أمفوتريسين ب
 | |
| البيانات السريرية | |
|---|---|
| مسارات الدواء | slow i.v.-infusion only |
| رمز ATC | |
| الحالة القانونية | |
| الحالة القانونية |
|
| بيانات الحركية الدوائية | |
| التوافر الحيوي | 100% (IV) |
| الأيض | renal |
| Elimination half-life | initial phase : 24 hours, second phase : approx. 15 days |
| الإخراج | 40% found in urine after single cumulated over several days biliar excretion also important |
| المعرفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.311 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
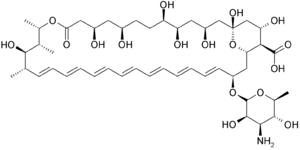
| التركيب | C47H73NO17 |
| الكتلة المولية | 924.084 |
أمفوتيريسين ب أمفوتيريسين ب , (Fungilin, Fungizone, Abelcet, AmBisome, Fungisome, Amphocil, Amphotec),هودواء مضاد للفطريات polyene, يستعمل حقنا في الوريد للعدوى الفطرية المركزية. ويستخلص من Streptomyces nodosus, a filamentous bacterium, في عام 1955 بواسطة شركة Squibb للأبحاث الدوائية من مزرعة streptomycete مستخلصة من تربة جمعت من Orinoco River region of Venezuela. إثنان من صور الدواء Amphotericin A و Amphotericin B قيد الإستعمال ولكن فقط B يستعمل ,لكونه أكثر فعالية in vivo. وفى الواقع الدواء متوافر ك plain Amphotericin B و ك cholesteryl sulfate complex , lipid complex, and as liposomal formulation. والتركيب الأخير قد طور لتحسين إحتمال الدواء بالنسبة للمريض , ولكن يمكن أن تظهر حراكا دوائيا مختلفا, مقارنة با أمفوتيريسين ب العادى.
الإستعمالات
خاصية المضادة للفطريات
صيغ أمفوتيريسين ب التى تستعمل عن طريق الفم تستعمل لعلاج thrush; وهى يفترض أن تكون غير سامة بالمقارنة بالصور المستخدمة للحقن الوريدى.واحدة من أهم الإستخدامات للصورة المستخدمة للحقن الوريدى هى لعلاج العديد من الأمراض المركزية(غير الجلدية السطحية),مثل المرضى السيئ الحال comorbidly immunocompromised patients. أمفوتيريسين ب يستعمل أيضا في tissue culture لمنع الفطريات من تلويث مزارع الخلايا البشرية. ويباع أمفوتيريسين ب في عبوات بتركيزات عالية, سواء بمفرده أو مع المضادات الحيوية مثل penicillin و streptomycin.
المفعول المضاد للأوليات
إستعمال وريدى آخر للأوليات مثل leishmaniasis [1][2] and primary amoebic meningoencephalitis.
كمضاد حيوي
يستعمل أيضا في الأصل heroic measure فىfebrile immunocompromised patients الذين لايستجيبون للمضادات الحيوية [بحاجة لمصدر]
نظرية العمل
كما مثل كل ال polyene antifungals, أمفوتيريسين ب يرتبط مع ergosterol, وهو غشاء كيميائى للفطر, مكونا ثقبا يؤدى الى K+ تسريب مؤديا الى موت خلية الفطر . ويعتقد أن أمفوتيريسين ب يتفاعل مع الغشاء الأستيرولى (ergosterol) لينتج aggregate يكون transmembrane channel Intermolecular hydrogen bonding interactions among hydroxyl, carboxyl and amino groups stabilize the channel in its open form, destroying activity and allowing the cytoplasmic contents to leak out
الآثار الجانبية
Amphotericin B is well-known for its severe and potentially lethal side effects. It is colloquially known among medical professionals as "amphoterrible" due to these side effects. Very often a serious acute reaction after the infusion (1 to 3 hours later) is noted consisting of high fever, shaking chills, hypotension, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, headache, dyspnea, and tachypnea. This reaction sometimes subsides with later applications of the drug and may in part be due to histamine liberation. An increase in prostaglandin-synthesis may also play a role. This nearly universal febrile response necessitates a critical (and diagnostically difficult) professional determination as to whether the onset of high fever is a novel symptom of a fast-progressing disease, or merely the induced effect of the drug. In order to decrease the likelihood and severity of the symptoms, initial doses should be low and increased slowly. Acetaminophen, pethidine, diphenhydramine and/or hydrocortisone have all been used to treat or prevent the syndrome, but the prophylactic use of these drugs is often limited by the patient's condition.
Intravenously administered Amphotericin B has also been associated with multiple organ damage in therapeutic doses. Nephrotoxicity (kidney damage) is a frequently reported side-effect, and can be severe and/or irreversible. It is much milder when delivered via liposomes (AmBisome) if possible. Electrolyte imbalances (e.g. hypokalemia and hypocalcemia) may also result. In the liver, increased liver enzymes and hepatotoxicity (up to and including fulminant liver failure) are common. In the circulatory system, several forms of anemia and other blood dyscrasias (leukopenia, thrombopenia), serious cardiac arrhythmias (including ventricular fibrillation), and even frank cardiac failure have been reported. Skin reactions, including serious forms, are also possible.
التفاعلات الدوائية
- Flucytosine : Toxicity of Flucytosine increased and vice versa
- Diuretics or Cisplatin : Increased renal toxicity and incrised risk of hypokalemia
- Corticosteroids : Increased risk of hypokalemia
- Cytostatic drugs : Increased risk of kidney damage, hypotension and bronchospasms.
- Other nephrotoxic drugs : Increased risk of serious renal damage. Monitor patients closely.
- Foscarnet, Ganciclovir, Tenofovir, Adefovir : Risk of hematological and renal side-effects of Amphotericin B increased.
- Transfusion of Leukocytes : Risk of pulmonal (lung) damage. Space intervals between the application of Amphotericin B and the transfusion and monitor pulmonary function.
Liposomal and lipid complex preparations
From studies it appears that liposomal amphotericin B preparations exhibit fewer side-effects while having similar efficacy. Various preparations have recently been introduced. All of these are more expensive than plain Amphotericin B.
AmBisome is a liposomal formulation of amphotericin B for injection, developed by NeXstar Pharmaceuticals (acquired by Gilead Sciences in 1999). It is marketed by Gilead in Europe and licensed to Astellas Pharma (formerly Fujisawa Pharmaceuticals) for marketing in the USA, and Sumitomo Pharmaceuticals in Japan.
Fungisome is a liposomal complex of Amphotericin B and being the latest and cheapest addition to the lipid formulations of Amphotericin B has many advantages. It is marketed by Lifecare Innovations of India. Other formulations include Amphotec (Intermune) and Abelcet (Enzon Pharmaceuticals).
Abelcet is not a liposomal preparation but rather a lipid complex preparation.
المراجع
- ^ Kafetzis DA, Velissariou IM, Stabouli S, Mavrikou M, Delis D, Liapi G (2005). "Treatment of paediatric visceral leishmaniasis: amphotericin B or pentavalent antimony compounds?". Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 25 (1): 26–30. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2004.09.011. PMID 15620822.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Veerareddy PR, Vobalaboina V, Ali N (2008). "Antileishmanial activity, pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution studies of mannose-grafted amphotericin B lipid nanospheres". J Drug Target: 1. doi:10.1080/10611860802528833. PMID 19089691.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
الروابط الخارجية
- Fungisome web site run by Lifecare Innovations
- AmBisome web site run by Astella Pharma
- "Special issue". Journal of Postgraduate Medicine. 51 (Suppl). 2005.
- CS1 errors: unsupported parameter
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Pages using infobox drug with unknown parameters
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- مقالات ذات عبارات بحاجة لمصادر
- گلعاد للعلوم
- مضادات الفطريات
- Polyketide antibiotics
- الأدوية الأساسية حسب منظمة الصحة العالمية