إينول
(تم التحويل من Enol)
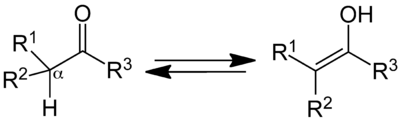
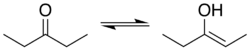
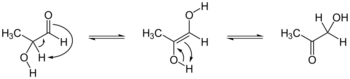
Generic Tautomerization Forming an Enol. Keto-form at left, enol at right. The α-hydrogen (H) deprotonated in the common base-catalysed reaction is indicated. R3=H, aldehyde case; R3=alkyl, ketone case; etc.. Groups R1 and R2 may be a variety of structures that influence the equilibrium, including alkyl, carbonyl-containing (for stabilized enols), and hydroxyl groups (in enediols).[بحاجة لمصدر]
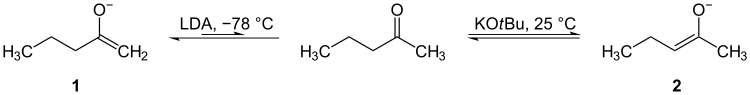
Ketone tautomerization, keto-form at left, enol at right. Ex. is 3-pentanone, a less stabilized enol.[بحاجة لمصدر]
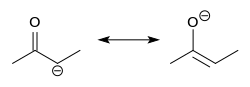
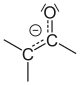
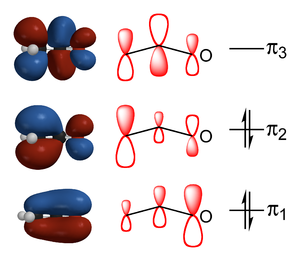
Enolate resonance structures, schematic representation of forms (see text regarding molecular orbitals); carbanion form at left, enolate at right; Ex. is 2-butanone, also a less stabilized enol.[بحاجة لمصدر]
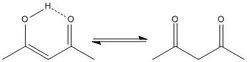
Ketone tautomerization, enol-form at left, keto at right. Ex. is 2,4-pentanedione, a hydrogen bond (---) stabilized enol.[بحاجة لمصدر]
Aldehyde tautomerization, enol-form at left, "keto" at right; Ex. is tartronaldehyde (reductone), an enediol-type of enol.[بحاجة لمصدر]
الإينولات Enols، وتعرف أيضاً باسم الألكينولات، هي نوع من البنى أو المركبات الوسيطة في الكيمياء العضوية والذي يمثل كألكين (اولفين) لديه مجموعة هيدروكسيل مرتبطة إلى إحدى ذرتي الكربون اللتان تؤلفان الرابطة المضاعفة. إن الإينولات والكربونيلات (مثل الألدهيدات والكيتونات) هي في أرض الواقع عبارة عن مصاوغات (إيزوميرات)، يدعى هذا تصاوغ صنوي كيتو-إينول (تصاوغ صنوي).[1]
صنوية الكيتو-إينول
تعريف ومقدمة
الصنوية في المركبات متعددة الكربونيل
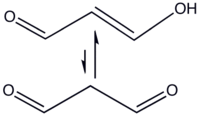
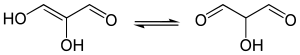
Malondialdehyde (propanedial) enolization. An example of a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound whose enol is stabilized by hydrogen bonding, leading to detection of a percent or less of the keto form at equilibrium.
الإينولات
عدم التمركز
نزع الپروتون الانتقائي في تشكيل الإينول
الإنديولات
Keto-enediol tautomerizations. Enediol in the center; acyloin isomers at left and right. Ex. is hydroxyacetone, shown at right.
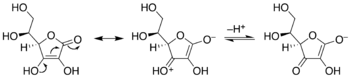
Conversion of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) to an enolate. Enediol at left, enolate at right, showing movement of electron pairs resulting in deprotonation of the stable parent enediol. A distinct, more complex chemical system, exhibiting the characteristic of vinylogy.
| أمثلة على الريدوتكونات | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
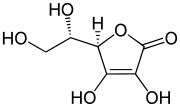
|
| حمض الگلوسيك | حمض الريدوكتيك | حمض الأسكوربيك (فيتامين ج) |
انظر أيضاً
وصلات خارجية
المصادر
- ^ Douglass F. Taber, 2015, "Synthesis of silyl enol ethers and related compounds," Organic Chemistry Portal (online), Reactions, Organic Synthesis Search, Categories, O-Si Bond Formation, see [www.organic-chemistry.org/synthesis/O1Si/silylenolethers.shtm], accessed 16 July 2015.
This article contains content from Wikimedia licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Please comply with the license terms.