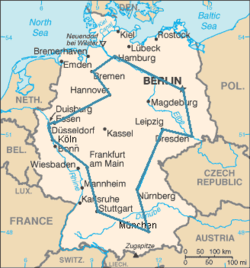
مسألة الرحالة التاجر
في نظرية المخططات ونظرية التعقيد التحسيبي، تُعرف "مسألة مندوب المبيعات المسافر" أو "مشكلة التاجر الرحالة" Travelling salesman problem كما يلي:
يريد تاجر أن يقوم بجولة كاملة يزور خلالها مدنا حيث يمر بكل المدن مرة واحدة و وحيدة ثم يعود إلى مدينة الانطلاق. المشكلة هي ما هو أقصر طريق؟؟
حول المشكلة
رغم أن صيغة المشكلة تبدو بسيطة, إلا أن الحل صعب جدا, فكلما زاد عدد المدن زادت صعوبة المشكل: يحتاج الحاسوب إلى حوالي قرنين من الزمن لإيجاد أقصر مسار يمر على 100 مدينة
فهذه المشاكل تصنف ضمن المشاكل الصعبة، و بعبارة أكثر دقة: المشاكل الحدودية غير المحددة الكاملة NP-complet.
انظر أيضا
- مسألة الرحالة الكندي
- Vehicle routing problem
- Route inspection problem
- Set TSP problem
- Seven Bridges of Königsberg
- Traveling repairman problem (minimum latency problem)
- مسألة الرحالة السائح
- Tube Challenge
الهوامش
- ^ Take one city, and take all possible orders of the other 14 cities. Then divide by two because it does not matter in which direction in time they come after each other:
المصادر
- Applegate, D. L.; Bixby, R. M.; Chvátal, V.; Cook, W. J. (2006), The Traveling Salesman Problem, ISBN 0691129932.
- Bellman, R. (1960), "Combinatorial Processes and Dynamic Programming", Combinatorial Analysis, Proceedings of Symposia in Applied Mathematics 10,, American Mathematical Society, pp. 217–249.
- Bellman, R. (1962), "Dynamic Programming Treatment of the Travelling Salesman Problem", J. Assoc. Comput. Mach. 9: 61–63, doi:.
- Christofides, N. (1976), Worst-case analysis of a new heuristic for the travelling salesman problem, Technical Report 388, Graduate School of Industrial Administration, Carnegie-Mellon University, Pittsburgh.
- Hassin, R.; Rubinstein, S. (2000), "Better approximations for max TSP", Information Processing Letters 75: 181–186, doi:.
- Held, M.; Karp, R. M. (1962), "A Dynamic Programming Approach to Sequencing Problems", Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics 10 (1): 196–210, doi:.
- Kaplan, H.; Lewenstein, L.; Shafrir, N.; Sviridenko, M. (2004), "Approximation Algorithms for Asymmetric TSP by Decomposing Directed Regular Multigraphs", In Proc. 44th IEEE Symp. on Foundations of Comput. Sci., pp. 56–65.
- Karp, R.M. (1982), "Dynamic programming meets the principle of inclusion and exclusion", Oper. Res. Lett. 1: 49–51, doi:.
- Kohn, S.; Gottlieb, A.; Kohn, M. (1977), "A Generating Function Approach to the Traveling Salesman Problem", ACM Annual Conference, ACM Press, pp. 294–300.
- Kosaraju, S. R.; Park, J. K.; Stein, C. (1994), "Long tours and short superstrings'", Proc. 35th Ann. IEEE Symp. on Foundations of Comput. Sci., IEEE Computer Society, pp. 166–177.
- Orponen, P.; Mannila, H. (1987), "On approximation preserving reductions: Complete problems and robust measures'", Technical Report C-1987–28, Department of Computer Science, University of Helsinki.
- Papadimitriou, C. H.; Yannakakis, M. (1993), "The traveling salesman problem with distances one and two", Math. Oper. Res. 18: 1–11, doi:.
- Serdyukov, A. I. (1984), "An algorithm with an estimate for the traveling salesman problem of the maximum'", Upravlyaemye Sistemy 25: 80–86.
- Woeginger, G.J. (2003), "Exact Algorithms for NP-Hard Problems: A Survey", Combinatorial Optimization – Eureka, You Shrink! Lecture notes in computer science, vol. 2570, Springer, pp. 185–207.
قراءات إضافية
- Applegate, D. L.; Bixby, R. E.; Chvátal, V.; Cook, W. J. (2006), The Traveling Salesman Problem: A Computational Study, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-12993-8.
- Arora, S. (1998), "Polynomial time approximation schemes for Euclidean traveling salesman and other geometric problems", Journal of the ACM 45 (5): 753–782, doi:, http://graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs468-06-winter/Papers/arora-tsp.pdf.
- Babin, Gilbert; Deneault, Stéphanie; Laportey, Gilbert (2005), Improvements to the Or-opt Heuristic for the Symmetric Traveling Salesman Problem, Cahiers du GERAD, G-2005-02, Montreal: Group for Research in Decision Analysis, http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.89.9953.
- Cook, William; Espinoza, Daniel; Goycoolea, Marcos (2007), "Computing with domino-parity inequalities for the TSP", INFORMS Journal on Computing 19 (3): 356–365, doi:.
- Cormen, T. H.; Leiserson, C. E.; Rivest, R. L.; Stein, C. (2001), "35.2: The traveling-salesman problem", Introduction to Algorithms (2nd ed.), MIT Press and McGraw-Hill, pp. 1027–1033, ISBN 0-262-03293-7.
- Dantzig, G. B.; Fulkerson, R.; Johnson, S. M. (1954), "Solution of a large-scale traveling salesman problem", Operations Research 2: 393–410, doi:, http://www.jstor.org/stable/166695.
- Garey, M. R.; Johnson, D. S. (1979), "A2.3: ND22–24", Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness, W.H. Freeman, pp. 211–212, ISBN 0-7167-1045-5.
- Goldberg, D. E. (1989), Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization & Machine Learning, New York: Addison-Wesley, ISBN 0201157675.
- Gutin, G.; Yeo, A.; Zverovich, A. (2002), "Traveling salesman should not be greedy: domination analysis of greedy-type heuristics for the TSP", Discrete Applied Mathematics 117 (1–3): 81–86, doi:.
- Gutin, G.; Punnen, A. P. (2006), The Traveling Salesman Problem and Its Variations, Springer, ISBN 0-387-44459-9 begin_of_the_skype_highlighting 0-387-44459-9 end_of_the_skype_highlighting.
- Johnson, D. S.; McGeoch, L. A. (1997), "The Traveling Salesman Problem: A Case Study in Local Optimization", in Aarts, E. H. L.; Lenstra, J. K., Local Search in Combinatorial Optimisation, John Wiley and Sons Ltd, pp. 215–310.
- Lawler, E. L.; Lenstra, J. K.; Rinnooy Kan, A. H. G.; Shmoys, D. B. (1985), The Traveling Salesman Problem: A Guided Tour of Combinatorial Optimization, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0-471-90413-9.
- MacGregor, J. N.; Ormerod, T. (1996), "Human performance on the traveling salesman problem", Perception & Psychophysics 58 (4): 527–539, http://www.psych.lancs.ac.uk/people/uploads/TomOrmerod20030716T112601.pdf.
- Mitchell, J. S. B. (1999), "Guillotine subdivisions approximate polygonal subdivisions: A simple polynomial-time approximation scheme for geometric TSP, k-MST, and related problems", SIAM Journal on Computing 28: 1298–1309, doi:, http://citeseer.ist.psu.edu/622594.html.
- Rao, S.; Smith, W. (1998), "Approximating geometrical graphs via 'spanners' and 'banyans'", Proc. 30th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 540–550.
- Rosenkrantz, Daniel J.; Stearns, Richard E.; Lewis, Philip M., II (1977), "An Analysis of Several Heuristics for the Traveling Salesman Problem", SIAM Journal on Computing 6 (5): 563–581, doi:.
- Vickers, D.; Butavicius, M.; Lee, M.; Medvedev, A. (2001), "Human performance on visually presented traveling salesman problems", Psychological Research 65 (1): 34–45, doi:, PMID 11505612.
- Walshaw, Chris (2000), A Multilevel Approach to the Travelling Salesman Problem, CMS Press.
- Walshaw, Chris (2001), A Multilevel Lin-Kernighan-Helsgaun Algorithm for the Travelling Salesman Problem, CMS Press.
وصلات خارجية
- Traveling Salesman Problem at Georgia Tech
- Traveling Salesman Problem by Jon McLoone based on a program by Stephen Wolfram, after work by Stan Wagon, Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
- optimap an approximation using ACO on GoogleMaps with JavaScript
- tsp an exact solver using Constraint Programming on GoogleMaps
- Demo applet of a genetic algorithm solving TSPs and VRPTW problems