مياه دولية
|
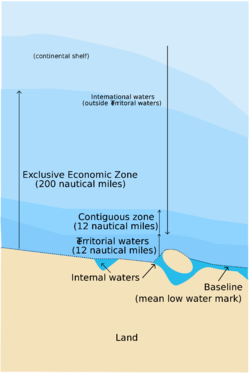
المياه الدولية أو المياه عبر الحدود International waters، هي مناطق المحيطات التي تقع خارج سلطة أي دولة. وتبدأ بشكل عام بعد 200 ميل بحري، من سواحل الدول المتاخمة للمحيطات. أما مناطق المحيطات التي تمارس الدول سلطتها عليها، فتسمى المياه الإقليمية.
في القانون الدولي، تعتبر أعالي البحار مفتوحة أمام أي دولة للصيد، والسفر، والبحث. وجميع الدول لها حقوق متساوية في أعالي البحار، ويجب أن تحترم كل منها حقوق الدُّول الأخرى.
يجب على جميع الدول أن تتبع القواعد الدولية، الخاصة بأعالي البحار، ففي ظل القانون الدولي، تُعتبر أعالي البحار مفتوحة أمام أي دولة للصيد، والسفر، والبحث. وجميع الدول لها حقوق متساوية في أعالي البحار، ويجب أن تحترم كل منها حقوق الدُّول الأخرى.
ويسمح القانون الدولي أثناء الحرب، للدول المحايدة، أن تواصل التجارة مع الدول الأخرى المحايدة، ومع الدول المتحاربة. ومع ذلك ففي مثل هذه الأوقات، يفترض ألاّ تنقل سفن الدول المحايدة التّجارة المحظورة في الحرب، (البضائع غير القانونية)، وتقرر الدول المتحاربة، المواد التي تعتبرها مهربات حرب.[1]
وهناك جدل طويل بين الدول، حول قانون البحر. فبين عامي 1986 و1982م، أصدرت الأمم المتحدة قوانين البحر، التي قد ترضي جميع الدول. وقد أدى هذا العمل إلى إقرار اتفاقية قانون البحر عام 1982م. وقد وُقِّعت أكثر من مائة من الدول الأعضاء في منظومة الأمم المتحدة على الاتفاقية. ولا تصبح هذه الاتفاقية رسمية إلا إذا صّدقت عليها 60 دولة.
وبوجه عام، تُعطي هذه الاتفاقية الدول الحقوق القصرية في التنقيب عن البترول، والغاز حتى مسافة 350 ميلاً بحريًا (648 كم) من الشاطئ، والصيد في حدود 200 ميل بحري، (370كم) من سواحلها، وفي حدود هاتين المائتي ميلٍ بحريّ، والتي تسمى المنطقة الاقتصادية الخالصة، يكون لجميع الدول حقوق أعالي البحار الخاصة بالملاحة، والطيران، ولكن تتحكم الدول الساحلية في جميع المصادر الاقتصادية في هذه المنطقة. وتتفق معظم الدول، على عدم اعتبار حق التعدين جزءًا من الحرية البحرية، ولكن يمكن أن ينشأ هذا الحق، بمقتضى نصوص معاهدة. ولهذا؛ لم تصبح الاتفاقية سارية إلا في عام 1994م. ومن الدول التي لم تصدق عليها: الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية وكندا. ورغم أن معظم نصوص المعاهدة هي بالفعل متبعة الآن.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الممرات المائية الدولية
نزاعات حول المياه الدولية
اتفاقيات المياه الدولية
اتفاقية عالمية
- International Freshwater Treaties Database (freshwater only).[2]
- The Yearbook of International Cooperation on Environment and Development profiles agreements regarding the Marine Environment, Marine Living Resources and Freshwater Resources.[3]
- 1972 لندن Convention on the Prevention of Marine Pollution by Dumping of Wastes and Other Matter (London Convention 1972).[4]
- 1973 لندن International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, 1973 MARPOL
- 1982 United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea (United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea, United Nations; especially parts XII–XIV).[5]
- 1997 United Nations Convention on the Law of Non-Navigational Uses of International Watercourses (CIW) - not ratified.[6]
- Transboundary Groundwater Treaty, Bellagio Draft - proposed, but not signed.[7]
- Other global conventions and treaties with implications for International Waters:
- 1971 Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.[8]
- 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity.[9]
اتفاقيات اقليمية
At least ten conventions are included within the Regional Seas Program of UNEP,[10] including:
- the Atlantic Coast of West and Central Africa;[11]
- the North-East Pacific (Antigua Convention);
- البحر المتوسط (اتفاقية برشلونة);
- the wider Caribbean (Cartagena Convention);
- the South-East Pacific;[12]
- the South Pacific (Nouméa Convention);
- the East African seaboard;[13]
- the Kuwait region (Kuwait Convention);
- the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden (Jeddah Convention).
Addressing regional freshwater issues is the 1992 Helsinki Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes (UNECE/Helsinki Water Convention)[14]
Water body-specific agreements
- Baltic Sea (Helsinki Convention on the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Baltic Sea Area, 1992)[15]
- Black Sea (Bucharest Convention)[16]
- Caspian Sea (Framework Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Caspian Sea)[17]
- Lake Tanganyika (Convention for the Sustainable Management of Lake Tanganyika)[18]
مؤسسات المياه الدولية
مؤسسات المياه العذبة
- اليونسكو International Hydrological Programme (IHP)
- اللجنة المشتركة الدولية between Canada and USA (IJC-CMI)
- The International Network of Basin Organizations (INBO)
- The International Shared Aquifer Resource Management project
- The International Water Boundary Commission (US Section) between Mexico and USA
- The International Water Management Institute (IWMI)
- The World Conservation Union Water and Nature Initiative (WANI)
مؤسسات البحار
- The International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- The International Seabed Authority
- The International Whaling Commission
- The UNEP Regional Seas Programme
- The UNESCO Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC)
- The International Ocean Institute
- The World Conservation Union Global Marine Program (GMP)
انظر أيضا
- Baseline
- Birth aboard aircraft and ships
- Continental shelf
- المنطقة الاقتصادية الخالصة
- حرية البحار
- Hugo Grotius
- مياه داخلية
- استعمار المحيطات
- مياه اقليمية
المصادر
- ^ أعالي البحار، الموسوعة المعرفية الشاملة
- ^ "International Freshwater Treaties Database". Transboundarywaters.orst.edu. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ Yearbook of International Cooperation on Environment and Development
Marine Environment[dead link]
Marine Living Resources[dead link]
Freshwater Resources[dead link] - ^ London Convention 1972[dead link]
- ^ "United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea". Un.org. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ "CIW" (PDF). Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ "Bellagio Draft" (PDF). Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ "Text of Ramsar Convention and other key original documents". Ramsar.org. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ Text of the Convention on Biological Diversity especially Articles 12-13, as related to transboundary aquatic ecosystems
- ^ "Regional Seas Program". Unep.org. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ "Convention for Co-operation in the Protection and Development of the Marine and Coastal Environment of the West and Central African Region; and Protocol (1981)". Sedac.ciesin.org. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ Lima Convention, 1986)
- ^ Nairobi Convention, 1985);
- ^ "Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes". Unece.org. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ "Convention on the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Baltic Sea Area". Helcom.fi. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- ^ Bucharest Convention, 1992), see also the Black Sea Commission
- ^ Framework Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Caspian Sea, 2003
- ^ Convention for the Sustainable Management of Lake Tanganyika, 2003
وصلات خارجية
- Bibliography on Water Resources and International Law Peace Palace Library
- The GEF International Waters Resource Centre (GEF IWRC)
- The Integrated Management of Transboundary Waters in Europe (TransCat)
- The International Water Law Project
- The International Water Resources Association (IWRA)
- FAO
- Ocean Atlas
- Transboundary Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) article
- OneFish fisheries research portal
- Regional Fisheries Bodies of the World portal
- The UNDP-GEF article describing international waters from which this article has been adapted.
- UNEP freshwater thematic portal on transboundary waters
- UNESCO thematic portals for oceans, water, coasts and small islands
- WaterWiki: A new Wiki-based on-line knowledge map and collaboration tool for Water-practitioners in the Europe & CIS region