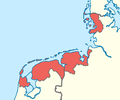
فريزيا
53°15′00″N 7°00′00″E / 53.25000°N 7.00000°E
| فريزيا | |
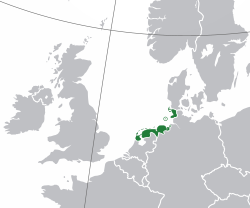
فريزيا في شمال غرب أوروپا | |
| Stateless nation | Frisians |
| الاستقلال | لم يحدث * |
| المساحة | 13482.73 كم² |
| التعداد | 2,655,391 |
| الكثافة | 197/كم² |
| اللغات | West Frisian North Frisian Saterland Frisian Low Saxon (Friso-Saxon) الهولندية (West Frisian Dutch, Stadsfries) الألمانية (Missingsch) Danish (Sønderjysk) |
| الدين الرئيسي | پروتستانت (كاثوليك في ساترلاند) |
| التوقيت • الصيفي |
CET (UTC+1) CEST (UTC+2) |
| Internet TLD | .frl |
| * الأجزاء المدمجة في كل من هولندا وألمانيا، بالترتيب، ولكن بدرجات متفاوتة من الاستقلال الذاتي للسكان الفريزيين. | |
فريزيا (Frisia ؛ قالب:Lang-fry؛ بالهولندية و ألمانية: Friesland[1], الإنگليزية القديمة: Freslond) هي منطقة ساحلية تاريخية على طول الركن الجنوبي الشرقي لبحر الشمال في ما هو اليوم جزء كبير من هولندا (Nederland)، بما في ذلك فريزلاند الحديثة، وأجزاء أصغر في شمال ألمانيا. فريزيا هي الوطن التقليدي للفريزيين، الشعب الجرماني الذي يتكلم اللغات الفريزية، التي تشكل مع اللغات الأنگلية (الإنگليزية ولغة الاسكوت) مجموعة اللغات الأنگلو-فريزية.
الأسماء
The names for "Frisia" in the local languages are (by direct translation and written in the related orthographic system):
- Frisland (Danish)
- Friesland (Dutch, German and West Frisian Dutch)
- Fraislaand (Dutch Low Saxon)
- Freesland (East Frisian Low Saxon)
- Fresklun (Fering-Öömrang North Frisian)
- Freeschlon (Goesharde North Frisian)
- Freesklöön (Halligen North Frisian)
- Friislon (Heligolandic North Frisian)
- Fräischlön (Karrharde North Frisian)
- Fraschlönj (Bökingharde North Frisian)
- Fräislound (Saterland Frisian)
- Friislön (Söl'ring North Frisian)
- Fryslân (West Frisian)
- Freesklön (Wiedingharde North Frisian)
The traditional meaning of these terms in the particular varieties rarely refers to the region Frisia as it is discussed in this article. Usually it is restricted to the local area and sometimes to something else, e.g. for the people of the North Frisian islands, Frisia and the Frisians are the area and the people on the mainland and in the Saterland the term Fräislound especially denotes to East Frisia.[2]
When the French occupied the Netherlands, the name for the Frisian department was Frise. In English, both terms, Frisia and Friesland are used.
الأقسام
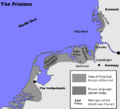
تنقسم فريزيا اعتيادياً إلى ثلاث قطاعات:
- West Frisia in the Netherlands corresponds roughly to:
- the province of Friesland
- the northern parts of the province of North Holland, historical West Friesland
- East Frisia in Lower Saxony, Germany corresponds roughly to:
- East Frisia in a narrower sense:
- the Aurich district
- the Emden district
- the Leer district
- the Wittmund district
- East Frisia in a wider sense (East Frisian peninsula):
- the Friesland district
- the Wilhelmshaven district
- the Saterland municipality
- the Butjadingen peninsula, historical Rüstringen
- the Wurster Nordseeküste municipality, historical Land Wursten
- East Frisia in a narrower sense:
- North Frisia in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany corresponds roughly to:
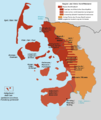
The three groups of the Frisian Islands (the West, East and North Frisian Islands) stretch more or less correspondingly along these three sections of the German Bight coast.
West Frisia corresponds roughly to the Dutch province of Friesland (Fryslân), the northern part of North Holland province (the historical region of West Friesland, the westernmost portion of the traditional region of West Frisia), and also modern Groningen province, though the Western Frisian language is only spoken in Friesland proper. Dialects with strong West Frisian substrates, including Low German and Low Franconian, are also spoken in West Frisia. In the northern province of Groningen, people speak Gronings, a Low Saxon dialect with a strong Frisian substrate. Rural Groningen was originally part of the Frisian lands "east of River Lauwers" and by law and language closer linked to East Frisia than to the west.
East Frisia includes areas located in the northwest of the German state of Lower Saxony, including the districts of Aurich, Leer, Wittmund and Friesland, as well as the urban districts of Emden and Wilhelmshaven, the Saterland, the Land Wursten and former Rüstringen ("Butjadingen peninsula"). East Frisia is also the name of a historical county in that region. Only people from that area consider themselves as East Frisians. The German name "Ostfriesland" distinguishes the former county from "Ost-Friesland", which means the whole eastern Frisian area.
The portions of North Frisia within the German state of Schleswig-Holstein are part of the district of Nordfriesland and stretch along the coast, including the coastal islands from the Eider River to the border of Denmark in the north. The North Sea island of Heligoland, while not part of the Nordfriesland district, is also part of traditional North Frisia. North Frisia was until the Second Schleswig War of 1864 part of Denmark or the Danish Duchy of Schleswig.
| القطاع | Sense | الأقسام | العلم | المساحة | التعداد | الكثافة السكانية |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East Frisia | Narrow | District of Aurich | 3،142 km2 (1،213 sq mi) | 465٬000 | 148/km2 (380/sq mi) | |
| Urban district of Emden | ||||||
| District of Leer | ||||||
| District of Wittmund | ||||||
| Wide | Peninsula of Butjadingen | 423.05 km2 (163.34 sq mi) | 45٬726 | 108/km2 (280/sq mi) | ||
| District of Friesland | 714.91 km2 (276.03 sq mi) | 172٬821 | 242/km2 (630/sq mi) | |||
| Urban district of Wilhelmshaven | ||||||
| Municipality of Saterland | 123.62 km2 (47.73 sq mi) | 13٬187 | 107/km2 (280/sq mi) | |||
| Municipality of Wurster Nordseeküste (Land Wursten) | 182.08 km2 (70.30 sq mi) | 16٬799 | 92/km2 (240/sq mi) | |||
| North Frisia | Archipelago of Heligoland | 1.7 km2 (0.66 sq mi) | 1٬356 | 798/km2 (2،070/sq mi) | ||
| District of Nordfriesland | 2،047 km2 (790 sq mi) | 162٬203 | 79/km2 (200/sq mi) | |||
| West Frisia | Province of Friesland | 3،349 km2 (1،293 sq mi) | 646٬305 | 193/km2 (500/sq mi) | ||
| Province of Groningen (Ommelanden) | 2،325 km2 (898 sq mi) | 582٬640 | 251/km2 (650/sq mi) | |||
| Historical region of West Friesland | 1،174.37 km2 (453.43 sq mi) | 549٬354 | 468/km2 (1،210/sq mi) | |||
اللغات
A half-million Frisians in the province of Friesland in the Netherlands speak West Frisian. Several thousand people in Nordfriesland and Heligoland in Germany speak a collection of North Frisian dialects. A small number of Saterland Frisian language speakers live in four villages in Lower Saxony, in the Saterland region of Cloppenburg county, just beyond the boundaries of traditional East Frisia. Many Frisians speak Low Saxon dialects which have a Frisian substratum known as Friso-Saxon, especially in East Frisia, where the local dialects are called Oostfreesk ('East Frisian') or Oostfreske Plattdüütsch (East Frisian Low Saxon). In the Provinces of Friesland and Groningen, and in North Frisia, there are also areas where Friso-Saxon dialects are predominantly spoken, such as Gronings. In West Frisia, there are West Frisian-influenced dialects of Dutch such as West Frisian Dutch and Stadsfries.
الخرائط
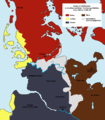
Frisian colonisation of the South West Coast of Jutland during the Viking Age (yellow)
التاريخ
Frisia has changed dramatically over time, both through floods and through a change in identity. It is part of the supposed Nordwestblock which is a hypothetical historic region linked by language and culture.
العصر الروماني
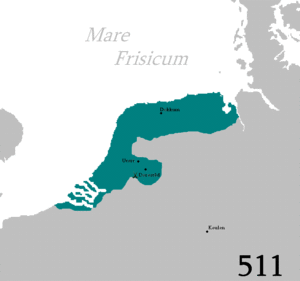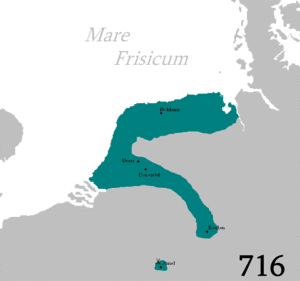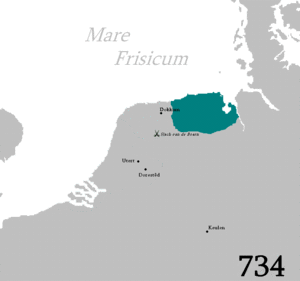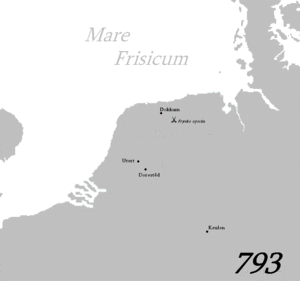
The people, later to be known as Frisii, began settling in Frisia in the 6th century BC. According to Pliny the Elder, in Roman times, the Frisians (or rather their close neighbours, the Chauci) lived on terps, man-made hills.[3] According to other sources, the Frisians lived along a broader expanse of the North Sea (or "Frisian Sea") coast.[أ]
Frisia at this time comprised the present provinces of Friesland and parts of North Holland and Utrecht.
العصور الوسطى المبكرة
Frisian presence during the Early Middle Ages has been documented from North-Western Flanders up to the Weser River Estuary. According to archaeological evidence, these Frisians were not the Frisians of Roman times, but the descendants of Anglo-Saxon immigrants from the German Bight, arriving during the Great Migration. By the 8th century, ethnic Frisians also started to colonize the coastal areas North of the Eider River under Danish rule. The nascent Frisian languages were spoken all along the southern North Sea coast.[4] Today, the whole region is sometimes referred to as Greater Frisia or Frisia Magna.
Distant authors seem to have made little distinction between Frisians and Saxons. The Byzantine Procopius described three peoples living in Great Britain: Angles, Frisians and Britons,[5] and the Danish author of Knútsdrápa celebrating the 11th-century Canute the Great used "Frisians" as a synonym of "English".[ب] The historian and sociologist George Homans has made a case for Frisian cultural domination in East Anglia since the 5th century, pointing to distinct land-holdings arrangements in carucates (these forming vills assembled in leets), partible inheritance patterns of common lands held in by kin, resistance to manorialism and other social institutions.[6] Some East Anglian sources called the mainland inhabitants Warnii, rather than Frisians.
During the 7th and 8th centuries, Frankish chronologies mention the northern Low Countries as the kingdom of the Frisians. According to Medieval legends, this kingdom comprised the coastal seelande provinces of the Netherlands, from the Scheldt River to the Weser River and further East. Archaeological research does not confirm this idea, as the petty kingdoms appear to have been rather small and short-lived.
The earliest Frisian records name four social classes, the ethelings (nobiles in Latin documents) and frilings, who together made up the "Free Frisians" who might bring suit at court, and the laten or liten with the slaves, who were absorbed into the laten during the Early Middle Ages, as slavery was not so much formally abolished, as evaporated.[ت] The laten were tenants of lands they did not own and might be tied to it in the manner of serfs, but in later times might buy their freedom.[6]
The basic land-holding unit for assessment of taxes and military contributions was - according to Homans - the ploegg (cf. "plow") or teen (cf. tithing, cf. "hundred"), which, however, also passed under other local names. The teen was pledged to supply ten men for the heer, or army. Ploegg or teen formed a unit of which the members were collectively responsible for the performance of any of the men. The ploegg or East Frisian rott was a compact holding that originated with a single lineage or kinship, whose men in early times went to war under their chief, and devolved in medieval times into a union of neighbors rather than kith and kin. Several, often three, ploeggs were grouped into a burar, whose members controlled and adjudicated the uses of pasturage (but not tillage) which the ploeggs held in common, and came to be in charge of roads, ditches and dikes. Twelve ploeggs made up a "long" hundred,[ث] responsible for supplying a hundred armed men, four of which made a go (cf. Gau). Homans' ideas, which were largely based on studies now considered to be outdated, have not been followed up by Continental scholars.
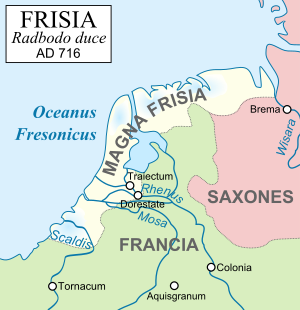
The 7th-century Frisian realm (650-734) under the kings Aldegisel and Redbad, had its centre of power in the city of Utrecht. Its ancient customary law was drawn up as the Lex Frisionum in the late eighth century. Its end came in 734 at the Battle of the Boarn, when the Frisians were defeated by the Franks, who then conquered the western part up to the Lauwers. Frankish troops conquered the area east of the Lauwers in 785, after Charlemagne defeated the Saxon leader Widukind. The Carolingians laid Frisia under the rule of grewan, a title that has been loosely related to count in its early sense of "governor" rather than "feudal overlord".[6]
During the 7th to 10th centuries, Frisian merchants and skippers played an important part in the international luxury trade, establishing commercial districts in distant cities as Sigtuna, Hedeby, Ribe, York, London, Duisburg, Cologne, Mainz, and Worms.
The Frisian coastal areas were partly occupied by Danish Vikings in the 840s, until these were expelled between 885 and 920. Recently, it been suggested that the Vikings did not conquer Frisia, but settled peacefully in certain districts (such as the islands of Walcheren and Wieringen), where they built simple forts and cooperated and traded with the native Frisians. One of their leaders was Rorik of Dorestad.
عصبة أوپشتالبوم
During the 12th century Frisian noblemen and the city of Groningen founded the Upstalsboom League under the slogan of 'Frisian freedom' to counter feudalizing tendencies. The league consisted of modern Friesland, Groningen, East Frisia, Harlingerland, Jever and Rüstringen. The Frisian districts in West Friesland West of the Zuiderzee did not participate, neither did the districts North of the Eider River along the Danish North Sea coast (Schleswig-Holstein). The former were occupied by the count of Holland in 1289, and the latter were governed by the Duke of Schleswig and the king of Denmark. The same holds true for the district of Land Wursten East of the Weser River. The Upstalsboom League was revived in the early 14th century, but it collapsed after 1337. By then the non-Frisian city of Groningen took the lead of the independent coastal districts.
القرن 15

The 15th century saw the demise of Frisian republicanism. In East Frisia a leading nobleman from the Cirksena-family managed to defeat his competitors with the help of the Hanseatic League. In 1464 he acquired the title of count of East Frisia. The king of Denmark was successful in subduing the coastal districts North of the Eider River. The Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen remained independent until 1498. By then Friesland was conquered by Duke Albert of Saxony-Meissen. The city of Groningen, which had started to dominate the surrounding rural districts, surrendered to count Edzard of East Frisia in 1506. The city conveyed its remaining privileges to the Habsburg Empire in 1536. The district of Butjadingen (formerly Rüstringen) was occupied by the Count of Oldenburg in 1514, the Land Wursten by the Prince-bishop of Bremen in 1525.
العصر الحديث
In the early 16th century, the pirate Pier Gerlofs Donia (Grutte Pier) challenged Saxon authority in Friesland during a prolonged guerrilla war, backed by the Duke of Guelders. He had several successes and was feared by Hollandic authorities, but he died as a farmer in 1520. According to the legend he was seven feet tall. A statue of Grutte Pier by Anne Woudwijk was erected in Kimswert in 1985.
In the 1560s many Frisans joined the revolt led by William of Orange against the Habsburg monarchy. In 1577 the province of Friesland became part of the nascent Dutch Republic, as its representatives signed the Union of Utrecht. The city of Groningen was conquered by the Dutch in 1594. Since then, membership of the Dutch Republic was perceived as a guarantee for the preservation of civil liberties. Actual power, however, was usurped by the landowning gentry. Protests against aristocratic rule led to a democratic movement in the 1780s.
المناطقية المعاصرة
During the late 19th and early 20th century, 'Frisian freedom' became the slogan of a regionalist movement in Friesland, demanding equal rights for the Frisian language and culture within the Netherlands. The West Frisian language and its urban dialects are spoken by the majority of the inhabitants. In East Frisia, the idea of Frisian freedom became entangled with regional sentiments as well, though the East Frisian language had been replaced by Low German dialects as early as the 15th century. In Groningen, on the other hand, Frisian sentiments faded away at the end of the 16th century. In North Frisia regional sentiments concentrate around the surviving North Frisian dialects, which are spoken by a sizeable minority of the population, though Lower German is far more widespread.
الأراضي الفريزية
- When West Friesland was conquered by the County of Holland in 1289, this was the end of a series of wars between the county of Holland and Friesland that started at the end of the 11th century. The Dutch conquest occurred immediately after the disastrous St. Lucia's flood in which many Frisians in the area were killed. After the conquest the district of West Friesland, which also comprised the islands of Wieringen, Texel, and Vlieland, had its own seats in the Estates of Holland and West Friesland. When the province of Holland was split up in the constitutional reform of 1840, West-Friesland became a part of North Holland. The name of West Friesland has also been used by an intercommunal administrative board (samenwerkingsregio) and a drainage board (waterschap). Until the current day a distinct West-Frisian language is spoken in West-Friesland (Westfries).
- Friesland became an independent member of the Dutch Republic in 1581. It is now a Dutch province, in 1996 renamed as Fryslân.
- The islands of Terschelling, Ameland, and Schiermonnikoog were independent seignories, which were integrated into the province of Friesland during the 19th and 20th centuries.
- Groningen, formerly Stad en Lande (the city of Groningen and its surroundings), became an independent member of the Dutch Republic in 1594. Now it is a Dutch province. As a rule, its inhabitants do not consider their province as a part of Frisia, though the area has many cultural ties with neighbouring East Frisia.
- East Frisia was an independent county since 1464, later a principality within the Holy Roman Empire until 1744. By then, it was annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia. After a period of Dutch and French rule, it became part of the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814, which was annexed by Prussia in 1866. Now it consists of several districts within ولاية ساكسونيا السفلى الاتحادية في جمهورية ألمانيا الاتحادية.
- Harlingerland was a seignory, inherited by the count of East Frisia in 1600.
- Jever was a seignory, annexed by the County of Oldenburg in 1573 and, after a prolonged period of Saxony-Anhalt, Russian, Dutch and French rule, reunited with Oldenburg in 1814. It is now part of the district of Friesland within ولاية ساكسونيا السفلى الاتحادية
- Kniphausen was a seignory, split off from the County of Oldenburg in 1667 and reunited with its surroundings in 1854 (effectively in 1813).
- Saterland was a tiny Frisian district under the Prince-bishop of Münster, in 1814 assigned to the مملكة هانوڤر.
- Butjadingen was a coastal republic, a remnant of the largely submerged district of Rüstringen. It was conquered by the Count of Oldenburg in 1514. After a period of Danish rule، أصبحت جزءاً من دوقية أولدنبورگ in 1774, which remained a more or less independent state within the German Empire until 1918. Butjadingen is now part of the district of Wesermarsch ضمن ولاية ساكسونيا السفلى الاتحادية.
- Land Wursten was a coastal republic, conquered by the Prince-bishop of Bremen in 1525. It became part of the Duchy of Bremen-Verden. The latter was, after a period of Swedish rule, integrated into the Kingdom of Hanover in 1715. It is now part of the district of Cuxhaven within the federal state of Lower Saxony.
- North Frisia correspond originally to the Uthlande in the Kingdom of Denmark, later North Frisia became a part of the Danish Duchy of Schleswig (or Southern Jutland, Sønderjylland) and of the royal enclaves (Kongerigske enklaver) of the Kingdom of Denmark. The duchy was conquered by Prussia in 1864. Now it forms a district within the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein. Helgoland is part of the district of Pinneberg. North Frisia was at no time part of the Holy Roman Empire.
العلم
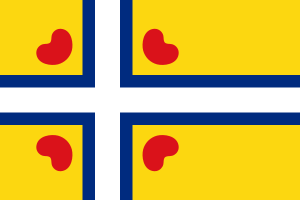

Although the Frisian regions have their own separate flags, Frisia as a whole has not historically had a flag of its own. A flag for a united Frisia, known as the Interfrisian Flag, was launched in September 2006 by the Groep fan Auwerk (English: Group of Aurich). This separatist group supports a united Frisia as a recognized country. The design was inspired by the Nordic Cross flag. The four pompeblêden (water lily leaves) represent the contemporary variety of the Frisian regions—North, South, West and East.[7]
This flag was not accepted by the Interfrisian Council.[8] But the council adopted the idea of an interfrisian flag and created an own design, containing elements of flags of the council's three sections. Neither flag is in wide use.
انظر أيضاً
- Eala Frya Fresena
- Frise
- الجزر الفريزية
- اللغات الفريزية
- Frisian-Frankish Wars
- Frisians
- قائمة حكام فريزيا
- German Bight
- يلاند
- أمة بلا دولة
- بحر وادن
ملاحظات
- ^ A more extensive, though outdated review of Frisia in Roman times is Springer, Lawrence A. (Jan 1953). "Rome's Contact with the Frisians". The Classical Journal. Northfield, MN: The Classical Association of the Middle West and South. 48 (4): 109–111. ISSN 0009-8353. JSTOR 3292503.
- ^ Ashdown, Margaret, ed. (1930). English and Norse documents : relating to the reign of Ethelred the Unready. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 138. OCLC 458533078. Noted by Homans.[6]
- ^ Homans describes Frisian social institutions, based on the summary by Siebs, Benno E. (1933). Grundlagen und Aufbau der altfriesischen Verfassung. Untersuchungen zur deutschen staats- und Rechtsgeschichte (in German). Vol. 144. Breslau: Marcus. OCLC 604057407.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) Siebs' synthesis was extrapolated from survivals detected in later medieval documents.[6] - ^ This is part of the evidence for a duodenary system, counting by multiples of twelve.[6]
الهامش
- ^ Grattan, Thomas Colley (1831). "The history of the Netherlands". Carey & Lea: 26.
friesland 1000.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ cf. Fort, Marron Curtis (1980): Saterfriesisches Wörterbuch. Hamburg, p.45.
- ^ Bos, Jurjen M. (2001). "Archaeological evidence pertaining to the Frisians in the Netherlands". In Munske, Horst H.; Århammar, Nils R. (eds.). Handbuch des Friesischen = Handbook of Frisian studies. Tübingen: Niemeyer. pp. 487–492. ISBN 9783484730489. Retrieved 2009-01-11.
- ^ "Frisian language". Encyclopedia Britannica (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2017-11-13.
- ^ Procopius (1914). The Wars. 8.20.11-46
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح Homans, George C. (1957). "The Frisians in East Anglia". The Economic History Review. New series. Wiley. 10 (2): 189–206. doi:10.2307/2590857. ISSN 0013-0117. JSTOR 2590857.
- ^ Description of the Interfrisian flag
- ^ Press release from the Interfrisian Council
ببليوگرافيا
- Albert Bantelmann, Rolf Kuschert, Albert Panten, Thomas Steensen: Geschichte Nordfrieslands. 2., durchges. u. aktualisierte Aufl., Westholst. Verlagsanstalt Boyens, Heide in Holstein 1996 (= Nordfriisk Instituut, Nr. 136), ISBN 3-8042-0759-6.
- Thomas Steensen: Geschichte Nordfrieslands von 1918 bis in die Gegenwart. Neuausg., Nordfriisk Instituut, Bräist/Bredstedt 2006 (= Geschichte Nordfrieslands, Teil 5; Nordfriisk Instituut, Nr. 190), ISBN 3-88007-336-8.
- Stefan Kröger - Das Ostfriesland-Lexikon. Ein unterhaltsames Nachschlagewerk, Isensee Verlag, Oldenburg 2006
- Ostfriesland im Schutze des Deiches. Beiträge zur Kultur- und Wirtschaftsgeschichte des ostfriesischen Küstenlandes, hrsg. im Auftrag der Niederemsischen Deichacht, 12 Bände, Selbstverlag, Pewsum u. a. 1969
- Onno Klopp -, Geschichte Ostfrieslands, 3 Bde., Hannover 1854–1858
- Hajo van Lengen - Ostfriesland, Kultur und Landschaft, Ruhrspiegel-Verlag, Essen 1978
- Hajo van Lengen (Hrsg.) - Die Friesische Freiheit des Mittelalters – Leben und Legende, Verlag Ostfriesische Landschaft 2003, ISBN 3-932206-30-4
- Franz Kurowski - Das Volk am Meer – Die dramatische Geschichte der Friesen, Türmer-Verlag 1984, ISBN 3-87829-082-9
- Karl Cramer - Die Geschichte Ostfrieslands. Ein Überblick, Isensee - Oldenburg
- Hermann Homann - Ostfriesland – Inseln, Watt und Küstenland, F. Coppenrath Verlag, Münster
- Manfred Scheuch - Historischer Atlas Deutschland, ISBN 3-8289-0358-4
- Karl-Ernst Behre / Hajo van Lengen - Ostfriesland. Geschichte und Gestalt einer Kulturlandschaft, Aurich 1995, ISBN 3-925365-85-0
- Tielke, Martin (ed.) - Biographisches Lexikon für Ostfriesland, Ostfries. Landschaftliche Verlag- u. Vertriebsges. Aurich, vol. 1 ISBN 3-925365-75-3 (1993), vol. 2 ISBN 3-932206-00-2 (1997), vol. 3 ISBN 3-932206-22-3 (2001)
وصلات خارجية
- Interfriesischerrat.de – Website of the Interfrisian Council
- Groepfanauwerk.com – Website of the Groep fan Auwerk
- Profile of Frisia at Eurominority.eu
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Articles containing ألمانية-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Articles containing إنگليزية القديمة (ح. 450-1100)-language text
- Articles containing دنماركية-language text
- Articles containing هولندية-language text
- Articles containing Low German-language text
- Articles containing East Frisian Low Saxon-language text
- Articles containing North Frisian-language text
- Articles containing Saterland Frisian-language text
- Articles containing West Frisian-language text
- Articles containing فرنسية-language text
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles with text in West Germanic languages
- فريزيا
- مناطق مقسمة
- مناطق تاريخية في هولندا
- مناطق تاريخية في ألمانيا