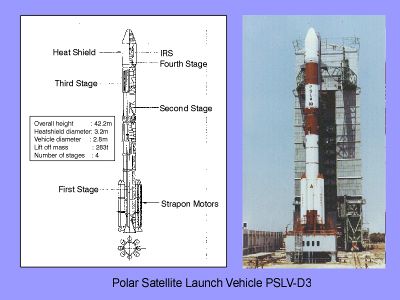
مركبة إطلاق السواتل القطبية
 PSLV-C8 (تنويعة CA) تحمل الساتل AGILE السابر بآشعتي x و γ ، وهو ملك ASI ينطلق من سريهاريكوتا | |
| الوظيفة | مركبة إطلاق متعددة المراحل |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | ISRO |
| Country of origin | |
| Size | |
| Height | 44 metres (144 ft) |
| Diameter | 2.8 metres (9 ft 2 in) |
| Mass | 294,000 kilograms (648,000 lb) |
| المراحل | 4 |
| Capacity | |
| الحمولة إلى LEO | 3,250 kilograms (7,170 lb) |
| الحمولة إلى SSO | 1,600 kilograms (3,500 lb) |
| الحمولة إلى GTO | 1,000 kilograms (2,200 lb) |
| تاريخ الإطلاق | |
| الحالة | Active |
| مواقع الإطلاق | سريهاريكوتا |
| إجمالي الإطلاقات | 15 |
| النجاح | 13 |
| الفشل | 1 |
| فشل جزئي | 1 |
| أول طيران | 20 سبتمبر 1993 |
| الصواريخ الرافعة | |
| عدد المعززات | 6 |
| المحركات | 1 صلب |
| الدفع | 502.600 kN |
| الاندفاع النوعي | 262 sec |
| زمن الحرق | 44 ثانية |
| الدافع | HTPB (صلب) |
| المرحلة الأولى | |
| المحركات | 1 صلب |
| الدفع | 4,860 kN |
| الاندفاع النوعي | 269sec |
| زمن الحرق | 105 ثانية |
| الدافع | HTPB (صلب) |
| المرحلة الثانية | |
| المحركات | 1 ڤيكاس |
| الدفع | 725 kN |
| الاندفاع النوعي | 293 sec |
| زمن الحرق | 158 ثانية |
| الدافع | N2O4/UDMH |
| المرحلة الثالثة | |
| المحركات | 1 صلب |
| الدفع | 328 kN |
| الاندفاع النوعي | 294 sec |
| زمن الحرق | 83 ثانية |
| الدافع | صلب |
| المرحلة الرابعة | |
| المحركات | 2 سائل |
| الدفع | 14 kN |
| الاندفاع النوعي | 308 sec |
| زمن الحرق | 425 ثانية |
| الدافع | MMH/UDMH |
مركبة إطلاق السواتل القطبية Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (هندي: ध्रुवीय उपग्रह प्रक्षेपण यान)، وعادة ما يعرف باختصار كلماته الإنگليزية PSLV، هو نظام إطلاق مرة واحدة تشغـِّله هيئة أبحاث الفضاء الهندية (ISRO). تم تطويرها لتتيح للهند إطلاق سواتل الاستشعار عن بعد الهندية (IRS) في مدارات شمسية التزامن، وهي الخدمة التي كانت، حتى صناعة PSLV، ممكنة تجارياً فقط من روسيا. ويمكن لPSLV أيضاً إطلاق سواتل صغيرة الحجم إلى مدار انتقال ثابت أرضياً (GTO). وقد ثبت إمكانية الاعتماد على PSLV وتنوع استخداماته عبر إطلاقه 30 مركبة فضائية (14 هندية و 16 من دول أخرى) إلى مدارات متعددة حتى الآن.[1] In April 2008, it successfully launched 10 satellites in one go, breaking a world record held by Russia.[2]
يتكلف اطلاق PSLV نحو 17 مليون دولار أمريكي لكل إطلاق.[3][4]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التكوين
التحكم
PSLV is developed with a group of wide-range control units.
| المرحلة 1 | المرحلة 2 | المرحلة 3 | المرحلة 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SITVC for Pitch & Yaw, Reaction control Thrusters for roll. SITVC in 2 PSOMs for roll control augmentation. | Engine Gimbal for Pitch & Yaw, Hot Gas Reaction Control Motor for roll control. | Flex Nozzle for Pitch & Yaw, PS4 RCS for roll control. | Engine Gimbal for Pitch, Yaw and roll On -off RCS for coast phase control. |
التنويعات
في الخدمة
- PSLV
The standard version of the PSLV has four stages using solid and liquid propulsion systems alternately and six strap-on boosters. It currently has capability to launch 1,600 kg to 622 km sun synchronous orbit.
- PSLV-CA
The PSLV-CA, with CA meaning "Core Alone", uses the core stages without any strap-on boosters. It currently has capability to launch 1,100 kg to 622 km sun synchronous orbit.[5]
- PSLV-XL
تاريخ الاطلاق
اعتبارا من 15 فبراير 2017[تحديث] the PSLV has made 39 launches, with 37 successfully reaching their planned orbits, one outright failure and one partial failure, yielding a success rate of 95% (or 97% including the partial failure). All launches have occurred from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), known before 2002 as the Sriharikota Range (SHAR).
| الرحلة | تنويعة الصاروخ | تاريخ/وقت الاطلاق (UTC) | منصة الاطلاق | الحمولة | كتلة الحمولة | النتيجة |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | PSLV-G | 20 September 1993 05:12 |
First | 846 kg | فشل | |
|
Maiden flight; attitude control failure at second stage separation.[6] | ||||||
| D2 | PSLV-G | 15 October 1994 05:05 |
First | 804 kg | نجاح | |
| D3 | PSLV-G | 21 March 1996 04:53 |
First | 920 kg | نجاح | |
| C1 | PSLV-G | 29 September 1997 04:47 |
First | 1250 kg | فشل جزئي | |
|
First operational flight; fourth stage under-performed resulting in lower than planned orbit. Satellite used own propulsion to move to correct orbit.[9] | ||||||
| C2 | PSLV-G | 26 May 1999 06:22 |
First | 1050 kg 45 kg 107 kg |
نجاح | |
|
First launch to have foreign satellites, and first to carry multiple satellites.[10][11] | ||||||
| C3 | PSLV-G | 22 October 2001 04:53 |
First | 1108 kg 94 kg 92 kg |
نجاح | |
|
First multi-orbit mission. TES and BIRD were injected into a nominal 568 km circular sun synchronous polar orbit, PROBA was injected into a 568 X 638 km elliptical orbit. Orbit was raised using RCS thrusters on fourth stage.[12][13] | ||||||
| C4 | PSLV-G | 12 September 2002 10:23 |
First | 1060 kg | نجاح | |
|
India's first launch to GTO. GTO payload capability has reached 1200 kg from 2002 onward, compared to 1050 kg previously. First use of lightweight carbon composite payload adapter.[14][15][16] | ||||||
| C5 | PSLV-G | 17 October 2003 04:52 |
First | 1360 kg | نجاح | |
|
Payload capability had been progressively increased by more than 600 kg since the first PSLV launch. Launch took place despite heavy rain.[17][18] | ||||||
| C6 | PSLV-G | 5 May 2005 04:45 |
Second | 1560 kg 42.5 kg |
نجاح | |
| C7 | PSLV-G | 10 January 2007 03:54 |
First | 680 kg 500 kg 56 kg 6 kg |
نجاح | |
|
First flight of hardware upgrade, first launch of reentry capsule (SRE).[20] | ||||||
| C8 | PSLV-CA | 23 April 2007 10:00 |
Second | 352 kg 185 kg |
نجاح | |
|
First flight of the 'Core-Alone' configuration. ISRO's first commercial launch (foreign satellite as the main payload).[21][22] | ||||||
| C10 | PSLV-CA | 21 January 2008 03:45 |
First | 295 kg | نجاح | |
|
ISRO's second commercial launch (foreign satellite as the main payload).[23][24] | ||||||
| C9 | PSLV-CA | 28 April 2008 03:53 |
Second | 690 kg 83 kg 8 kg 6.5 kg 3.5 kg 3 kg 2.2 kg 1 kg 1 kg 0.75 kg |
نجاح | |
| C11 | PSLV-XL | 22 October 2008 00:52 |
Second | 1380 kg | نجاح | |
|
First flight of the PSLV-XL configuration, first Indian Lunar probe.[27][28] | ||||||
| C12 | PSLV-CA | 20 April 2009 01:15 |
Second | 300 kg 40 kg |
نجاح | |
| C14 | PSLV-CA | 23 September 2009 06:21 |
First | 960 kg 8 kg 8 kg 1 kg 1 kg 1 kg 1 kg |
نجاح | |
|
Rubin 9.1 and 9.2 intentionally remained attached to the fourth stage. SwissCube-1 was the first Swiss satellite, and ITUpSAT1 was the first satellite to be constructed in Turkey.[31][32][33][34][35][36] | ||||||
| C15 | PSLV-CA | 12 July 2010 03:52 |
First | 694 kg 117 kg 6.5 kg 1 kg 0.95 kg |
نجاح | |
|
AISSat-1 and TIsat are part of NLS-6.[37][38][39][40][41][42][43] | ||||||
| C16 | PSLV-G | 20 April 2011 04:42 |
First | 1206 kg 106 kg 92 kg |
نجاح | |
| C17 | PSLV-XL | 15 July 2011 11:18 |
Second | 1410 kg | نجاح | |
| C18 | PSLV-CA | 12 October 2011 05:31 |
First | 1000 kg 10.9 kg 3 kg 28.7 kg |
نجاح | |
| C19 | PSLV-XL | 26 April 2012 00:17 |
First | 1850 kg | نجاح | |
| C21 | PSLV-CA | 9 September 2012 04:23 |
First | 720 kg 50 kg 15 kg |
نجاح | |
|
mRESINS tested avionics for future PSLV launches. ISRO's third commercial launch (foreign satellite as the main payload). ISRO's 100th mission.[50][51] | ||||||
| C20 | PSLV-CA | 25 February 2013 12:31 |
First | 409 kg 148 kg 74 kg 14 kg 14 kg 6.5 kg 0.8 kg |
نجاح | |
|
TUGSAT-1 and UniBRITE were the first Austrian satellites.[52][53][54] | ||||||
| C22 | PSLV-XL | 1 July 2013 18:11 |
First | 1425 kg | نجاح | |
|
India's first regional navigation satellite.[55] | ||||||
| C25 | PSLV-XL | 5 November 2013 09:08 |
First | 1350 kg | نجاح | |
| C24 | PSLV-XL | 4 April 2014 11:44 |
First | 1432 kg | نجاح | |
| C23 | PSLV-CA | 30 June 2014 04:22 |
First | 714 kg 15 kg 15 kg 14 kg 7 kg |
نجاح | |
|
ISRO's fourth commercial launch (foreign satellite as the main payload).[60] | ||||||
| C26 | PSLV-XL | 16 October 2014 20:02 |
First | 1425.4 kg | نجاح | |
|
Seventh PSLV-XL and third Navigation Satellite launch.[61][62] | ||||||
| C27 | PSLV-XL | 28 March 2015 11:49 |
Second | 1425 kg | نجاح | |
|
Eighth PSLV-XL and fourth Navigation Satellite launch.[63] | ||||||
| C28 | PSLV-XL | 10 July 2015 16:28 |
First | 447 kg 447 kg 447 kg 91 kg 7 kg |
نجاح | |
|
At the time it was the heaviest commercial mission (1439 kg) successfully accomplished using a launch vehicle assembled by ISRO.[64][65] | ||||||
| C30 | PSLV-XL | 28 September 2015 04:30 |
First | 1650 kg 68 kg 5.5 kg 4 kg 4 kg 4 kg 4 kg |
نجاح | |
|
Launch of India's first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory and ISRO's first launch of US satellites.[66] | ||||||
| C29 | PSLV-CA | 16 December 2015 12:30 |
First | 400 kg 123 kg 13 kg 78 kg 3.4 kg - |
نجاح | |
|
Commercial launch of 6 Singaporean satellites. Fourth stage re-ignition demonstrated successfully after payload deployment.[68][69][70] | ||||||
| C31 | PSLV-XL | 20 January 2016 04:01 |
Second | 1425 kg | نجاح | |
|
IRNSS-1E, fifth navigation satellite of the seven satellites constituting the IRNSS space segment launched. It carries two types of payloads – navigation payload and ranging payload. This is the eleventh time ‘XL’ configuration is being flown.[71][72][73] | ||||||
| C32 | PSLV-XL | 10 March 2016 10:31 |
Second | 1425 kg |
نجاح | |
|
IRNSS-1F, sixth navigation satellite of the seven satellites constituting the IRNSS space segment launched. It carries two types of payloads – navigation payload and ranging payload. This is the twelfth time ‘XL’ configuration is being flown. IRNSS-1F carries Corner Cube Retro Reflectors for laser ranging.[74] Launch initially scheduled for 10:30 was delayed by one minute to avoid space debris.[75] | ||||||
| C33 | PSLV-XL | 28 April 2016 07:20 |
First | 1425 kg |
نجاح | |
|
IRNSS-1G, last navigation satellite of the seven satellites constituting the IRNSS space segment launched. India's own navigational system, the set-up for which was completed will be called NAVIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation)[76][77][78][79][80] | ||||||
| C34 | PSLV-XL | 22 June 2016 03:55 |
Second |
|
|
نجاح |
|
ISRO's Cartosat-2C and 19 other satellites launched.[81][82][83][84][85][86] | ||||||
| C35 | PSLV-G | 26 September 2016 03:42 |
First | 371 kg 117 kg 103 kg 44 kg 10 kg 8 kg 7 kg 5.25 kg |
نجاح | |
|
ISRO's longest PSLV satellite launch mission. First mission of PSLV in which it launched its payloads into two different orbits.[87][88][89][90][91][92] | ||||||
| C36 | PSLV-XL | 7 December 2016 04:55 |
First | 1235 kg | نجاح | |
| C37 | PSLV-XL | 15 February 2017
03:58 |
First | 730 kg 8.4 kg 9.7 kg 1.1 kg 1.7 kg 3 kg 4.3 kg 4.2 kg 4.7 kg x 88 Nos. 4.6 kg x 8 Nos. |
نجاح | |
|
PSLV-C37 successfully carried and deployed a record 104 satellites in the Sun-synchronous orbit.[99][100][101][102][103][104] | ||||||
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
المصادر
- * means Second Launch Pad.
الهامش
- ^ PSLV-C11 Successfully Launches Chandrayaan-1
- ^ "India sets its sights on the Moon". BBC. 2008-10-21. Retrieved 2008-10-23.
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ "ISRO Annual Report 2006 - Space Transportation". ISRO.
- ^ IRS-1E
- ^ IRS-P2
- ^ IRS-P3
- ^ IRS-1D
- ^ PSLV-C2
- ^ "Current Science".
- ^ Ramakrishnan, S.; Somanath, S.; Balakrishnan, S. S. (2002-01-01). "Multi-Orbit Mission by PSLV-C3 and Future Launch Opportunities".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ PSLV-C3
- ^ PSLV-C4
- ^ International reference guide to space launch systems, Fourth Edition, p. 330, ISBN 1-56347-591-X
- ^ "PSLV-C4/METSAT Mission". ISRO.gov.in. Retrieved February 2015.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ PSLV-C5
- ^ "Frontline: A remote-sensing success". The Hindu. Chennai, India.
- ^ PSLV-C6
- ^ PSLV-C7
- ^ "PSLV-C8 blasts off with Italian payload". Rediff.com.
- ^ First commercial launch of PSLV-C8 successful-India-The Times of India
- ^ PSLV-C10
- ^ NDTV - ISRO Launches Israeli Satellite
- ^ Delfi-C3 Mission status page
- ^ PSLV Rocket Launches 10 Satellites
- ^ PSLV C11
- ^ T.S. Subramanian (23 October 2008). "Chandrayaan-1 bound for Moon". The Hindu. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ^ PSLV C12
- ^ "India launches spy satellite RISAT-2". IBNLive.
- ^ ":: Bharat-Rakshak.com - Indian Military News Headlines ::".
- ^ ISRO - CUBESATS
- ^ "News Archives: The Hindu". The Hindu.
- ^ "Oceansat 2, 6 nanosats launched in 20 mins by ISRO". The Indian Express.
- ^ "Satnews Publishers: Daily Satellite News".
- ^ First Turkish-Made Satellite Launched From India
- ^ Nanosatellite Launch Service 6. "UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ More info
- ^ PSLV CA-C15 Countdown
- ^ eZ Systems. "Home - Norwegian Space Centre".
- ^ "NSSDC Master Catalog (Entry-ID: 2010-035E)". NASA. 16 August 2013. Retrieved 1 May 2014.
- ^ "SUPSI Space Lab".
- ^ "ISRO to launch five satellites on July 12". IANS. Sify. 3 July 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- ^ T.S., Subramanian (19 April 2011). "PSLV-C16 launch today". The Hindu. Chennai, India. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ^ "PSLV-C17".
- ^ T.S. Subramanian. "ISRO-developed computer helped PSLV-C17 put satellite in orbit". The Hindu.
- ^ Megha-Tropiques / PSLV-C18 scheduled for take off on 12 October 2011 at 11:00:00 IST
- ^ "VesselSat 1, 2, 3". Gunter's Space. Retrieved 2011-10-10.
- ^ M. Dinesh Varma. "PSLV-C19 puts RISAT-1 in orbit". The Hindu.
- ^ "Isro prepares for historic 100th mission". The Times Of India. 22 August 2012.
- ^ "100 missions of ISRO" (PDF). Retrieved 1 August 2016.
- ^ "Indian rocket launches asteroid hunter, 6 other satellites". NBC. 25 February 2013. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- ^ "India to launch seven satellites on February 25". DNA India. 15 February 2013. Retrieved 17 February 2013.
- ^ Smartphone nanosatellite Space researchers at the University of Surrey's Surrey Space Centre (SSC) and SSTL have developed STRaND-1 "SSTL.co.uk" retrieved 14 Feb 2012
- ^ "PSLV-C22 Successfully Launches IRNSS-1A, India's First Navigation Satellite" (Press release). ISRO. 2 July 2013. Retrieved 2 July 2013.
- ^ "The Indian Herald".
- ^ "India to launch Mars mission on Nov 5". Hindustan Times. 2013-10-22. Retrieved 2013-11-07.
- ^ "PSLV". Space.skyrocket.de. Retrieved 2013-11-07.
- ^ "Navigational satellite IRNSS 1-B launch set for March 31". The Indian Express. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- ^ "PSLV C23 to lift-off on June 30 with five foreign satellites". Retrieved 26 June 2014.
- ^ "Indian PSLV lofts IRNSS-1C satellite". Retrieved 16 October 2014.
- ^ "PSLV-C26/IRNSS-1C" (PDF). Retrieved 16 October 2014.
- ^ "India's Fourth Navigational Satellite IRNSS-1D Launched From Sriharikota". Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- ^ Manish Raj (10 July 2015). "Isro successfully launches PSLV-C28 carrying 5 UK satellites". Times of India. Retrieved 11 July 2015.
- ^ Dennis S. Jesudasan (10 July 2015). "PSLV C-28 launches five UK satellites". The Hindu. Retrieved 11 July 2015.
- ^ "ASTROSAT, India's first astronomical mission, set for September 28 launch". PTI. Economic Times. 16 September 2015. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- ^ http://www.isro.gov.in/sites/default/files/pslv-c29brochure.pdf
- ^ Patil, Vijaykumar (14 Nov 2015). "ISRO to launch five satellites in December".
- ^ "SaRC fact sheet" (PDF).
- ^ "ISRO Successfully Tests Multiple Burn Fuel Engine During Launch of Six Singaporean Satellites".
- ^ "SHAR set to launch 2 satellites in March 2016".
- ^ "ISRO's RLV-TD Project Likely to be Delayed". The New Indian Express. Retrieved 2015-12-28.
- ^ "PSLV-C31/IRNSS-1E - ISRO". www.isro.gov.in. Retrieved 2016-01-12.
- ^ http://www.isro.gov.in/launcher/pslv-c32-irnss-1f
- ^ "PSLV C32/ IRNSS 1F UPDATE: The launch time is revised to 16:01 hr (IST) for collision avoidance as per the space debris studies. Countdown status normal. - ISRO". www.isro.gov.in. Retrieved 2016-03-16.
- ^ http://www.prajasakti.com/Content/1748605
- ^ "ISRO scientists in Ahmedabad uses 'spares' for weather satellite to save cost and time". The Indian Express. 2016-02-05. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ "నేడు పిఎస్ఎల్వి-సి32 కౌంట్డౌన్ | Prajasakti::Telugu Daily". www.prajasakti.com. Retrieved 2016-03-16.
- ^ "IRNSS full fleet could be a month late". The Hindu (in الإنجليزية). 2016-03-17. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 2016-04-16.
- ^ "PSLV-C33/IRNSS-1G - ISRO". www.isro.gov.in. Retrieved 2016-04-20.
- ^ http://www.isro.gov.in/sites/default/files/brochure-pslv_c34.pdf
- ^ http://www.andhrajyothy.com/Artical?SID=200026
- ^ "ISRO to launch record 22 satellites in single mission in June".
- ^ "Satmaxvalier".
- ^ "PSLV-C34". Retrieved 16 June 2016.
- ^ "Mission Readiness Review (MRR) committee and Launch Authorisation Board (LAB) have cleared the 48 hr countdown starting at 09:26hr IST on Monday, June 20, 2016 and the launch of PSLV-C34/Cartosat-2 Series Satellite Mission for Wednesday, June 22, 2016 at 09:26hr IST".
- ^ "రెండు ప్రయోగాలకు సిద్ధమవుతోన్న ఇస్రో".
- ^ "సెప్టెంబర్లో షార్ నుండి రెండు ప్రయోగాలు".
- ^ "ISRO to launch 5 satellites in Septemeber [sic]".
- ^ http://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/scatsat-1.htm
- ^ "IIT-B's feat: Mumbai's first satellite to lift off on September 26".
- ^ "PSLV-C35 Successfully Launches Eight Satellites into Two Different Orbits in a Single Flight".
- ^ "Noorul Islam University bets big on NIUSAT".
- ^ "Resourcesat-2A launch on November 28".
- ^ "డిసెంబర్ 7న పీఎస్ఎల్వీ ప్రయోగం".
- ^ "డిసెంబర్ 7న మరో ఉపగ్రహ ప్రయోగం".
- ^ "PSLV C36/ Resourcesat-2A".
- ^ "PSLV C36 / Resourcesat-2A Brochure".
- ^ "ISRO to launch record 103 satellites in one go in February".
- ^ "ISRO centres set for the record launch of 104 satellites at one go by February 15".
- ^ "పీఎస్ఎల్వీ సీ–37 ప్రయోగ సమయం మార్పు".
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ "పీఎస్ఎల్వీ సి-37 ప్రయోగ సమయం మార్పు".
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ "ISRO to launch record 83 satellites in one go in January". Indian Express. Retrieved 2016-12-27.
- ^ http://www.thenational.ae/uae/science/uae-nanosatellite-to-launch-this-month