فلوكونازول
 | |
 | |
| البيانات السريرية | |
|---|---|
| فئة السلامة أثناء الحمل | |
| مسارات الدواء | Oral, IV, topical |
| رمز ATC | |
| الحالة القانونية | |
| الحالة القانونية |
|
| بيانات الحركية الدوائية | |
| التوافر الحيوي | >90% |
| ارتباط الپروتين | 11–12% |
| الأيض | Hepatic 11% |
| Elimination half-life | 30 hours (range 20-50 hours) |
| الإخراج | Renal 61–88% |
| المعرفات | |
| |
| رقم CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.156.133 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
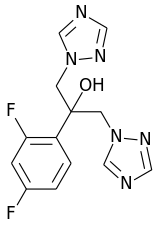
| التركيب | C13H12F2N6O |
| الكتلة المولية | 306.271 g/mol |
فلوكونازول فلوكونازول INN هو triazole مضاد للفطريات يستعمل للوقاية والعلاج من العدوى الفطرية السطحية(الجلدية)و المركزية. وفى صورة المسحوق يبدو كمسحوق بللورى, وهو قليل الذوبان في الماء ويذوب في الكحول .[1] It is commonly marketed under the trade name Diflucan or Trican (Pfizer).
الفارماكولولوجى
نظرية العمل
مثل معظم مجموعة imidazole و triazole المضادة للفطريات , فإن فلوكونازول يحبط عمل الإنزيم cytochrome P450 14α-demethylase]]. Mammalian demethylase activity is much less sensitive to fluconazole than fungal demethylase وهذا التثبيط يمنع تكوين lanosterol الى ergosterol, وهو مكون أساسى للفطر ولغشائه السيتوبلازمى . ويؤدى الى تراكم متزايد ل 14α-methyl sterols [2] فلوكونازول في الأساس موقف لنمو الفطريات ومع ذلك يمكن أن يعد قاتلا للفطريات مع فصائل معينة في نظام علاجى خاص مرتبط بالجرعة
الميكروبيولوجى
فلوكونازول فعال ضد تلك الأنواع من الفطريات :
- Blastomyces dermatitidis
- Candida spp. (except C. krusei and C. glabrata)
- Coccidioides immitis
- Cryptococcus neoformans
- Epidermophyton spp.
- Histoplasma capsulatum
- Microsporum spp.
- Trichophyton spp.
الحراك الدوائى
يمتص فلوكونازول تماما خلال ساعتين وهو مايطلق عليه الإتاحة الحيوية Bioavailability وهو لايتأثر كثيرا بغياب حمض المعدة.وقيست تركيزاته في البول و الدموع وفى الجلد فوجد أنها تقريبا 10 أضعاف تركيزات البلازما , بينما وجدت تركيزات اللعاب و البلغم (المخاط)و سوائل المهبل تماما مثل تركيزات البلازما تقريبا, بعد جرعة واحدة تتراوح بين 100مج-400مج يوميا, ووجد أن elimination half-life]] ل فلوكونونازول تتبع zero order kinetics ووجد أن 10% فقط من معدل تخلص الجسم من العقار هى ناتجة من تمثيله في الجسم, والبقية تفرز في البول وفى العرق . والمرضى الذين يعانون من قصور كلوي, سوف يكونون معرضون للخطر من الجرعات الزائدة, كما مع المرضى الذين يستعملون العقار warfarin.
الإستعمالات السريرية
دواعى الإسستعمال
Fluconazole is indicated for the treatment and prophylaxis of fungal infections where other antifungals have failed or are not tolerated (e.g. due to adverse effects), including:[4]
- Candidiasis caused by susceptible strains of Candida
- Tinea corporis, tinea cruris or tinea pedis
- Onychomycosis
- Cryptococcal meningitis
Fluconazole can be used first-line for the following indications:[4]
- Coccidioidomycosis
- Cryptococcosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Prophylaxis of candidiasis in immunocompromised people
الجرعات
Dosage, varies with indication and between patient groups, ranging from: a two week course of 150 mg/day for vulvovaginal candidiasis, to 150–300 mg once weekly for resistant skin infections or some prophylactic indications. 50–600 mg/day may be used for systemic or severe infections, and in urgent infections such as meningitis caused by yeast 800 mg/day have been used. Pediatric doses are measured at 6-12 mg/kg/d . A loading dose will be indicated when entering a daily dosage schedule, for example a loading dose of 200 mg on the first day is commonly used with 150 mg/day following that.[4]
مضادات الإستعمال
Fluconazole is contraindicated in patients with:[4]
- Known hypersensitivity to fluconazole or other azole antifungals
- Concomitant use of cisapride, due to risk of serious cardiac arrhythmias (relative contraindication).
تحذيرات
Fluconazole therapy has been associated with QT interval prolongation, which may lead to serious cardiac arrhythmias. Thus it is used with caution in patients with risk factors for prolonged QT interval such as electrolyte imbalance or use of other drugs which may prolong the QT interval (particularly cisapride).
Fluconazole has also rarely been associated with severe or lethal hepatotoxicity and liver function tests are usually performed regularly during prolonged fluconazole therapy. Additionally, it is used with caution in patients with pre-existing liver disease.[2]
High concentrations of fluconazole have been detected in human breast milk from patients receiving fluconazole therapy, thus its use is not recommended in breastfeeding mothers.[2]
آثار جانبية
Adverse drug reactions associated with fluconazole therapy include:[4]
- Common (≥1% of patients): rash, headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and/or elevated liver enzymes
- Infrequent (0.1–1% of patients): anorexia, fatigue, constipation
- Rare (<0.1% of patients): oliguria, hypokalaemia, paraesthesia, seizures, alopecia, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, thrombocytopenia, other blood dyscrasias, serious hepatotoxicity including hepatic failure, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions
- Very rare: prolonged QT interval, torsades de pointes
التفاعلات مع الأدوية الأخرى
Fluconazole is an inhibitor of the human cytochrome P450 system, particularly the isozymes CYP2C9 and CYP3A4. In theory, therefore, fluconazole decreases the metabolism and increases the concentration of any drug metabolised by these enzymes. Additionally, its potential effect on QT interval increases the risk of cardiac arrhythmia if used concurrently with other drugs that prolong the QT interval.
المراجع
- ^ MP Biomedicals[1]
- ^ أ ب ت Pfizer Australia Pty Ltd. Diflucan (Australian Approved Product Information). West Ryde (NSW): Pfizer Australia; 2004.
- ^ Sweetman S, editor. Martindale: The complete drug reference. 34th ed. London: Pharmaceutical Press; 2004. ISBN 0-85369-550-4
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج Rossi S, editor. Australian Medicines Handbook 2006. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook; 2006. ISBN 0-9757919-2-3
انظر أيضا
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Infobox-drug molecular-weight unexpected-character
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- مضادات الفطريات
- تريازولات
- فايزر
- الأدوية الأساسية حسب منظمة الصحة العالمية