myers | 1887 | Monroe | Robert E. Lee (1807–1870), commander of the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War | 1022.95 | 822٬453 | 804 ميل² (2٬082 كم²) |
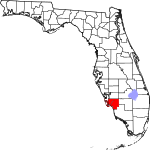
|
| مقاطعة Leon | 073 | Tallahassee | 1824 | Gadsden | Juan Ponce de León (1474–1521), Spanish explorer who named Florida | 445.83 | 297٬369 | 667 ميل² (1٬728 كم²) |
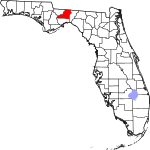
|
| مقاطعة Levy | 075 | Bronson | 1845 | Alachua | David Levy Yulee (1810–1886), one of the state's original United States Senators | 40.48 | 45٬260 | 1٬118 ميل² (2٬896 كم²) |
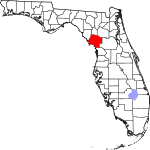
|
| مقاطعة Liberty | 077 | Bristol | 1855 | Gadsden | The patriotic ideal of liberty | 9.09 | 7٬603 | 836 ميل² (2٬165 كم²) |
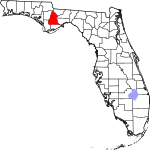
|
| مقاطعة Madison | 079 | Madison | 1827 | Jefferson | James Madison (1751–1836), fourth President of the United States | 26.30 | 18٬198 | 692 ميل² (1٬792 كم²) |
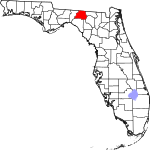
|
| مقاطعة Manatee | 081 | Bradenton | 1855 | Hillsborough | The manatee, or sea cow, is native to Florida waters. | 579.12 | 429٬125 | 741 ميل² (1٬919 كم²) |
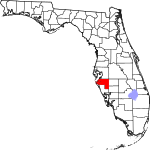
|
| مقاطعة Marion | 083 | Ocala | 1844 | Alachua, Hillsborough, and Mosquito | Francis Marion (c. 1732–1795), military officer during the American Revolution | 251.05 | 396٬415 | 1٬579 ميل² (4٬090 كم²) |
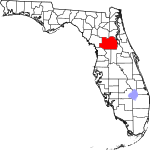
|
| مقاطعة Martin | 085 | Stuart | 1925 | Palm Beach | John W. Martin (1884–1958), governor of Florida at time of creation of the county | 291.38 | 162٬006 | 556 ميل² (1٬440 كم²) |
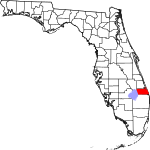
|
| مقاطعة Miami-Dade | 086 | Miami | 1836 | Monroe named Dade until 1997 |
City of Miami and Francis L. Dade (c. 1793–1835), Major in the United States Army during the Second Seminole War | 1374.02 | 2٬673٬837 | 1٬946 ميل² (5٬040 كم²) |
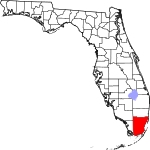
|
| مقاطعة Monroe | 087 | Key West | 1823 | St. Johns | James Monroe (1758–1831), fifth President of the United States | 81.95 | 81٬708 | 997 ميل² (2٬582 كم²) |
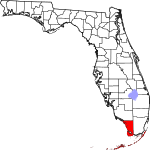
|
| مقاطعة Nassau | 089 | Fernandina Beach | 1824 | Duval | Duchy of Nassau in Germany | 150.15 | 97٬899 | 652 ميل² (1٬689 كم²) |
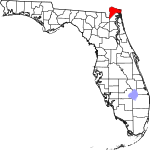
|
| مقاطعة Okaloosa | 091 | Crestview | 1915 | Santa Rosa and Walton | A Choctaw word meaning "a pleasant place," "black water", or "beautiful place" | 231.28 | 216٬482 | 936 ميل² (2٬424 كم²) |
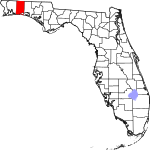
|
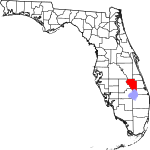
| مقاطعة Okeechobee | 093 | Okeechobee | 1917 | Osceola and St. Lucie | Lake Okeechobee, which was in turn is from the Hitchiti words for "big water" | 52.21 | 40٬412 | 774 ميل² (2٬005 كم²) |
|
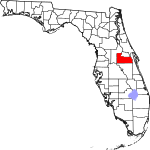
| مقاطعة Orange | 095 | Orlando | 1824 | St. Johns named Mosquito until 1845 |
The fruit that was the county's main product | 1599.92 | 1٬452٬726 | 908 ميل² (2٬352 كم²) |
|
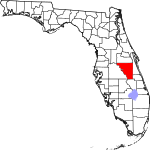
| مقاطعة Osceola | 097 | Kissimmee | 1887 | Brevard and Orange | Osceola (1804–1838), a leader of the Seminole during the Second Seminole War | 319.63 | 422٬545 | 1٬322 ميل² (3٬424 كم²) |
|
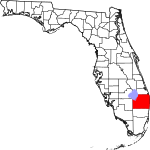
| مقاطعة Palm Beach | 099 | West Palm Beach | 1909 | ميامي-ديد | The county's large amounts of palm trees | 746.55 | 1٬518٬477 | 2٬034 ميل² (5٬268 كم²) |
|
| مقاطعة Pasco | 101 | Dade City | 1887 | Hernando | Samuel Pasco (1834–1917), United States Senator at the time of creation of the county | 817.17 | 608٬794 | 745 ميل² (1٬930 كم²) |
|
| مقاطعة Pinellas | 103 | Clearwater | 1912 | Hillsborough | From the Spanish Punta Piñal, or "Point of Pines" | 3434.78 | 961٬739 | 280 ميل² (725 كم²) |
|
| مقاطعة Polk | 105 | Bartow | 1861 | Brevard and Hillsborough | James K. Polk (1795–1849), the 11th President of the United States | 419.95 | 787٬404 | 1٬875 ميل² (4٬856 كم²) |
|
| مقاطعة Putnam | 107 | Palatka | 1849 | Alachua and St. Johns | Benjamin A. Putnam (1801–1869), soldier during the Second Seminole War and Floridian legislator | 103.51 | 74٬731 | 722 ميل² (1٬870 كم²) |
|
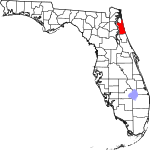
| مقاطعة St. Johns | 109 | St. Augustine | 1821 | One of the two original counties | Name derived from the St. Johns River, which in turn derives its name from San Juan del Puerto | 503.84 | 306٬841 | 609 ميل² (1٬577 كم²) |
|
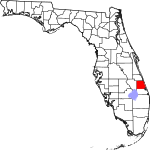
| مقاطعة St. Lucie | 111 | Fort Pierce | 1905 | Brevard | Saint Lucy (283–304), the Christian martyr | 627.10 | 358٬704 | 572 ميل² (1٬481 كم²) |
|
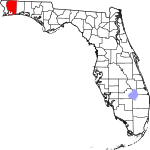
| مقاطعة Santa Rosa | 113 | Milton | 1842 | Escambia | Santa Rosa Island, which is in turn named for Saint Rosa de Viterbo (1235–1252), a saint born in Viterbo, Italy | 195.15 | 198٬268 | 1٬016 ميل² (2٬631 كم²) |
|
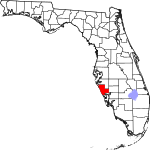
| مقاطعة Sarasota | 115 | Sarasota | 1921 | Manatee | Native American word, of uncertain meaning, for the area | 808.19 | 462٬286 | 572 ميل² (1٬481 كم²) |
|
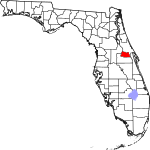
| مقاطعة Seminole | 117 | Sanford | 1913 | Orange | The Seminole Native American tribe | 1554.45 | 478٬772 | 308 ميل² (798 كم²) |
|
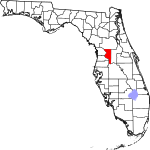
| مقاطعة Sumter | 119 | Bushnell | 1853 | Marion | Thomas Sumter (1734–1832), general in the American Revolution | 265.51 | 144٬970 | 546 ميل² (1٬414 كم²) |
|
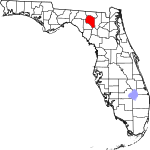
| مقاطعة Suwannee | 121 | Live Oak | 1858 | Columbia | The Suwannee River, a 266-mile long river in northern Florida | 66.00 | 45٬411 | 688 ميل² (1٬782 كم²) |
|
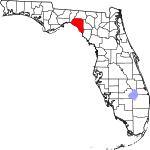
| مقاطعة Taylor | 123 | Perry | 1856 | Madison | Zachary Taylor (1784–1850), 12th President of the United States | 20.43 | 21٬283 | 1٬042 ميل² (2٬699 كم²) |
|
| مقاطعة Union | 125 | Lake Butler | 1921 | Bradford | Named for the area's residents united desire to split into a separate county | 64.42 | 15٬460 | 240 ميل² (622 كم²) |
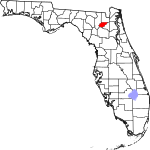
|
| مقاطعة Volusia | 127 | DeLand | 1854 | Orange | The port of Volusia, whose etymology is uncertain; possibly derived from the Native American word for "Land of the Euchees," the term for the area's native inhabitants | 523.68 | 579٬192 | 1٬106 ميل² (2٬865 كم²) |
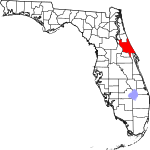
|
| مقاطعة Wakulla | 129 | Crawfordville | 1843 | Leon | The Wakulla River, itself named for a Spanish corruption of a Timucuan word used to describe the body of water, but that is of uncertain meaning | 57.95 | 35٬178 | 607 ميل² (1٬572 كم²) |
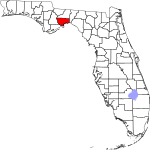
|
| مقاطعة Walton | 131 | DeFuniak Springs | 1824 | Escambia and Jackson | George Walton, first Secretary of Florida Territory | 78.74 | 83٬304 | 1٬058 ميل² (2٬740 كم²) |
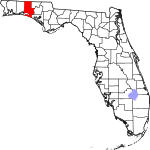
|
| مقاطعة Washington | 133 | Chipley | 1825 | Jackson and Walton | George Washington (1732–1799), first President of the United States | 43.82 | 25٬414 | 580 ميل² (1٬502 كم²) |
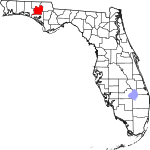
|
مقاطعات سابقة
Fayette County was created in 1832 from the portion of Jackson County east of the Chipola River, with county seat at Ochesee (now in Calhoun County east of Altha).[14][15] In 1834 it was merged back into Jackson County.[16]
مقاطعات تغيرت أسماؤها
Five counties in Florida have been renamed. Most renamings occurred between 1845 and 1861, during the first sixteen years of Florida's statehood. One occurred in 1997, when Dade County changed its name to Miami-Dade County.
| County[5] | Dates[5] | Etymology[5] | Fate[5] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benton County | 1844–1850 | Thomas Benton (1782–1858), U.S. Senator from Missouri who supported the Armed Occupation Act of 1842 that many Floridians wanted in order to evict Native Americans | Original name of county was Hernando County, and the name was changed back to that in 1850 |
| Dade County | 1836–1997 | Francis L. Dade (c. 1793–1835), Major in the United States Army during the Second Seminole War | Changed to Miami-Dade County in 1997, in order to benefit from the City of Miami's internationally recognizable name |
| Mosquito County | 1824–1845 | Taken from the name the Spanish had given the entire coast, "Los Mosquitos" | Mosquito had already repeatedly ceded land to other counties by 1845, when it was renamed Orange County |
| New River County | 1858–1861 | The New River | Renamed to Bradford County in 1861 |
| St. Lucie County | 1844–1855 | Saint Lucy (283–304), the Christian martyr | Renamed Brevard County in 1855 |
مقاطعات مقترحة
| County[5] | Proposal date[5] | Etymology[5] | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bloxham County | 1915[17] | William D. Bloxham (1835–1911), 13th and 17th governor of Florida | county seat at Williston |
| Leigh Read County | 1842 | Leigh Read, legislator | proposed renaming of Mosquito County |
| Miami County[18] | 1947 | مدينة ميامي | consolidated city-county |
| Ocean County | 1991 | المحيط الأطلسي | Jacksonville Beaches |
انظر أيضاً
- فلوريدا
- List of municipalities in Florida
- List of former municipalities in Florida
- List of places in Florida
- List of county seats in Florida
- List of census-designated places in Florida
للاستزادة
- Utley, Geo. B. (1908). "Origin of the County Names in Florida". Florida Historical Society Quarterly. 1 (3): 29–35. Retrieved May 25, 2018.
المراجع
- المحددة
- ^ "A Guide to Alachua County's History". Alachua County Florida. Archived from the original on October 6, 2006. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^ "Explore Census Data". data.census.gov. Retrieved 2021-12-07.
- ^ "About Florida's Counties". Florida Association of Counties. Archived from the original on October 4, 2012. Retrieved January 20, 2010.
- ^ "Demographics". Wakulla County Chamber of Commerce. Retrieved 2012-01-30.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ ر "Florida County Maps". Florida Center for Instructional Technology – University of South Florida. Retrieved January 16, 2010.
- ^ "Florida QuickFacts". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved September 2, 2021. (2020 Census)
- ^ أ ب "United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) County FIPS Code Listing". United States Environmental Protection Agency. Archived from the original on October 8, 2012. Retrieved April 24, 2008.
- ^ أ ب "NACo – Find a county". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on October 25, 2007. Retrieved April 24, 2008.
- ^ Newberry Library, Atlas of Historical County Boundaries: Florida, accessed May 2014
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts: Florida". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 30, 2023.
- ^ "Florida QuickFacts". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 2, 2013. Retrieved April 23, 2008. (2008 Census estimates)
- ^ Morris, Allen, Florida Place Names
- ^ أ ب Eriksen, John M., Brevard County, Florida...A Short History to 1955
- ^ "An Act to organise a county to be called the County of Fayette". ActNo. 53of1832.
- ^ "An Act, more accurately to define the boundaries of Fayette County, and for other purposes". ActNo. 31 (Chapter 688)of1833.
- ^ "An Act to repeal certain acts organizing the County of Fayette". ActNo. 26 (Chapter 765)of1834.
- ^ "An Act Providing for the Creation of Bloxham County in the State of Florida, and for the Organization and the Government Thereof". ActNo. 130 (Chapter 6936)of1915.
- ^ "An Act Providing the Manner, Method and Means of the Election and Creation of a Charter Board in the Territory now Comprising Dade County; Providing for the Drafting and Adopting of the Charter Prepared by Said Board for Said Territory; Providing for the Election of Commissioners of a New Political Subdivision in the Territory now Comprising Dade County to be Known as the County of Miami; Providing the Effective Date of Said Charter and the Time the Board of Commissioners Shall Take Office; and Providing that This Act Shall not Become Effective Until the Joint Resolution No. 407 has Been Approved by the Qualified Electors of Dade County and of the State of Florida as a Whole". ActNo. 853 (Chapter 24467)of1947.
- العامة
- Atlas of Florida, revised edition. Edward A. Fernald & Elizabeth D. Purdum, editors (University Press of Florida, 1996). "Evolution of Counties", pp. 98–99.