العظاءة (كوكبة)
| كوكبة | |
 | |
| الاختصار | Lac |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Lacertae |
| النطق | /læˈkɜːrtə/, genitive /læˈkɜːrti/ |
| الرمزية | the Lizard |
| الصعود المستقيم | 22.5h {{{2}}}m |
| الميل | +45° {{{2}}}′ |
| الربع | NQ4 |
| المساحة | 201 sq. deg. (68th) |
| النجوم الرئيسية | 5 |
| باير/فلامستيد stars | 17 |
| نجوم بكواكب | 12 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 0 |
| نجوم ضمن 10.00 pc (32.62 س.ض.) | 1 |
| ألمع نجم | α Lac (3.76m) |
| أجرام مسييه | 0 |
| الكوكبات المتاخمة | Andromeda Cassiopeia Cepheus Cygnus Pegasus |
| Visible at latitudes between +90° and −40°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of October. | |
العظاءة (Lacerta) أو السحلية هي كوكبة من 88 معترف بها من قبل الاتحاد الفلكي الدولي. تتواجد 20 درجة شرق ذنب الدجاجة، تم ضمه إلى الاطلس الفلكي من قبل العالم الفلكي يوهانس هفليوس سنة 1690. وهى كوكبة صغيرة ذات نجوم خافتة تقع بين كوكبة الدجاجة و كوكبة المرأة المسلسلة.
المساحة
تغطي مساحة سماوية تبلغ نحو 201 درجة مربعة حددها فلكيو العصر الحديث حيث لا تاريخ لها ولا أساطير تدور حولها.
السمات البارزة
Lacerta is typical of Milky Way constellations: no bright galaxies, nor globular clusters, but instead open clusters, for example NGC 7243, the faint planetary nebula IC 5217 and quite a few double stars. It also contains the prototypic blazar BL Lacertae. Lacerta contains no Messier objects.
النجوم
Alpha Lacertae is a blue-white hued main-sequence star of magnitude 3.8, 102 light-years from Earth. It has a spectral type of A1 V[1] and is an optical double star. Beta Lacertae is far dimmer, a yellow giant of magnitude 4.4, 170 light-years from Earth.[2]
Roe 47 is a multiple star consisting of five components (magnitudes 5.8, 9.8, 10.1, 9.4, 9.8).
ADS 16402 is a binary star system in Lacerta, around which a planet orbits with some unusual properties.[3] The Jupiter-sized planet exhibits an unexpectedly low density, about the same as cork. This planet is dubbed HAT P-1.
EV Lacertae is a rapidly spinning magnitude 10 red dwarf with a strong magnetic field. It is a flare star that can emit powerful flares potentially visible to the naked eye, thousands of times more energetic than any from Earth's sun.
HD 215441 (22h 44m.2 / +55° 35') is known as Babcock's Magnetic Star. Source: Sky Catalogue 2000.0 Volume 2: Double Stars, Variable Stars and Nonstellar Objects, page xlv, chapter Glossary of Selected Astronomical Names.
Deep-sky objects
NGC 7243 is an open cluster 2500 light-years from Earth, visible in small amateur telescopes. It has a few dozen "scattered" stars, the brightest of which are of the 8th magnitude.[2]
BL Lacertae is the prototype of the BL Lacertae objects, which appear to be dim variable stars but are actually the variable nuclei of elliptical galaxies; they are similar to quasars.[2] It lent its name to a whole type of celestial objects, the BL Lacertae objects (a subtype of blazar). The object varies irregularly between magnitudes 14 and 17 over a few days.
التاريخ
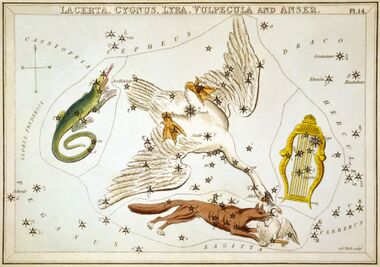
Centred on a region of the sky without apparently bright stars, Lacerta was apparently not regarded as a constellation by ancient Western astronomers. Johannes Hevelius created the constellation in 1687 and initially named it "Stellio" (the stellion), a lizard with star-like dorsal spots found along the Mediterranean coast.[4]
Other Europeans who sought to name this new constellation[محل شك] included Augustin Royer, who created Sceptrum et Manus Iustitiae (the Hand of Justice and Sceptre) to honor Louis XIV in 1670, and Johann Elert Bode, who created Frederici Honores (Frederick's Glory) to honor Frederick the Great in 1787. Both Sceptrum and Frederici Honores are now obsolete, while Lacerta still survives.[2]
المكافئون
Although not included in ancient star charts of Europe and the Near East, the stars of Lacerta, along with some in the eastern portion of Cygnus, were coincidentally combined by early Chinese astronomers into their "Flying serpent".[4] Similarly, the Chumash people of California call this part of the sky 'Lizard' and include it in multiple stories.[بحاجة لمصدر]
Namesakes
USS Lacerta (AKA-29) was an attack cargo ship in the United States navy named after the constellation.
انظر أيضاً
المصادر
مؤمن, عبد الأمير (2006). قاموس دار العلم الفلكي. بيروت، لبنان: دار العلم للملايين. {{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter: |طبعة أولى coauthors= (help)
المراجع
- ^ Cowley, A.; Cowley, C.; Jaschek, M.; Jaschek, C. (April 1969), "A study of the bright A stars. I. A catalogue of spectral classifications", Astronomical Journal 74: 375–406, doi:, Bibcode: 1969AJ.....74..375C.
- ^ أ ب ت ث Ridpath & Tirion 2001, pp. 164-165.
- ^ Puzzling Puffy Planet, Less Dense Than Cork, Is Discovered - New York Times
- ^ أ ب Allen 1899, p. 251.

