تابوت تبنيت
| Tabnit sarcophagus | |
|---|---|
 The sarcophagus, Istanbul Archaeology Museums | |
| الخامة | Basalt |
| الكتابة | Phoenician |
| أنشئت | c.500 BC |
| أُكتشفت | 1887 |
| الموقع الحالي | Istanbul Archaeology Museums |
The Tabnit sarcophagus is the sarcophagus of the Phoenician King of Sidon Tabnit (ruled c. 549–539 BC),[1] the father of King Eshmunazar II. It is decorated with two separate and unrelated inscriptions – one in Egyptian hieroglyphs and one in the Phoenician alphabet. The latter contains a curse for those who open the tomb, promising impotency and loss of an afterlife.
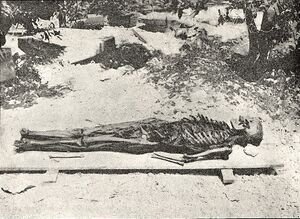
It has been dated to early fifth century BC, and was unearthed in 1887 by Osman Hamdi Bey at the Royal necropolis of Ayaa east of Sidon together with the Alexander Sarcophagus and other related sarcophagi. Tabnit's body was found floating perfectly preserved in the original embalming fluid.[2][3] Both the sarcophagus and Tabnit's decomposed skeleton are now in the Istanbul Archaeology Museums.[4]
The sarcophagus, together with the Sarcophagus of Eshmunazar II, were possibly acquired by the Sidonians following their participation in the Battle of Pelusium during the First Achaemenid conquest of Egypt,[5] and served as models for later Phoenician sarcophagi.[6] The Phoenician text is considered to have a "remarkable" similarity to that of the Shebna inscription from Jerusalem.[7]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Discovery
At the beginning of 1887, Mehmed Sherif Effendi, the owner of a piece of land known as Ayaa, obtained a permit from the local authorities to quarry stone for the construction of a new building. On 2 March 1887, Cherif reported to the Kaymakam of Sidon, Sadik Bey, that he had discovered a well at the bottom of which there might be tombs. Sadik Bey examined the site and spotted a vault containing two sarcophagi through a hole in the eastern wall of the well. He escalated the matter to the Vali of the Syria vilayet, Rashid Nashid Pasha, and the Governor of Beirut Nassouhi Bey, and entrusted the well to the care of Essad Effendi from the gendarmerie of Sidon.[8]
According to the American missionary narrative, the tombs were discovered in 1887 by the American Presbyterian minister William King Eddy (the father of William A. Eddy). William Wright sent a letter to The Times with news of Eddy's discovery and imploring the British Museum to "take immediate measures to secure these treasures and prevent their falling into the hands of the vandal Turk". This alerted the new curator of the fledgling Istanbul Archaeological Museum, Osman Hamdi Bey, who arranged for a full excavation and the transfer of the sarcophagi to Istanbul.[9]
During the excavation, the workmen opened the Tabnit sarcophagus and found "a human body floating in perfect preservation in a peculiar fluid". Whilst Hamdi Bey was at lunch, the workmen overturned the sarcophagus and poured the fluid out, such that the "secret of the wonderful fluid was again hidden in the Sidon sand". Notably, after the "peculiar fluid" left the sarcophagus, the body started to become un-preservable.[10][2] Hamdi Bey noted in 1892 that he had kept a portion of the sludge that remained in the bottom of the sarcophagus.[11]
Inscription

The inscription is known as KAI 13. The Egyptian hieroglyphic inscription shows that the sarcophagus was originally intended for an Egyptian general named "Pen-Ptah" (pꜣ-n-pth).[12] Transcribed in equivalent Hebrew letters, the Phoenician text is readable by a modern Hebrew speaker, with a few distinctions: as is customary in Phoenician, the direct object marker is written אית (ʾyt) instead of את (ʾt) in Hebrew, and relative clauses ('which', 'who') are introduced with אש (ʾš) instead of אשר (ʾšr) in Hebrew.[13] Among less common words in modern Hebrew, the inscription uses חרץ for gold (Biblical חָרוּץ) and אר for the verb 'to gather' (אָרוּ 'they gathered', Biblical אָרָה).[14]
| Phoenician letters | Equivalent Hebrew letters | Transliteration | Restored pronunciation | English translation |
| 𐤀𐤍𐤊 𐤕𐤁𐤍𐤕 𐤊𐤄𐤍 𐤏𐤔𐤕𐤓𐤕 𐤌𐤋𐤊 𐤑𐤃𐤍𐤌 𐤁𐤍 𐤀𐤔𐤌𐤍𐤏𐤆𐤓 𐤊𐤄𐤍 𐤏𐤔𐤕𐤓𐤕 𐤌𐤋𐤊 𐤑𐤃𐤍𐤌 𐤔𐤊𐤁 𐤁𐤀𐤓𐤍 𐤆 𐤌𐤉 𐤀𐤕 𐤊𐤋 𐤀𐤃𐤌 𐤀𐤔 𐤕𐤐𐤒 𐤀𐤉𐤕 𐤄𐤀𐤓𐤍 𐤆 𐤀𐤋 𐤀𐤋 𐤕𐤐𐤕𐤇 𐤏𐤋𐤕𐤉 𐤅𐤀𐤋 𐤕𐤓𐤂𐤆𐤍 𐤊 𐤀𐤉 𐤀𐤓 𐤋𐤍 𐤊𐤎𐤐 𐤀𐤉 𐤀𐤓 𐤋𐤍 𐤇𐤓𐤑 𐤅𐤊𐤋 𐤌𐤍𐤌 𐤌𐤔𐤃 𐤁𐤋𐤕 𐤀𐤍𐤊 𐤔𐤊𐤁 𐤁𐤀𐤓𐤍 𐤆 𐤀𐤋 𐤀𐤋 𐤕𐤐𐤕𐤇 𐤏𐤋𐤕𐤉 𐤅𐤀𐤋 𐤕𐤓𐤂𐤆𐤍 𐤊 𐤕𐤏𐤁𐤕 𐤏𐤔𐤕𐤓𐤕 𐤄𐤃𐤁𐤓 𐤄𐤀 𐤅𐤀𐤌 𐤐𐤕𐤇 𐤕𐤐𐤕𐤇 𐤏𐤋𐤕𐤉 𐤅𐤓𐤂𐤆 𐤕𐤓𐤂𐤆𐤍 𐤀𐤋 𐤉𐤊𐤍 𐤋𐤊 𐤆𐤓𐤏 𐤁𐤇𐤉𐤌 𐤕𐤇𐤕 𐤔𐤌𐤔 𐤅𐤌𐤔𐤊𐤁 𐤀𐤕 𐤓𐤐𐤀𐤌 |
אנכ תבנת כהן עשתרת מלך צדנם בן אשמנעזר כהן עשתרת מלך צדנם שכב בארן ז מי את כל אדם אש תפק אית הארן ז אל אל תפתח עלתי ואל תרגזן כ אי אר לנ כסף אי אר לנ חרץ וכל מנם משד בלת אנכ שכב בארן ז אל אל תפתח עלתי ואל תרגזן כ תעבת עשתרת הדבר הא ואם פתח תפתח עלתי ורגז תרגזן אל יכן לך זרע בחים תחת שמש ומשכב את רפאם |
ʾnk tbnt khn ʿštrt mlk ṣdnm bn ʾšmnʿzr khn ʿštrt mlk ṣdnm škb bʾrn z my ʾt kl ʾdm ʾš tpq ʾyt hʾrn z ʾl ʾl tptḥ ʿlty wʾl trgzn k ʾy ʾrln ksp ʾy ʾr ln ḥrṣ wkl mnm mšd blt ʾnk škb bʾrn z ʾl ʾl tptḥ ʿlty wʾl trgzn k tʿbt ʿštrt hdbr hʾ wʾm ptḥ tptḥ ʿlty wrgz trgzn ʾl ykn lk zrʿ bḥym tḥt šmš wmškb ʾt rpʾm |
1 ʼanôkî Tabnît kôhen ‛Aštart milk Ṣîdônîm bin 2 ʼEšmûn‛azar kôhén ‛Aštart milk Ṣîdônîm šôkéb bâʼarôn |
I, Tabnit, priest of Astarte, king of Sidon, the son of Eshmunazar, priest of Astarte, king of Sidon, am lying in this sarcophagus. Whoever you are, any man that might find this sarcophagus, don't, don't open it and don't disturb me, for no silver is gathered with me, no gold is gathered with me, nor anything of value whatsoever, only I am lying in this sarcophagus. Don't, don't open it and don't disturb me, for this thing is an abomination to Astarte. And if you do indeed open it and do indeed disturb me, may you not have any seed among the living under the sun, nor a resting-place with the Rephaites. |
Dating
Both the Tabnit sarcophagus and the Sarcophagus of Eshmunazar II are thought to originally date from the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt, which had its capital at Sais.[6] This is partially due to their resemblance to similar sarcophagi such as the Psamtik II-era Horkhebit sarcophagus from Saqqara, now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Notes
- ^ "Middle East Kingdoms Ancient Central Levant States - Sidon". Kessler Associates. Retrieved 23 May 2017.
- ^ أ ب Gubel, Eric (2003), "Phönizische Anthropoide Sarkophage by Katja Lembke", Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research 332: 98–100, doi:
- ^ Torrey 1902, pp. 168–9 (footnote).
- ^ İstanbul Archaeological Museums
- ^ Nitschke 2007, p. 71.
- ^ أ ب Nitschke 2007, p. 72.
- ^ Hays, Christopher B. (January 2010). "Re-Excavating Shebna's Tomb: A New Reading of Isa 22,15–19 in its Ancient Near Eastern Context". Zeitschrift für die Alttestamentliche Wissenschaft. 122 (4). doi:10.1515/ZAW.2010.039.
The similarity of the inscription to that of Tabnit of Sidon (KAI1.13, COS2.56) is remarkable, extending even to the assertion that there are no precious metals within."
- ^ Hamdi Bey & Reinach 1892a, p. I.
- ^ Jessup 1910, p. 507a.
- ^ Jessup 1910, p. 507b.
- ^ Hamdi Bey & Reinach 1892, pp. 101–103.
- ^ "The Context of Scripture Online | Scholarly Editions". scholarlyeditions.brill.com (in الإنجليزية). Brill.
- ^ Maria Giulia Amadasi Guzzo; Gary A. Rendsburg (2013). "Phoenician/Punic and Hebrew". Encyclopedia of Hebrew Language and Linguistics. Koninklijke Brill. 3, P–Z. ISBN 978-90-04-17642-3.
- ^ أ ب HAELEWYCK, Jean-Claude (2011). "L'inscription phénicienne de Tabnit (KAI 13) Essai de vocalisation". Res Antiquae, Safran Publishers. VIII.
- ^ "Metropolitan Museum of Art". www.metmuseum.org.
References
- Hamdi Bey, Osman; Reinach, Théodore (1892) (in fr), Une nécropole royale à Sidon, doi:, http://digi.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/diglit/hamdybey1892bd1 (editio princeps)
- Hamdi Bey, Osman; Reinach, Théodore (1892a) (in fr), Une nécropole royale à Sidon: fouilles: Planches, doi:, http://digi.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/diglit/hamdybey1892bd2 (Plates)
- Jessup, Henry Harris (1910), Fifty-Three Years In Syria, 2, Fleming H. Revell Company, p. 507, https://archive.org/stream/fiftythreeyearsi011830mbp#page/n129/mode/2up
- Gottheil, Richard (1889), "The Inscription of Tabnit", Hebraica 5 (2): 197, doi:
- Bommas, Martin (2006), "Die hieroglyphischen Texte auf dem Sarg des Tabnit", Orientalia 75 (1): 15, https://books.google.com/books?id=aOA8xpJZhjgC&pg=PA1
- Assmann, Jan, "Zur Baugeschichte der Königsgruft von Sidon", Archäologischer Anzeiger: 690–716, http://archiv.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/propylaeumdok/1700/1/Assmann_Zur_Baugeschichte_der_Koenigsgruft_von_Sidon_1963.pdf
- Nitschke, Jessica (2007), Perceptions of Culture:Interpreting Greco-Near Eastern Hybridity in the Phoenician Homeland, University of California, Berkeley, https://www.academia.edu/1561148
- Torrey, Charles (1902), "A Phoenician Royal Inscription", Journal of the American Oriental Society 23: 156–173, doi:
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- 5th-century BC inscriptions
- 1887 archaeological discoveries
- Phoenician inscriptions
- KAI inscriptions
- Kings of Sidon
- Multilingual texts
- Phoenician sarcophagi
- 5th-century BC artifacts
- Royal necropolis of Ayaa
- Archaeological discoveries in Lebanon
- Ancient Egyptian sarcophagi