سلوك السرب

سلوك السرب Swarm behaviour أو swarming، هو سلوك جماعي تظهره المجموعات، خاصة الحيوانات، ذوات الحجم الماثل مجتمعة معاً، متجمهرة حول نفس النقطة أو قد تتحرك أو تهاجر في جماعات في نفس الاتجاه. ويعتبر موضوع متعدد التخصصات بشكل كبير.[1] كمصطلح، يُطلق سلوك السرب بصفة خاصة على الحشرات، لكن يمكن إطلاقه أيضاً على أي مجموعات أو حيوانات أخرى تُظهر نفس السلوك. عادة ما يستخدم مصطلح السرب للإشارة إلى سلوك السرب في الطيور، والقطيع للإشارة إلى سلوك السرب في رباعيات الأرجل، والأفواج للإشارة إلى سلوك السرب في الأسماك. كذلك تتجمع العوالق النباتية في أسراب ضخمة تسمى فقاعات، بالرغم من أن هذه العضيات تعتبر طحالب وكونها لا تندفع ذاتياً بعيداً عن الحيوانات. بتوسيع المصطلح، يمكن إطلاقه أيضاً على المجموعات الغير حيوانية والتي تظهر سلوكاً مشابهاً، كما في سرب الروبوت، وسرب الزلازل، أو سرب النجوم.
تم محاكاة سلوك السرب في الحاسوب عام 1986 ببرنامج محاكاة boids.[2] يحاكي هذا البرنامج عوامل بسيطة (boids) القابلة للتحريك تبعاً لمجموعة من القواعد الأساسية. هذا النموذج تم تصميمه في الأصل لتقليد سلوك أسراب الطيور، ولكن يمكن تطبيقه أيضاً على أسراب الأسماك وغيرها من الكيانات المتجمعة الأخرى.
النماذج
النماذج الرياضية

النماذج التطورية
العوامل
التنظيم الذاتي

التولد
Stigmergy
ذكاء السرب
الخوارزميات
خوارزمية مستعمرة النمل
الجسيمات ذاتية الدفع
– needs Java |
تحسين سرب الجزيئات
الإيثار
التجمع الحيوي
الحشرات
النمل

النحل
الصراصير
الجراد

هجرة الحشرات
الطيور

هجرة الطيور

– from The Trials of Life |
الحياة البحرية
الأسماك
هجرة الطيور
الكريليات
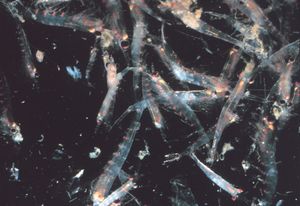
مجذافيات الأرجل
Photo: School of herrings ram feeding on a swarm of copepods.
Swarms of jellyfish also prey on copepods
فقاعات الطحالب
النباتات
عضيات أخرى
الجراثيم
رباعيات الحركة
البشر
الروبوت

العسكرية
معرض الصور
أساطير
انظر أيضاً
المصادر
- ^ Bouffanais, Roland. Design and Control of Swarm Dynamics (First ed.). Springer. ISBN 978-981-287-750-5.
- ^ Reynolds CW (1987). "Flocks, herds and schools: A distributed behavioral model". Computer Graphics. 21 (4): 25–34. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.103.7187. doi:10.1145/37401.37406. ISBN 0-89791-227-6.
- ^ "Swarmanoid project".
- ^ Self driven particle model Archived 2012-10-14 at the Wayback Machine Interactive simulations, 2005, University of Colorado. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةBallerini et al - ^ Pitcher et al. 1982.
- ^ Photographer: Mark van Coller
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةKushleyev2013 - ^ "Dive and Discover: Scientific Expedition 10: Antarctica". Retrieved 2008-09-03.
- ^ Crowd modelling: Simulating the behaviour of crowds of people, or swarms of animals, has both frivolous and important uses The Economist, 5 March 2009.
- ^ Fisher, Len (2009) The perfect swarm: the science of complexity in everyday life Page 57. Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-01884-0
المراجع
- Blum C and Merkle D (2008) Swarm intelligence: introduction and applications Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-74088-9.
- Camazine S, Deneubourg JL, Franks NR, Sneyd J, Theraulaz G and Bonabeau E (2003) Self-Organization in Biological Systems Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-11624-2.
- Fisher L (2009) The perfect swarm: the science of complexity in everyday life Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-01884-0.
- Kennedy JF, Kennedy J, Eberhart RC and Shi Y (2001) Swarm intelligence Morgan Kaufmann. ISBN 978-1-55860-595-4.
- Krause, J (2005) Living in Groups Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-850818-2
- Lim CP, Jain LC and Dehuri S (2009) Innovations in Swarm Intelligence Springer. ISBN 978-3-642-04224-9.
- Miller, Peter (2010) The Smart Swarm: How understanding flocks, schools, and colonies can make us better at communicating, decision making, and getting things done Penguin, ISBN 978-1-58333-390-7
- Nedjah N and Mourelle LdM (2006) Swarm intelligent systems Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-33868-0.
- Sumpter, David JT (2010) Collective Animal Behavior Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-14843-4.
- Vicsek A, Zafeiris A (2012). "Collective motion". Physics Reports. 517 (3–4): 71–140. arXiv:1010.5017. Bibcode:2012PhR...517...71V. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2012.03.004.












![Salps arranged in chains form huge swarms.[9]](/w/images/thumb/6/63/Salp.jpg/120px-Salp.jpg)
![People swarming through an exit do not always behave like a fluid.[10][11]](/w/images/thumb/5/54/Crowd_04378.JPG/120px-Crowd_04378.JPG)