نهر إيلي
| Ili | |
|---|---|
 Ili River | |
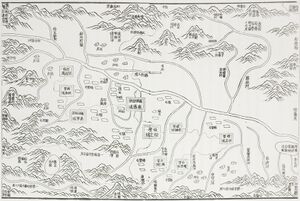
 خريطة حوض تصريف بحيرة بلخاش تبين نهر إيلي وروافده | |
| الموقع | |
| البلدان | قزاقستان والصين |
| السمات الطبيعية | |
| المنبع | |
| ⁃ الموقع | أنهار تكس وكونس |
| ⁃ المنسوب | تيان شان |
| المصب | |
- الموقع | بحيرة بلخاش |
| الطول | 1,439 km (894 mi) |
| مساحة الحوض | 140,000 km2 (54,000 sq mi) |
| التدفق | |
| ⁃ المتوسط | 480 m3/s (17,000 cu ft/s) |
 | |
| الاسم الرسمي | Ili River Delta and South Lake Balkhash |
| التوصيف | 1 January 2012 |
| الرقم المرجعي | 2020[1] |
The Ili (ويغور: ئىلى دەرياسى، أ.ل.أ.: Ili deryasi، خ.ج.و.: Ili dəryasi؟; بالقزخية: Ile, ئله; روسية: Или; Chinese: 伊犁河; pinyin: Yīlí Hé, دونگان: Йили хә, Xiao'erjing: اِلِ حْ; بالمنغولية: Ил, literally "Bareness") is a river situated in Northwest China and Southeastern Kazakhstan. It flows from the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture of the Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region to the Almaty Region in Kazakhstan.
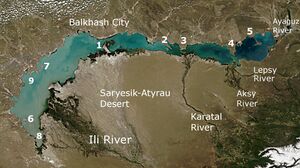
It is 1,439 kilometres (894 mi) long (including its source river Tekes),[2] 815 kilometres (506 mi) of which is in Kazakhstan. The river originates from the Tekes and Künes rivers in Eastern Tian Shan. The Ili drains the basin between the Tian Shan and the Borohoro Mountains. Flowing into Lake Balkhash, the Ili forms a large delta with vast wetland regions of lakes, marshes and vegetation.[3][4]
أصل الاسم
Earlier mentions of Ili river can be traced back to قاموس محمود القشغري للغات التوركية، ديوان لغات الترك (المكتوب في 1072–74). In the book, the author defines it in the following way: "Ili, the name of a river. Turkic tribes of Yaghma, Tokhsi and Chiglig live on its banks. Turkish countries regard the river as their Jayhoun (Amu Darya)."[5] The name possibly originated from Uyghur word Il, meaning hook, resembling the river's geographical shape.[6]
المنطقة الصينية
The upper Ili Valley is separated from the Dzungarian Basin in the north (by the Borohoro Mountains), and from the Tarim Basin in the south (by the Tian Shan). This region was the stronghold of the Qing administration in Xinjiang in the late 18th and 19th centuries. It was occupied by Russia from 1871 to 1881 (from the Yaqub Beg rebellion until the Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1881)).
Presently, the region forms part of Xinjiang's Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture. The main city of the region, Yining (Kulja), is located on the northern side of the river (about 100 kilometres (62 mi) upstream from the international border). Until the early 1900s, the city was commonly known under the same name as the river, 伊犁 (Pinyin: Yīlí; Wade-Giles: Ili). Qapqal Xibe Autonomous County in located on the southern side, which is home to many of the China's Xibe people (who resettled there in the 18th century as part of the Manchu Garrison).
There are at least two dams on the Ili's tributary: the Kash River (喀什河) in Nilka County, at 43°51′40″N 82°50′52″E / 43.86111°N 82.84778°E and 43°51′14″N 82°48′08″E / 43.85389°N 82.80222°E. At least two dams have been constructed on the Ili's left tributary, the Tekes River, and the Qiapuqihai Hydropower Station (恰甫其海水电站) in Tokkuztara County (43°18′14″N 82°29′05″E / 43.30389°N 82.48472°E). There is also another smaller dam at 43°23′41″N 82°29′20″E / 43.39472°N 82.48889°E, on the border of Tokkuztara and Künes Counties.
المنطقة القزخية
The region of Kazakhstan partially drained by the Ili and its tributaries is known in Kazakh as Zhetysu ('Seven Rivers'). In Russian it is known as Semirechye (meaning the same).
The Kapshagay Hydroelectric Power Plant was constructed between 1965 and 1970 near Kapchagay in the middle reaches of the Ili River.[7] This currently comprises the Kapchagay Reservoir, an artificial 110 kilometres (70 mi) long lake north of Almaty.
The Tamgaly-Tas, a protected site that comprises rock drawings, is located 20 kilometres (12 mi) downstream along the Ili River. The name Tamgaly in Kazakh means "painted" or "marked place" (Tas means "stone").
دلتا الإيلي
The Ili River flows into the southeastern edge of Lake Balkhash, where it forms a large delta of about 8,000 square kilometres (3,100 sq mi). The delta is situated between the Saryesik-Atyrau Desert and the Taukum Desert. An area of 9,766 km2 (3,771 sq mi) within the delta has been designated as a Ramsar Site. This site has 427 species of plants and 345 species of animals, including important populations of rare species (Dalmatian pelican, goitered gazelle, marbled polecat, white-headed duck, red-breasted goose, ship sturgeon, and others).[1] The delta has also become popular amongst anglers for its wels catfish, which can grow up to over 300 lb (140 kg). The Ili river ranks third in Kazakhstan after the Irtysh river and the Ural river in terms of water content.
The Government of Kazakhstan plans to join the three sanctuaries Balkash, Karoy and Kukan (situated in the delta) into one National Park.[8] Until 1948, the delta was a refuge of the extinct Caspian tiger. An introduction of the Siberian tiger to the delta has been proposed on account that it is a genetically close relative of the Caspian tiger. A large population of wild boar, the main prey base of the Caspian tiger, can be still found in the delta. There is also a small population of roe deer. In the drier steppes to the south of the delta live saiga antelopes and goitered gazelles.
Reintroduction of the Bactrian deer, another prey of the Caspian tiger, is currently under consideration. Another potential prey species considered to be reintroduced is the Asiatic wild ass.[9]
ارتباطات تاريخية
The Ili River treaty of 638 AD formalized the division of the Western Turkic Kaganate (552–638 AD) into the Nushibi and the Dulu. It also established the Ili River as the border between the two states.[10] In the 21st century, increasing need for water in both China and Kazakhstan makes the management of the cross-border Ili River a topic of concern for environmentalists and politicians in Kazakhstan (who feel that their country may not get enough water flowing in from China any more).[11]
The amount of precipitation in summer reaches 150-250 cubic meters.
الصيد
On the river, the most popular type of fishing is fishing of catfish, one of the largest aquatic predators, which may reach 5 meters in length and weigh up to 300 kg. Smaller specimens are usually within 50–100 kg.
معرض صور
The "singing dune" at Altyn-Emel National Park
الروافد
الروافد الرئيسية للإيلي هي، من المنابع إلى المصب:[2]
المراجع
- ^ أ ب "Ili River Delta and South Lake Balkhash". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- ^ أ ب Или, Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- ^ Ili River
- ^ Ili river Kazakhstan
- ^ Mahmud Kashgari, Dīwānu l-Luġat al-Turk (En: Compendium of the languages of the Turks). Vol I, p124. 1072–1074
- ^ Adil Arup, Ili atalghusi heqqide (Etymology of Ili), Journal of Ili Darya, in Uyghur, 2007
- ^ Kezer, K.; Matsuyama, H. (2006). "Decrease of river runoff in the Lake Balkhash basin in Central Asia". Hydrological Processes. 20 (6): 1407–1423. Bibcode:2006HyPr...20.1407K. doi:10.1002/hyp.6097.
- ^ Masha Vinokurova (Press officer), Olga Pereladova (Head of the WWF Central Asia Programme): Kazakhstan names large inland delta, WWF Information February, 2012
- ^ Hartmut Jungius (2010). Feasibility Study on the Possible Restoration of the Caspian Tiger in Central Asia Archived 2011-11-17 at the Wayback Machine. WWF
- ^ Zuev Yu.L., The strongest tribe, Almaty, 2004, pp. 55–6,
- ^ Stone, Richard (2012-07-27), "For China and Kazakhstan, No Meeting of the Minds on Water", Science 337 (6093): 405–407, doi:, PMID 22837504, Bibcode: 2012Sci...337..405S, http://211.144.68.84:9998/91keshi/Public/File/41/337-6093/pdf/405.full.pdf[dead link]
- Или, река Семиречинской области (The Ili River), in Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary
- Articles with dead external links from November 2017
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Infobox mapframe without OSM relation ID on Wikidata
- Articles containing قزخ-language text
- Articles containing روسية-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Articles containing Chinese-language text
- Articles containing Dungan-language text
- Articles containing منغولية-language text
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- أنهار قزخستان
- أنهار شينجيانگ
- مواقع على طريق الحرير
- أنهار دولية في آسيا
- مشروع إعادة توطين النمر السيبيري
- روافد بحيرة بلخاش
- مواقع رامسار في قزاقستان
- صفحات مع الخرائط