مسرد مصطلحات الكيمياء
مسرد مصطلحات الكيمياء
| Contents: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z — انظر أيضا |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
- صفر مطلق - a theoretical condition concerning a system at zero Kelvin where a system does not emit or absorb energy (all atoms are at rest)
- accuracy - how close a value is to the actual or true value; also see precision
- حمض - a compound that, when dissolved in water, gives a pH of less than 7.0 or a compound that donates a hydrogen ion
- acid anhydride - a compound with two acyl groups bound to a single oxygen atom
- acid dissociation constant - an equilibrium constant for the dissociation of a weak acid
- actinides - the fifteen chemical elements that are between actinium (89) and lawrencium (103)
- activated complex - a structure that forms because of a collision between molecules while new bonds are formed
- addition reaction - within organic chemistry, when two or more molecules combine to make a larger one
- aeration - the mixing of air into a liquid or solid
- alkali metals - the metals of Group 1 on the periodic table
- alkaline earth metals - the metals of Group 2 on the periodic table
- allomer - a substance that has different composition than another, but has the same crystalline structure
- allotropy - elements that can have different structures (and therefore different forms), such as Carbon (diamonds, graphite, and fullerene)
- anion - negatively charge ions
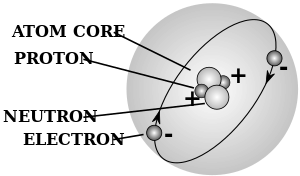
- ذرة atom - a chemical element in its smallest form, and is made up of neutrons and protons within the nucleus and electrons circling the nucleus
- رقم ذري - the number representing an element which corresponds with the number of protons within the nucleus
- atomic orbital - the region where the electron of the atom may be found
B
- base - a substance that accepts a proton and has a high pH; a common example is sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
- biochemistry - the chemistry of organisms
- boiling - the phase transition of liquid vaporizing
- رابطة كيميائية bond - the attraction and repulsion between atoms and molecules that is a cornerstone of chemistry
- burette (also buret) - glassware used to dispense specific amounts of liquid when precision is necessary (e.g. titration and resource dependent reactions)
C
- cation - positively charged ion
- centrifuge - equipment used to separate substances based on density by rotating the tubes around a centred axis
- cell potential - the force in a galvanic cell that pulls electron through reducing agent to oxidizing agent
- قانون كيميائي Chemical Law - certain rules that pertain to the laws of nature and chemistry - examples
- تفاعل كيميائي chemical reaction - the change of one or more substances into another or multiple substances
- colloid - mixture of evenly dispersed substances, such as many milks
- الاحتراق - هو تفاعل ناشر للحرارة بين an oxidant and fuel with heat and often light
- compound - a substance that is made up of two or more chemically bonded elements
- condensation - the phase change from gas to liquid
- موصل كهربي conductor - material that allows electric flow more freely
- covalent bond - chemical bond that involves sharing electrons
- بلورة crystal - a solid that is packed with ions, molecules or atoms in an orderly fashion
- cuvette - glassware used in spectroscopic experiments. It is usually made of plastic, glass or quartz and should be as clean and clear as possible
D
- deionization - the removal of ions, and in water's case mineral ions such as sodium, iron and calcium
- deliquescence - substances that absorb water from the atmosphere to form liquid solutions
- deposition - settling of particles within a solution or mixture
- dipole - electric or magnetic separation of charge
- dipole moment - the polarity of a polar covalent bond
- dissolution or solvation - the spread of ions in a solvent
- double bond - sharing of two pairs of electrons
E

- earth metal - see alkaline earth metal
- electrolyte - a solution that conducts a certain amount of current and can be split categorically as weak and strong electrlytes
- electrochemical cell - using a chemical reaction's current, electromotive force is made
- electromagnetic radiation - a type of wave that can go through vacuums as well as material and classified as a self-propagating wave
- electromagnetism - fields that have electric charge and electric properties that change the way that particles move and interact
- electromotive force - a device that gains energy as electric charges pass through it
- electron - a subatomic particle with a net charge that is negative
- electron shells - an orbital around the atom's nucleus that has a fixed number electrons (usually two or eight)
- electric charge - a measured property (coulombs) that determine electromagnetic interaction
- element - an atom that is defined by its atomic number
- energy - A system's ability to do work
- entropy - the amount of energy not available for work in a closed thermodynamic system (usually symbolized as S)
- enzyme - a protein that speeds up (catalyses) a reaction
- eppendorf tube - generalized and trademarked term used for a type of tube; see microcentrifuge
F
- freezing - phase transition from liquid to solid
- Faraday constant - a unit of electrical charge widely used in electrochemistry and equal to ~ 96,500 coulombs.
- It represents 1 mol of electrons, or the Avogadro number of electrons: 6.022 × 1023 electrons. F = 96 485.339 9(24) C/mol
- Faraday's law of electrolysis - a two part law that Michael Faraday published about electrolysis
- the mass of a substance altered at an electrode during electrolysis is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity transferred at that electrode
- the mass of an elemental material altered at an electrode is directly proportional to the element's equivalent weight.
- frequency - number of cycles per unit of time. Unit: 1 hertz = 1 cycle per 1 second
G
- galvanic cell - battery made up of electrochemical with two different metals connected by salt bridge
- gas - particles that fill their container though have no definite shape or volume
- geochemistry - the chemistry of and chemical composition of the Earth
H
- halogens - Group 17 on the Periodic Table and are all non-metals
I
- inorganic compound - compounds that do not contain carbon, though there are exceptions (see main article)
- inorganic chemistry - a part of chemistry concerned with inorganic compounds
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) -
- insulator - material that resists the flow of electric current
- ion - a molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons
- ionic bond - electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
- ionization -The breaking up of a compound into separate ions.
K
- kinetic energy -
L
M
- metal -
- melting -
- methylene blue - a heterocyclic aromatic chemical compound with the molecular formula C16H18N3SCl
- microcentrifuge - a small plastic container that is used to store small amounts of liquid
- mole - abbreviated mol - a measurement of an amount of substance; a single mole contains approximately 6.022×1023 units or entities
- a mole of water contains 6.022×1023 H2O molecules
- molecule - a chemically bonded number of atoms that are electrically neutral
- molecular orbital - region where an electron can be found in a molecule (as opposed to an atom)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
N
- neutron - a neutral unit or subatomic particle that has no net charge
- neutrino - a particle that can travel at speeds close to the speed of light and are created as a result of radioactive decay
- nucleus - the centre of an atom made up of neutrons and protons, with a net positive charge
- noble gases - group 18 elements, those whose outer electron shell is filled
- non-metal - an element which is not metallic
- nuclear - of or pertaining to the atomic nucleus
- number density – a measure of concentration of countable objects (atoms, molecules, etc.) in space; number per volume
O
- orbital - may refer to either an atomic orbital or a molecular orbital
- organic compound - compounds that contain carbon
- organic chemistry - a part of chemistry concerned with organic compounds
P
- plasma -
- poor metal -
- potential energy
- precipitate -
- precision -
- photon - a carrier of electromagnetic radiation of all wavelength (such as gamma rays and radio waves)
- proton - a positive unit or subatomic particle that has a positive charge
- protonation -
Q
- Quantum mechanics - the study of how atoms, molecules, subatomic particles, etc. behave and are structured
- quarks -
- quarts -
R
- radiation - energy in the form of waves or subatomic particles when there is a change from high energy to low energy states
- radioactive decay - the process of an unstable atomic nucleus losing energy by emitting radiation
S
- s-block elements - Group 1 and 2 elements (alkali and alkaline metals), which includes Hydrogen and Helium
- salts - ionic compounds composed of anions and cations
- salt bridge - devices used to connection reduction with oxidation half-cells in an electrochemical cell
- saline solution - general term for NaCl in water
- Schrödinger equation - quantum state equation which represents the behaviour of an election around an atom
- semiconductor - an electrically conductive solid that is between a conductor and an insulator
- single bond - sharing of one pair of electrons
- sol - a suspension of solid particles in liquid. Artificial examples include sol-gels.
- solid - one of the states of matter, where the molecules are packed close together, there is a resistance of movement/deformation and volume change; see Young's modulus
- solute - the part of the solution that is mixed into the solvent (NaCl in saline water)
- solution - homogeneous mixture made up of multiple substances. It is made up of solutes and solvents.
- solvent - the part of the solution that dissolves the solute (H2O in saline water)
- spectroscopy - study of radiation and matter, such as X-ray absorption and emission spectroscopy
- speed of light - the speed of anything that has zero rest mass (Energyrest = mc² where m is the mass and c is the speed of light)
- Standard conditions for temperature and pressure or SATP - a standardisation used in order compare experimental results (25 °C and 100.000 kPa)
- state of matter - matter having a homogeneous, macroscopic phase; gas, plasma, liquid, and solid are the most well known (in increasing concentration)
- sublimation - a phase transition from solid to gas
- subatomic particles - particles that are smaller than an atom; examples are protons, neutrons and electrons
- substance - material with definite chemical composition
T
- talc - a mineral representing the one on the Mohs Scale and composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula H2Mg3(SiO3)4 or Mg3Si4O10(OH)2
- temperature - the average energy of microscopic motions of particles
- theoretical yield - see yield
- theory - a model describing the nature of a phenomenon
- thermal conductivity - a property of a material to conduct heat (often noted as )
- thermochemistry - the study of absorption/release of heat within a chemical reaction
- thermodynamics - the study of the effects of changing temperature, volume or pressure (or work, heat, and energy) on a macroscopic scale
- thermodynamic stability - when a system is in its lowest energy state with its environment (equilibrium)
- thermometer - device that measures the average energy of a system
- titration - the process of titrating one solution with another, also called volumetric analysis
- torr - a unit to measure pressure (1 Torr is equivalent to 133.322 Pa or 1.3158×10−3 atm
- transition metal - elements that have incomplete d sub-shells, but also may be referred to as the d-block elements
- triple bond - the sharing of three pairs of electrons within a covalent bond (example N2)
- triple point - the place where temperature and pressure of three phases are the same (Water has a special phase diagram)
- Tyndall effect - the effect of light scattering by colloidal (mixture where one substance is dispersed evenly through another) or suspended particles
U
- UN number - a four digit code used to note hazardous and flammable substances
- uncertainty - a characteristic that any measurement that involves estimation of any amount cannot be exactly reproducible
- Uncertainty principle - knowing the location of a particle makes the momentum uncertain, while knowing the momentum of a particle makes the location uncertain
- unit cell - the smallest repeating unit of a lattice
- unit factor - statements used in converting between units
- universal or ideal gas constant - proportionality constant in the ideal gas law (0.08206 L·atm/(K·mol))
V
- valence electron - the outermost electrons of an atom, which are located in electron shells
- Valence bond theory - a theory explaining the chemical bonding within molecules by discussing valencies, the number of chemical bonds formed by an atom
- van der Waals force - one of the forces (attraction/repulsion) between molecules
- van 't Hoff factor - ratio of moles of particles in solution to moles of solute dissolved
- vapor - when a substance is below the critical temperature while in the gas phase
- vapour pressure - pressure of vapour over a liquid at equilibrium
- vaporization - phase change from liquid to gas
- viscosity - the resistance of a liquid to flow (oil)
- volt - one joule of work per coulomb - the unit of electrical potential transferred
- voltmeter - instrument that measures the cell potential
- volumetric analysis - see titration
W
- water - H2O - a chemical substance, a major part of cells and Earth, and covalently bonded
- wave function - a function describing the electron's position in a three dimensional space
- work - the amount of force over distance and is in terms of joules (energy)
X
- X-ray - form of ionizing, electromagnetic radiation, between gamma and UV rays
- X-ray diffraction - a method for establishing structures of crystalline solids using singe wavelength X-rays and looking at diffraction pattern
- X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy - a spectroscopic technique to measure composition of a material
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Y
- yield - the amount of product produced during a chemical reaction
Z
- zone melting - a way to remove impurities from an element by melting it and slowly travel down an ingot (cast)