قائمة أضلع أندرا پرادش
| Districts of Andhra Pradesh | |
|---|---|
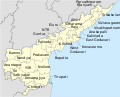
 Andhra Pradesh Political Map | |
| التصنيف | Districts |
| الموقع | Andhra Pradesh |
| العدد | 26 districts |
| عدد السكان | Parvathipuram Manyam – 9,25,340 (lowest); Nellore – 24,69,712 (highest) |
| المساحة | Visakhapatnam – 1,048 km2 (405 sq mi) (smallest); Prakasam – 14,322 km2 (5,530 sq mi) (largest) |
| الحكومة | Government of Andhra Pradesh |
| التقسيمات | Revenue Divisions of Andhra Pradesh |
The state of Andhra Pradesh has 26 districts. Visakhapatnam district is the smallest district in area while Prakasam district is the largest. Nellore district is the most populous whereas Parvathipuram Manyam district is the least populous district. The districts are further divided into two or more revenue divisions, which are further subdivided into mandals for administrative purposes.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
History
At the time of Independence the present day Andhra Pradesh was a part of the Madras State. The telugu speaking dominant regions Kostaandhra and Rayalaseema were separated from Madras State to form Andhra State in 1953.[1]
As Andhra State, it consisted of 11 districts which are Anantapur, Chittoor, East Godavari, Guntur, Kadapa, Krishna, Kurnool, Nellore, Srikakulam, Visakhapatnam and West Godavari.[2][3]
As a result of the 1956 States Reorganisation Act, the state's boundaries were re-organized following linguistic lines. On 1 November 1956, the Andhra State and the Telangana region of the Hyderabad State were merged to form the Andhra Pradesh which is retrospectively referred to as United Andhra Pradesh.
As united Andhra Pradesh, it consisted of 21 district's, with 10 districts of Telangana region.[بحاجة لمصدر] In the year 1959, Bhadrachalam and Nuguru Venkatapuram taluks of East Godavari district, which are on the other side of the Godavari River, were merged into Khammam district on grounds of geographical contiguity and administrative viability. Similarly Aswaraopeta part of West Godavari District was added to Khammam district and Munagala taluk belonging to Krishna district was added to Nalgonda district in the same year.[4]
The number of districts became 23 with the formation of Prakasam district from the parts of Guntur, Nellore and Kurnool district's in 1970 and Vizianagaram district from parts of Visakhapatnam and Srikakulam districts in 1979.
After the bifurcation of the United Andhra Pradesh in 2014, the Andhra region now known as Andhra Pradesh was left with 13 districts but was given several tribal-dominated mandals from the Khammam district of the Telangana as part of the Polavaram project. These mandals were added to the East Godavari and West Godavari district's respectively.[5][6][7][8]
On 26 January 2022, the Government of Andhra Pradesh had proposed 13 new districts by issuing a draft notification under the Andhra Pradesh Districts (Formation) Act, 1974, Section 3(5).[9][10] After taking the objections and suggestions received from the public into consideration, the government has published the final notification on 3 April 2022. With effect from 4 April 2022 the newly formed districts came into effect as specified in the schedule.[11][12][13] At present there are 26 districts spread across 3 cultural regions: Uttaraandhra, Kostaandhra and Rayalaseema.
Timeline
Districts
The state is further divided into 26 districts, with North Andhra comprising six districts, Coastal Andhra comprising 12 districts, and Rayalaseema comprising eight districts.[14] These districts are made up of 76 revenue divisions,[15] 679 mandals[15] and 13,324 village panchayats as part of the administrative organisation.[16]
North Andhra:
Coastal Andhra:
Rayalaseema:
| S.No | Code[17] | Official name | Headquarters | Past District | Revenue divisions |
Mandals | Population | Area (in sq.km) |
Density (per sq.km) |
Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SRI | Srikakulam | Srikakulam | 3 | 30 | 21,91,471 | 4,591 | 477.34 | 
| |
| 2 | PAR | Parvathipuram Manyam | Parvathipuram | Srikakulam, Vizianagaram. | 2 | 15 | 9,25,340 | 3,659 | 252.89 | 
|
| 3 | VIZ | Vizianagaram | Vizianagaram | 3 | 27 | 19,30,811 | 4,122 | 468.42 | 
| |
| 4 | VIS | Visakhapatnam | Visakhapatnam | 2 | 11 | 19,59,544 | 1,048 | 1869.79 | 
| |
| 5 | ALL | Alluri Sitharama Raju | Paderu | East Godavari, Visakhapatnam, Vizianagaram. | 3 | 22 | 9,53,960 | 12,251 | 77.87 | 
|
| 6 | ANA | Anakapalli | Anakapalli | Visakhapatnam | 2 | 25 | 17,26,998 | 4,292 | 402.38 | 
|
| 7 | KAK | Kakinada | Kakinada | East Godavari | 2 | 21 | 20,92,374 | 3,019 | 693.07 | 
|
| 8 | EAS | East Godavari | Rajamahendravaram | 2 | 19 | 18,32,332 | 2,561 | 715.48 | 
| |
| 9 | KON | Dr. B. R. Ambedkar Konaseema | Amalapuram | East Godavari | 3 | 22 | 17,19,093 | 2,083 | 825.30 | 
|
| 10 | ELU | Eluru | Eluru | West Godavari | 3 | 27 | 20,06,737 | 6,579 | 305.02 | 
|
| 11 | WES | West Godavari | Bhimavaram | 3 | 20 | 18,44,898 | 2,278 | 809.88 | 
| |
| 12 | NTR | NTR | Vijayawada | Krishna | 3 | 20 | 22,18,591 | 3,316 | 669.06 | 
|
| 13 | KRI | Krishna | Machilipatnam | 3 | 26 | 17,35,079 | 3,775 | 459.62 | 
| |
| 14 | PAL | Palnadu | Narasaraopeta | Guntur | 3 | 28 | 20,41,723 | 7,298 | 279.76 | 
|
| 15 | GUN | Guntur | Guntur | 2 | 18 | 20,91,075 | 2,443 | 855.95 | 
| |
| 16 | BAP | Bapatla | Bapatla | Guntur Prakasam | 3 | 25 | 15,86,918 | 3,829 | 414.45 | 
|
| 17 | NEL | Sri Potti Sriramulu Nellore | Nellore | 4 | 38 | 24,69,712 | 10,441 | 236.54 | 
| |
| 18 | PRA | Prakasam | Ongole | 3 | 39 | 22,88,026 | 14,322 | 159.76 | 
| |
| 19 | KUR | Kurnool | Kurnool | 3 | 26 | 22,71,686 | 7,980 | 284.67 | 
| |
| 20 | NAN | Nandyal | Nandyal | Kurnool | 3 | 30 | 17,81,777 | 9,682 | 184.03 | 
|
| 21 | ANA | Anantapuramu | Anantapuram | 3 | 32 | 22,41,105 | 10,205 | 219.61 | 
| |
| 22 | SSS | Sri Sathya Sai | Puttaparthi | Anantapuramu | 4 | 32 | 18,40,043 | 8,925 | 206.17 | 
|
| 23 | CUD | YSR | Kadapa | 4 | 36 | 20,60,654 | 11,228 | 183.53 | 
| |
| 24 | ANN | Annamayya | Rayachoti | Chittoor, YSR | 3 | 30 | 16,97,308 | 7,954 | 213.39 | 
|
| 25 | TIR | Tirupati | Tirupati | Chittoor, Nellore | 4 | 34 | 21,96,984 | 8,231 | 266.92 | 
|
| 26 | CHI | Chittoor | Chittoor | 4 | 32 | 18,72,951 | 6,855 | 273.22 | 
|
- Source:[12]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
See also
- List of mandals in Andhra Pradesh
- List of districts in India
- List of revenue divisions in Andhra Pradesh
References
- ^ "History of Andhra Pradesh". The Hans India (in الإنجليزية). 1 نوفمبر 2020. Archived from the original on 3 أبريل 2022. Retrieved 3 أبريل 2022.
- ^ "AP new districts: First formed under the empire, Andhra Pradesh's map shaped and reshaped over two centuries". The Times of India (in الإنجليزية). 30 مارس 2022. Retrieved 3 أبريل 2022.
- ^ "New districts in AP: Experts want the government to walk the talk". The Hindu (in الإنجليزية). 2 أبريل 2022. Archived from the original on 3 أبريل 2022. Retrieved 3 أبريل 2022.
- ^ ANI (12 نوفمبر 2013). "GoM on Andhra bifurcation to elicit views of political parties". Business Standard India. Retrieved 14 مارس 2023.
- ^ "Andhra Pradesh takes control of seven mandals in Khammam". Deccan Chronicle (in الإنجليزية). 3 سبتمبر 2014. Retrieved 3 أبريل 2022.
- ^ "List of seven mandals to be included in AP". The Hans India (in الإنجليزية). 11 يوليو 2014. Retrieved 3 أبريل 2022.
- ^ "TS gives up on 7 transferred mandals". The Hindu (in الإنجليزية). 19 أغسطس 2014. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 14 مارس 2023.
- ^ "Parliament passes bill on Polavaram project". The Hindu (in الإنجليزية). 14 يوليو 2014. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 14 مارس 2023.
- ^ "Doubling the number of districts in Andhra Pradesh: The proposal and the criticism". The Indian Express (in الإنجليزية). 31 يناير 2022. Retrieved 11 مارس 2023.
- ^ Raghavendra, V. (26 يناير 2022). "With creation of 13 new districts, AP now has 26 districts". The Hindu. ISSN 0971-751X. Archived from the original on 26 يناير 2022. Retrieved 26 يناير 2022.
- ^ "New districts to come into force on April 4". The Hindu. 30 مارس 2022. Retrieved 3 أبريل 2022.
- ^ أ ب "Here's how new ap map looks after districts reorganisation". 3 أبريل 2022. Retrieved 17 أبريل 2023.
- ^ "Andhra Pradesh to have 13 new districts from April 4". india.com (in الإنجليزية). 31 مارس 2022. Retrieved 3 أبريل 2022.
- ^ V., Raghavendra (4 أبريل 2022). "Jagan launches 13 new districts of Andhra Pradesh". The Hindu. Retrieved 21 أغسطس 2024.
- ^ أ ب DOP 2023, p. 431.
- ^ Monthly bulletin (PDF). Ministry of Panchayat raj, Government of India. 2022. p. 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 يونيو 2023. Retrieved 3 يونيو 2023.
- ^ "NIC Policy on format of e-mail Address" (PDF). www.mail.nic.in. 11 سبتمبر 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 سبتمبر 2008. Retrieved 15 فبراير 2021.
Sources
- DOP (2023). Socio economic survey 2022–23 (PDF). Government of AP. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 مارس 2024. Retrieved 24 أبريل 2023.
External links
 Media related to قائمة أضلع أندرا پرادش at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to قائمة أضلع أندرا پرادش at Wikimedia Commons
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Use Indian English from August 2016
- All Wikipedia articles written in Indian English
- Use dmy dates from August 2016
- Articles with unsourced statements from March 2023
- Andhra Pradesh-related lists
- Lists of districts in India
- Districts of Andhra Pradesh
- صفحات مع الخرائط