قائمة محاكم المناطق والأراضي في الولايات المتحدة
| هذا المقال جزء من سلسلة عن |
| سياسة الولايات المتحدة |
|---|
 |
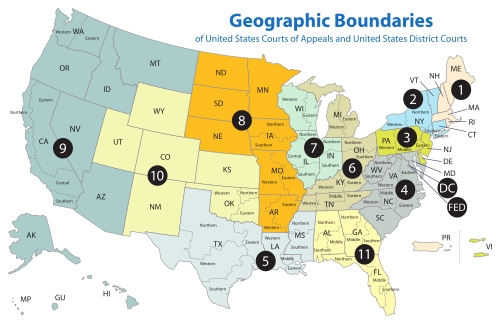
هناك 94 active United States district and territorial courts.[1] Each of the 50 states has between one and four district courts, and the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico each have a district court.
The insular areas of Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the United States Virgin Islands each have one territorial court; these courts are called "district courts" and exercise the same jurisdiction as district courts,[2][3] but differ from district courts in that territorial courts are Article IV courts, with judges who serve ten-year terms rather than the lifetime tenure of judges of Article III courts, such as the district court judges.[3]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التعريف
The district courts were established by Congress under Article III of the United States Constitution. The courts hear civil and criminal cases, and each is paired with a bankruptcy court.[2] Appeals from the district courts are made to one of the 13 courts of appeals, organized geographically. The number of district courts in a court of appeals' circuit varies between one and thirteen, depending on the number of states in the region and the number of districts in each state. The formal naming convention for the district courts is "United States District Court for" followed by the district name. Each district court has one or more meeting places at which it holds hearings and conducts business. Many federal courthouses are named after notable judges, such as the Thurgood Marshall United States Courthouse in New York City or the Hugo L. Black Courthouse in Birmingham. The largest courthouse is the Thomas F. Eagleton United States Courthouse, which serves the Eastern District of Missouri.[4]
The largest courts by number of judges are the Central District of California and the Southern District of New York, each with 28 judgeships. The smallest are the District for the Northern Mariana Islands and the District of Guam, with one judgeship each.
المحاكم الناشطة












- المفتاح
| Citation | الاختصارات المستخدمة للإشارة لأحكام المحكمة. |
| تأسست | The date the district court was established as a court or the date it was subdivided from a larger district. |
| القضاة | The number of judgeships authorized for the district. |
| أماكن الانعقاد | The number of locations at which the court hears cases. |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
المحاكم المنحلة

Note: Defunct courts do not include courts consisting of an entire state that were later subdivided.
| Name | Citation | Established | Disestablished |
|---|---|---|---|
| District of Edenton | — | 1794 | 1797 |
| District of New Bern | — | 1794 | 1797 |
| District of Wilmington | — | 1794 | 1797 |
| District of East Jersey | — | 1801 | 1802 |
| District of West Jersey | — | 1801 | 1802 |
| District of Potomac | — | 1801 | 1802 |
| District of Norfolk | — | 1801 | 1802 |
| District of Albemarle | — | 1802 | 1872 |
| District of Cape Fear | — | 1802 | 1872 |
| District of Pamptico | — | 1802 | 1872 |
| District of Orleans | — | 1804 | 1812 |
| Eastern District of Illinois | E.D. Ill. | 1905 | 1978 |
| District of China | — | 1906 | 1943 |
| Eastern District of South Carolina | E.D.S.C. | 1911 | 1965 |
| Western District of South Carolina | W.D.S.C. | 1911 | 1965 |
| District of the Canal Zone | D.C.Z. | 1914 | 1982 |
| District of Berlin | D.Berlin | 1955 | 1990 |
محاكم انقسمت
| Name | Citation | Established | Subdivided |
|---|---|---|---|
| District of Alabama | D. Ala. | April 21, 1820 | March 10, 1824 |
| District of Arkansas | D. Ark. | June 15, 1836 | March 3, 1851 |
| District of California | D. Cal. | July 27, 1866[5] | August 5, 1886 |
| District of Florida | D. Fla. | March 3, 1845 | February 23, 1847 |
| District of Georgia | D. Ga. | September 24, 1789 | on August 11, 1848 |
| District of Illinois | D. Ill. | March 3, 1819 | February 13, 1855 |
| District of Indiana | D. Ind. | March 3, 1817 | April 21, 1928 |
| District of Iowa | D. Iowa | March 3, 1845 | July 20, 1882 |
| District of Kentucky | D. Ky. | September 24, 1789 March 8, 1802[6] |
February 13, 1801 February 12, 1901 |
| District of Louisiana | D. La. | April 8, 1812 February 13, 1845 July 27, 1866 |
March 3, 1823 March 3, 1849 On March 3, 1881 |
| District of Michigan | D. Mich. | July 1, 1836 | February 24, 1863 |
| District of Mississippi | D. Miss. | April 3, 1818 | June 18, 1838 |
| District of Missouri | D. Mo. | March 16, 1822 | March 3, 1857 |
| District of New York | D.N.Y. | September 24, 1789 | April 9, 1814 |
| District of North Carolina | D.N.C. | June 4, 1790 March 3, 1797 |
June 9, 1794 April 29, 1802 |
| District of Ohio | D. Ohio | February 19. 1803 | February 10, 1855 |
| District of Pennsylvania | D. Pa. | September 24, 1789 | April 20, 1818 |
| District of Tennessee | D. Tenn. | January 31, 1797 March 8, 1802[7] |
February 13, 1801 April 29, 1802 |
| District of Texas | D. Tex. | December 29, 1845 | February 21, 1857 |
| District of Virginia | D. Va. | September 24, 1789 March 8, 1802 June 11, 1864 |
February 13, 1801 February 4, 1819 February 3, 1871 |
| District of Washington | D. Wash. | April 5, 1890 | March 2, 1905 |
| District of West Virginia | D.W.Va. | June 11, 1864 | January 22, 1901 |
| District of Wisconsin | D. Wis. | May 29, 1848 | June 30, 1870 |
انظر أيضاً
References
- General
- Association of Legal Writing Directors (December 2002). ALWD Citation Manual: A Professional System of Citation (PDF). New York, New York: Aspen Publishers. pp. 431–438. ISBN 978-0-7355-3640-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Federal Judicial History Office (2009). "The U.S. District Courts and the Federal Judiciary". History of the Federal Judiciary. Federal Judicial Center. Retrieved 2009-05-24.
- "U.S. Courts | Frequently Asked Questions". Administrative Office of the U.S. Courts. Archived from the original on 2009-02-26. Retrieved 2009-06-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
- Specific
- ^ "United States District Courts". Administrative Office of the U.S. Courts. Archived from the original on 2008-12-05. Retrieved 2009-06-15.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ أ ب Article III Judges Division (2001-08-01). "An Introduction for Judges and Judicial Administrators in Other Countries" (PDF). The Federal Court System in the United States. Administrative Office of the United States Courts. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-05-13. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ أ ب "Territorial Courts". History of the Federal Judiciary. Federal Judicial Center. Archived from the original on May 14, 2009. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Thomas F. Eagleton Courthouse". St. Louis - Eastern Division. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ California was originally established with two district courts on September 28, 1850; these districts were merged into a single District of California on July 27, 1866.
- ^ The District of Kentucky was abolished on February 13, 1801 by the Judiciary Act of 1801, 2 Stat. 89, and was restored with the repeal of this Act on March 8, 1802, 2 Stat. 132. U.S. District Courts of Kentucky, Legislative history, Federal Judicial Center.
- ^ The District of Tennessee was abolished on February 13, 1801 by the Judiciary Act of 1801, 2 Stat. 89, and was restored with the repeal of this Act on March 8, 1802, 2 Stat. 132. U.S. District Courts of Tennessee, Legislative history, Federal Judicial Center.