لغة هولندية
| الهولندية | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nederlands | ||
| النطق | [ˈneːdərlɑnts] | |
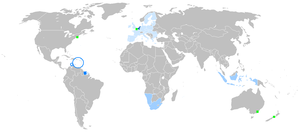
| تـُستخدم في | لغة محلية في هولندا، بلجيكا (فلاندرز وبروكسل)، سورينام، أروبا، الأنتيل الهولندية، إندونسيا، الفلاندرز الفرنسية (فرنسا)، الراين السفلي (ألمانيا).
وعلى الرغم من اشتقاق أفريكانز من الهولندية، إلا أنها تُعتبر لغة عيارية مستقلة، في جنوب أفريقيا وناميبيا. جاليات مهاجرين معتبرة في أستراليا، البرازيل، كندا، نيوزيلندا والولايات المتحدة؛ وأقليات استعمارية سابقة صغيرة في إندونسيا. لغة رسمية في الاتحاد الاوروبي وبنلوكس واتحاد أمم أمريكيا الجنوبية. | |
| إجمالي المتكلمين | أهلها: 23 مليون: 23 مليون ناطق بالهولندية كلغة أولى، زائد 4 مليون يتكلمون الهولندية كلغة ثانية، كما يوجد 7 مليون متكلم بالأفريكانز كلغة أولى، زائد 10 مليون يتكلمون الأفريكانز كلغة ثانية.[بحاجة لمصدر]
إجمالي: 27 مليون (هولندية: 23/27 مليون, أفريكانز: 7/17 مليون) | |
| الترتيب | 40 من 6,000 لغة في قائمة لغات العالم.[1] تقديرات أخرى: 48 (حسب أسلوب العد)؛ 37 (حسب Nederlandse Taalunie[2]) | |
| عائلة لغات | هندو-أوروبية
| |
| نظام الكتابة | الأبجدية اللاتينية (التنويعة الهولندية) | |
| الوضع الرسمي | ||
| لغة رسمية في | ||
| ينظمها | Nederlandse Taalunie (اتحاد اللغة الهولندية) | |
| أكواد اللغة | ||
| ISO 639-1 | nl | |
| ISO 639-2 | dut (B) | nld (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | nld | |
| ملاحظة: هذه الصفحة قد تتضمن رموز صوتية من IPA مكتوبة باليونيكود. انظر جدول IPA للإنجليزية لمفتاح نطق مبني على الإنجليزية. | ||
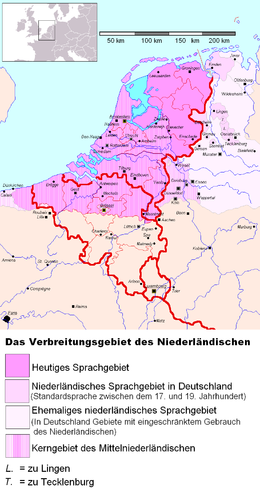
اللغة الهولندية إحدى اللغات الفرنكونية السفلى يبلغ عدد ناطقيها حوالي 22 مليون وتعتبر لغة رئيسية في كل من هولندا وبلجيكا.
تعود أصول اللغة الهولندية إلى القرن الخامس الميلادي مع زحاف الصوامت الجرماني الأول Germanic Consonant Shift الذي فصل اللغة الفرنكية القديمة Frankish عن اللغات الجرمانية الغربية. وتعود تسمية «الهولندية» إلى المنطقة الأهم تاريخياً وهي «هولندا» Holland وأيضاً إلى «الأراضي المنخفضة» Nederlands حيث تُعدّ اللغة الرسمية فيها، كما هي في بلاد فلاندر Flander في شمالي بلجيكا التي تحدّ هولندا من الجنوب حيث يتكلم الناس لهجات متعددة من الهولندية يطلق عليها الفلمنكية Vlaams تشوبها أحياناً كلمات وتعابير فرنسية - وللفلمنكية لهجات متعددة مثل الشرقية والغربية (أو الزيلندية Zealandic) واللمبورغية والبرابانتية - وتسود هذه اللغة في بعض المستعمرات الهولندية السابقة، مثل سورينام وجزر الأنتيل الهولندية. أما الأفريقانية Afrikaans - التي صارت لغة منفصلة عن الهولندية ومستقلة بذاتها - فقد سادت في جنوب إفريقيا إلى أن حلّت الإنكليزية محلها مع انتهاء حكم التمييز العنصري هناك.
التصنيف
- اللغات الهندو-أوروپية
- الجرمانية
- الجرمانية الغربية
- Low Frankish languages or Dutch → Nederlands
- الجرمانية الغربية
- الجرمانية
التوزيع الجغرافي
الوضع الرسمي
Dutch is an official language of هولندا, Belgium, Suriname, Aruba and the Netherlands Antilles. The Dutch, Flemish and Surinamese governments coordinate their language activities in the Nederlandse Taalunie ('Dutch Language Union'). Dutch was an official language in South Africa up until 1961 (it had fallen into disuse after Afrikaans became an official language in 1925). A noticeable minority of the inhabitants of New Zealand, 16,347 (0.4%) claim sufficient fluency in Dutch to carry on an everyday conversation.[3]
Standaardnederlands or Algemeen Nederlands ('Common Dutch', abbreviated to AN) is the standard language as taught in schools and used by authorities in the Netherlands, Flanders, Suriname, Aruba and the Netherlands Antilles. The Dutch Language Union defines what is AN and what is not.
Since efforts to uplift people came to be considered rather presumptuous, the earlier name Algemeen Beschaafd Nederlands ('Common Civilized Dutch') and its abbreviation ABN have been replaced with Algemeen Nederlands and thus AN. The implicit insinuation that people who spoke dialect or with an accent were not civilized was thus removed.
هولندا
بلجيكا
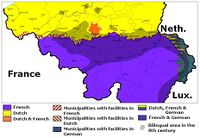
الفلاندرز
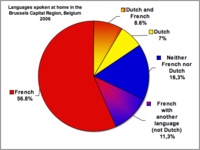
بروكسل
والونيا
سورينام
المنظمات الدولية
Dutch is, apart from the Dutch Language Union (NTU) itself, an official language of the European Union, the Benelux, the Belgium-Luxembourg Economic Union and the Union of South American Nations. It is used unofficially in the Caribbean Community. Afrikaans is a working language in the Southern African Development Community.
أفريكانز في جنوب أفريقيا وناميبيا
الأصوات
الحروف المتحركة
| IPA chart Dutch monophthongs |
|---|
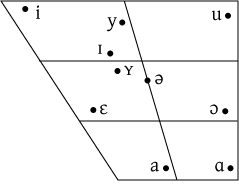
|
| IPA chart Dutch diphthongs |
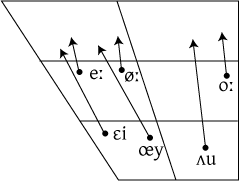
|
| الرمز | مثال | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| IPA | IPA | orthography | الترجمة |
| ɪ | kɪp | kip | 'دجاج' |
| i | bit | biet | 'beetroot' |
| ʏ | ɦʏt | hut | 'كوخ' |
| y | fyt | fuut | 'grebe' |
| ɛ | bɛt | bed | 'سرير' |
| eː | beːt | beet | 'يعض' |
| ə | də | de | 'ال' |
| øː | nøːs | neus | 'أنف' |
| ɑ | bɑt | bad | 'bath' |
| aː | zaːt | zaad | 'seed' |
| ɔ | bɔt | bot | 'bone' |
| oː | boːt | boot | 'boat' |
| u | ɦut | hoed | 'hat' |
| ɛi | ɛi, ʋɛin | ei, wijn | 'egg', 'wine' |
| œy | œy | ui | 'onion' |
| ʌu | zʌut, fʌun | zout, faun | 'salt', 'faun' |
الحروف الساكنة
| Bilabial | Labio- dental |
Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | |
| Plosive | p b | t d | k g1 | ʔ ² | ||||
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||||
| Fricative | f v ³ | s z ³ | ʃ ʒ 4 | x ɣ ³ | ʁ 5 | ɦ | ||
| Approximant | ʋ 6 | j | ||||||
| Lateral | l | ɫ |
Where symbols for consonants occur in pairs, the left represents the voiceless consonant and the right represents the voiced consonant.
Notes:
- [g] is not a native phoneme of Dutch and only occurs in borrowed words, like goal.
- [ʔ] is not a separate phoneme in Dutch, but is inserted before vowel-initial syllables within words after /a/ and /ə/ and often also at the beginning of a word.
- In some dialects, notably that of Amsterdam, the voiced fricatives have almost completely merged with the voiceless ones, and /v/ is usually realized as [f], /z/ is usually realized as [s], and /ɣ/ is usually realized as [x].
- [ʃ] and [ʒ] are not native phonemes of Dutch, and usually occur in borrowed words, like show and bagage (baggage). And even then they are usually realized as [sʲ] and [zʲ] respectively. However, /s/ + /j/ phoneme sequences in Dutch are often realized as [sʲ], like in the word huisje (='little house'). In dialects that merge s and z /zj/ often is realized as [sʲ].
- The realization of the /r/ phoneme varies considerably from dialect to dialect. In "standard" Dutch, /r/ is realized as [r]. In many dialects it is realized as the voiced uvular fricative [ʁ] or even as the uvular trill [ʀ].
- The realization of the /ʋ/ varies considerably from the Northern to the Southern and Belgium dialects of the Dutch language. In the South, including Belgium, it is sometimes realized as [w]. Some, mainly Hollandic, dialects nearly pronounce it like [v].
| Symbol | Example | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPA | IPA | orthography | English translation | |
| p | pɛn | pen | 'pen' | |
| b | bit | biet | 'beetroot' | |
| t | tɑk | tak | 'branch' | |
| d | dɑk | dak | 'roof' | |
| k | kɑt | kat | 'cat' | |
| g | goːl | goal | 'goal' (sports) | |
| m | mɛns | mens | 'human being' | |
| n | nɛk | nek | 'neck' | |
| ŋ | ɛŋ | eng | 'scary' | |
| f | fits | fiets | 'bicycle' | |
| v | oːvən | oven | 'oven' | |
| s | sɔk | sok | 'sock' | |
| z | zeːp | zeep | 'soap' | |
| ʃ | ʃaːɫ | sjaal | 'shawl' | |
| ʒ | ʒyːʁi | jury | 'jury' | |
| x | ɑxt | acht | 'eight' | |
| ɣ | ɣaːn | gaan | 'to go' | |
| r | rɑt | rat | 'rat' | |
| ɦ | ɦut | hoed | 'hat' | |
| ʋ | ʋɑŋ | wang | 'cheek' | |
| j | jɑs | jas | 'coat' | |
| l | lɑnt | land | 'land / country' | |
| ɫ | ɦeːɫ | heel | 'whole' | |
| ʔ | bəʔaːmən | beamen | 'to confirm' | |
التاريخ
سار الكاتب الإنساني ديرك كورنرت Dirk Coornhert ت(1522-1590) على خطى إرازموس Erasmus، ووضع أول مبادئ للغة الهولندية القياسية الحديثة ونحوها، وكان لنشر ترجمة الكتاب المقدس إلى الهولندية عام 1637 دوره هو الآخر في إرساء قواعدها. وفي هذه اللغة عدد كبير من الصوائت البسيطة (14) وأربعة صوائت مدغمة diphthong وثلاثة وعشرون حرفاً صامتاً، ولا وجود فيها لحرف الجيم g، بيد أنه دخل عليها مع الكلمات المستعارة من اللغات الأخرى، مثل goal إلا أنه ينطق x (خاء مخففة). والهولندية لغة تصريفية inflectional تؤدي فيها أواخر الكلمات الدور الأساس في إعطاء المعنى وفي الإعراب، وينتج من ذلك نظام تسلسل للكلمات خاص جداً ومختلف عما هي عليه الحال في الإنكليزية[ر] مثلاً، ويقترب من ذاك المتبع في اللغات الاسكندناڤية. ويتم في الهولندية تأليف الأسماء المركّبة - مثل hondenhot (منزل الكلب) - في كلمة أو اسم واحد في حين تفصل الإنكليزية الأسماء واحدها عن الآخر؛ مما يسمح بظهور كلمات طويلة مثل wapenstilstandsonderhandeling (مباحثات خاصة لوقف إطلاق النار)، بيد أن الطريقة الإنكليزية آخذة بالانتشار.
تستخدم الهولندية الأبجدية اللاتينية، وهي من اللغات الأوربية الأغنى بالمفردات التي تتجاوز 350.000 كلمة. وتتميز بتكرار الحرف الواحد بسبب وجود الأسماء المركّبة التي ينتهي أحدها بحرف ويبدأ به الاسم التالي، مثل voorraaddoos (صندوق المؤن). ومن الكلمات والعبارات اليومية باللغة الهولندية: Hoi /Hallo مرحباً، Ja/ Jawel نعم، Nee/Neen لا، Dank u wel شكراً جزيلاً، Ik weet niet أنا لا أعلم.
تغير الأصوات على مر التاريخ
Dutch (with the exception of the Limburg dialects) did not participate in the second Germanic (High German) Sound Shift - compare German machen /-x-/ Dutch maken, English make, German Pfanne /pf-/, Dutch pan, English pan, German zwei /ts-/, Dutch twee, English two.
Dutch underwent a few changes of its own. For example, words in -old or -olt lost the l in favor of a diphthong as a result of vocalisation. Compare English old, German alt, Dutch oud.
Germanic */uː/ turned into /y/ through palatalization, which sound in turn became a diphthong /œy/, spelt 〈ui〉. Long */iː/ also diphthongized to /ɛi/, spelt 〈ij〉.
The phoneme /ɡ/ became a voiced velar fricative /ɣ/, or a voiced palatal fricative /ʝ/ (in the South: Flanders, Limburg, Brabant).
النحو
 مقالة مفصلة: النحو الهولندي
مقالة مفصلة: النحو الهولندي
الحروف المتحركة
طالع أيضاً
هامش
- ^ (هولندية) G. De Moor in Taalschrift. Tijdschrift over taal en taalbeleid, Dec. 1, 2007.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةTaalunie - ^ Statistics New Zealand - Concerning Language 2004 - Profile of First Language Retention
وصلات خارجية
- The Dutch Language – Dutch Department of Foreign Affairs
- History of the Dutch Language
- Sampa for Dutch
- Dutch and Afrikaans with Japanese translation incl.sound files
المعاجم